Understanding the ionosphere excessive within the Earth’s environment is necessary on account of its results on communications programs, satellites and essential chemical options together with the ozone layer. New insights into the exercise of excessive vitality electrons have come from a simulation research led by geophysicist Yuto Katoh at Tohoku College, reported within the journal Earth, Planets and House.
“Our outcomes make clear the sudden function of the geomagnetic discipline surrounding the Earth in defending the environment from high energy electrons,” says Katoh.
The ionosphere is a large area between roughly 60 and greater than 600 kilometers above the Earth’s floor. It incorporates electrically charged particles which are a mix of ions and free electrons generated by the interplay of the environment with radiation from the sun.
Polar areas of the ionosphere are subjected to a very regular and energetic stream of incoming electrons in a course of known as electron precipitation. These “relativistic” electrons transfer at near the velocity of sunshine, the place the consequences of Einstein’s relativity idea turn out to be ever extra vital. They collide with fuel molecules and contribute to many phenomena within the ionosphere, together with colourful auroral shows. The processes are closely influenced by the consequences of the geomagnetic discipline on the charged particles concerned.
The Tohoku group, with colleagues in Germany and different establishments in Japan, developed a complicated software program code that targeted explicit consideration on simulating the consequences of a comparatively unstudied “mirror drive” on the electron precipitation. That is attributable to the magnetic force performing on charged particles below the affect of the geomagnetic discipline.
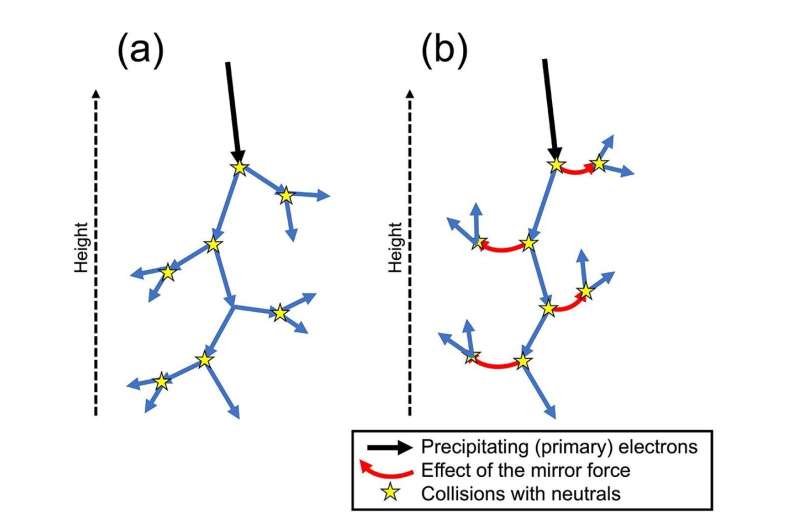
The simulations demonstrated how the mirror drive causes relativistic electrons to bounce again upwards, to an extent depending on the angles at which the electrons arrive. The anticipated results imply that electrons collide with different charged particles increased within the ionosphere than beforehand suspected.
Illustrating one instance of the importance of this work, Katoh feedback, “Precipitating electrons that handle to go by way of the mirror drive can attain the center and decrease environment, contributing to chemical reactions associated to variations in ozone ranges.” Decreased ozone ranges on the poles attributable to atmospheric air pollution cut back the safety ozone affords dwelling organisms from ultraviolet radiation.
Katoh emphasizes the important thing theoretical advance of the analysis is in revealing the stunning significance of the geomagnetic discipline and the mirror drive in defending the decrease environment from the consequences of electron precipitation actions by protecting them additional away.
“We have now now began a venture to mix the simulation research used on this work with actual observations of the polar ionosphere to construct even deeper understanding of those essential geophysical processes,” says Katoh.
Extra data:
Yuto Katoh et al, Impact of the mirror drive on the collision fee on account of energetic electron precipitation: Monte Carlo simulations, Earth, Planets and House (2023). DOI: 10.1186/s40623-023-01871-y
Supplied by
Tohoku University
Quotation:
Geomagnetic discipline protects Earth from electron showers (2023, August 3)
retrieved 3 August 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-08-geomagnetic-field-earth-electron-showers.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




