Spica can level you to Omega Centauri
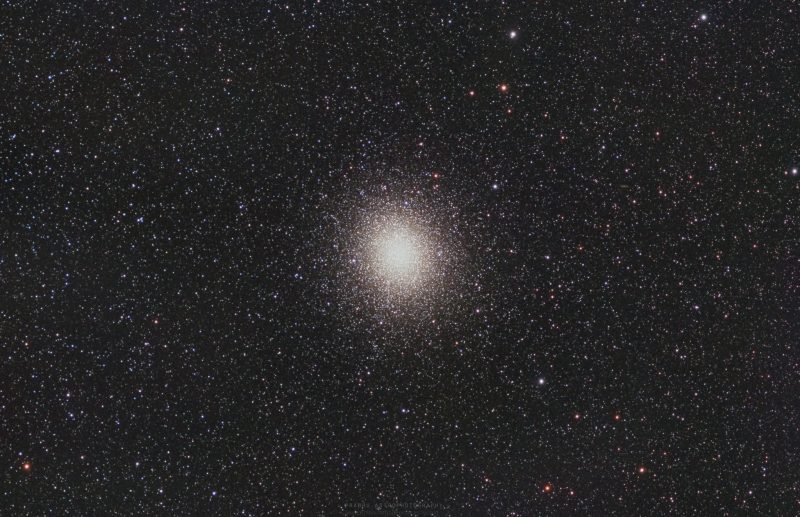
The well-known star Omega Centauri cluster is the most important and most interesting globular star cluster seen to the attention alone. It incorporates a few of our Milky Way galaxy’s most historical stars. And the intense star Spica can assist you discover it.
In Northern Hemisphere spring, Spica and Omega Centauri climb up highest for the evening within the hour or so after midnight. Once they’re at their highest level – as seen from the Northern Hemisphere – a line drawn from Spica drawn straight down towards the southern horizon factors to Omega Centauri.
And since the celebrities return to the sky about 4 minutes earlier with every passing day, Spica and Omega Centauri can be up highest for the evening round one hour earlier in mid-April (12 midnight or 1 a.m. DST), and two hours earlier by the tip of April (11 p.m. or 12 DST), and so forth.

Last chance to get a moon phase calendar! Only a few left. On sale now.
How can I discover Spica?
Seeing Omega Centauri could be very particular, partly as a result of you possibly can see it along with your eye alone, assuming you have got a dark enough sky. Only a few of the 150 or so globular star clusters within the Milky Way galaxy are seen with out optics.
However how will you first discover Spica? It’s simple … for those who stay within the Northern Hemisphere. That’s as a result of you need to use the well-known Massive Dipper asterism to level to Spica. Simply “comply with the arc” within the Massive Dipper’s deal with to the intense orange star Arcturus. Then “pace on to Spica,” as present within the chart under.
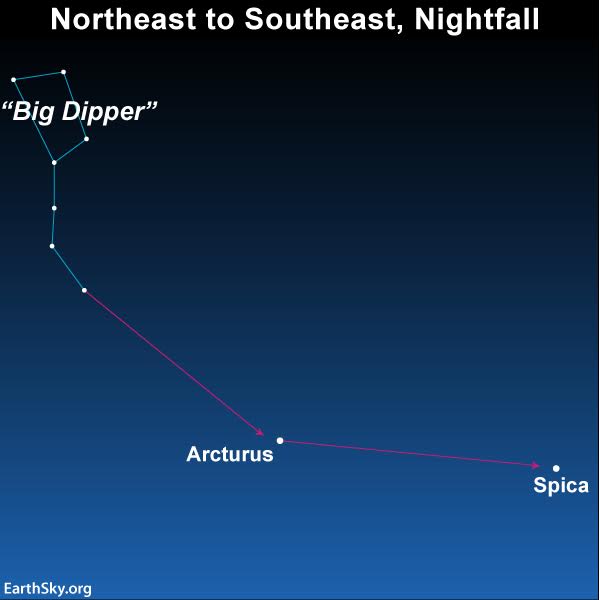
Look after they’re highest
So – when Spica is highest within the south for Northern Hemisphere viewers – Omega Centauri is, too.
When Spica is highest, search for Omega Centauri about 35 degrees instantly under it. A fist at arm’s size approximates 10 levels.
You’ll be able to see Omega Centauri with the unaided eye in case your sky is dark enough and for those who’re far sufficient south on the Earth. Folks residing south of 35 degrees north latitude have a practical likelihood of recognizing the cluster over the southern horizon, although Omega Centauri has been seen as far north as Point Pelee National Park in Canada (42 degrees north latitude). Omega Centauri appears like a faint (and probably fuzzy) star.
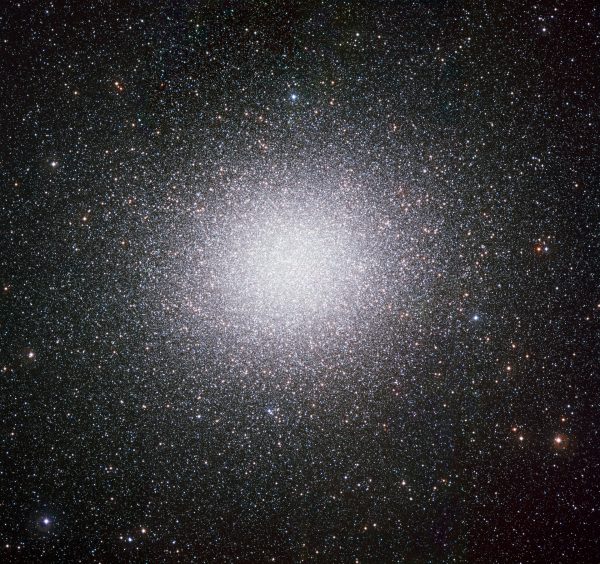

View from the Southern Hemisphere?
After all, Omega Centauri is superior from the Southern Hemisphere.
As seen from the Southern Hemisphere, Spica and Omega Centauri move extra practically overhead. They nonetheless transit at roughly the identical time (1 a.m. early April, midnight in mid-April, 11 p.m. in early Could). They’re nonetheless positioned about 35 levels aside.
From the Southern Hemisphere, you’ve bought an exquisite approach to discover this cluster. And, certainly, your view of the cluster can be higher than within the north, as a result of Omega Centauri can be greater in your sky.
To get in its basic neighborhood on the sky’s dome, search for the well-known Southern Cross, which, formally, is the constellation Crux. In Crux – seen in binoculars – is the Jewel Box, an open star cluster with about 100 members, whose stars are coloured purple, white and blue.
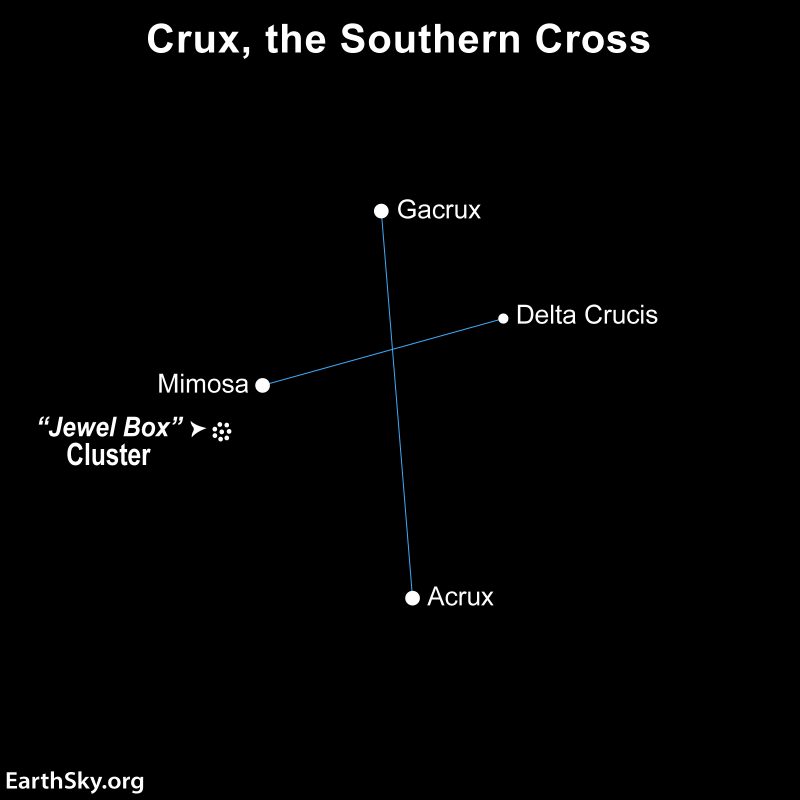
When you can find the Southern Cross and the Jewel Field, you’ll additionally discover Omega Centauri. Seek the advice of the chart under for its location.
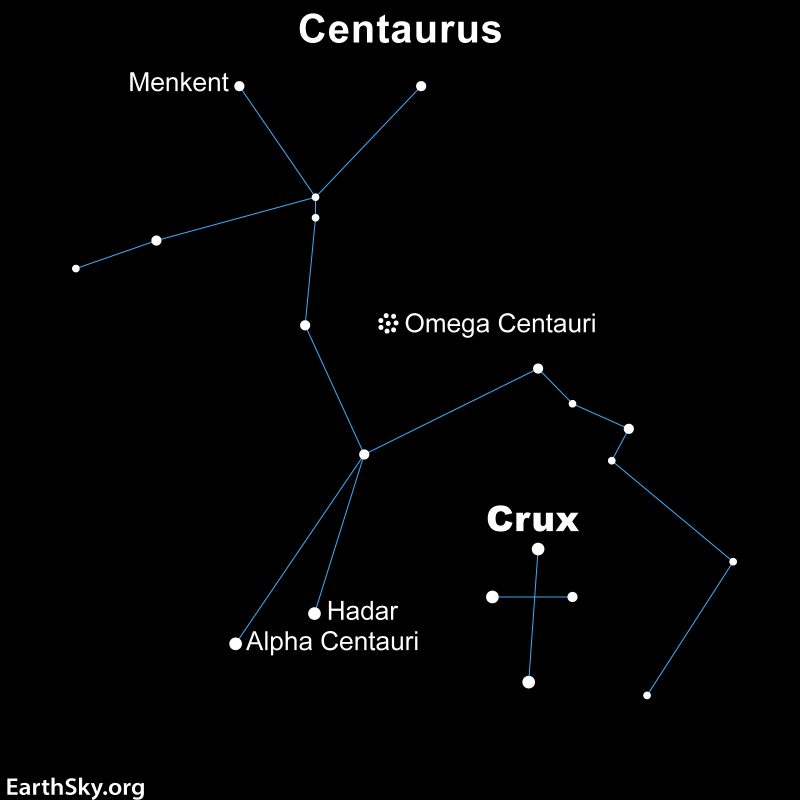
Backside line: Within the spring, the intense star Spica can lead you to the Omega Centauri globular cluster. From the Southern Hemisphere, star hop from the Southern Cross, to the Jewel Field star cluster, after which to Omega Centauri. Binoculars or a telescope present it greatest. Like all globular clusters, Omega Centauri is greatest seen by way of a telescope. You then see it as a globe-shaped stellar metropolis, teeming with an estimated 10 million stars!
EarthSky astronomy kits are perfect for beginners. Order today from the EarthSky store




