What occurs when a star will get too near a large black hole? It will get shredded, after all! This month (August 22, 2023), scientists said they’ve accomplished a forensic examine of 1 such star that met this destiny. Telescopes analyzed parts left behind by the star – together with nitrogen and carbon – nonetheless lingering close to the black hole. The researchers stated the weather got here from contained in the star, which accurately had its insides ripped out and spewed into space.
The researchers – with NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory and ESA’s XMM-Newton space telescopes – published their new peer-reviewed paper in The Astrophysical Journal Letters on August 21, 2023.
When stars come too shut
Astronomers name this violent phenomenon a tidal disruption event. Gravitational forces create intense tides that tear the star aside. The trailing a part of the ensuing stream of gasoline escapes the system, whereas the main half swings again round, surrounding the black hole with a disk of particles. The gravity of a large black hole is so highly effective that even giant stars don’t stand a lot of an opportunity.
The destruction additionally causes a flare, which astronomers can see in optical mild, ultraviolet mild and X-rays. The flare occurs because the star’s particles disk is heated up. That’s what occurred for this specific tidal disruption occasion additionally, within the ASASSN-14li system.
Lead writer Jon Miller of the College of Michigan stated:
We’re seeing the center of what was once a star. The weather left behind are clues we will comply with to determine what kind of star met its demise.
ASASSN-14li was a novel occasion
The ASASSN-14li occasion, whereas just like different such cataclysms, was additionally fairly notable for just a few causes.
First, astronomers found it in November 2014. It was the closest tidal disruption occasion to Earth recorded within the earlier decade, at 290 million light-years. Whereas being the closest such occasion, it nonetheless wasn’t truly “shut” to us, per se!
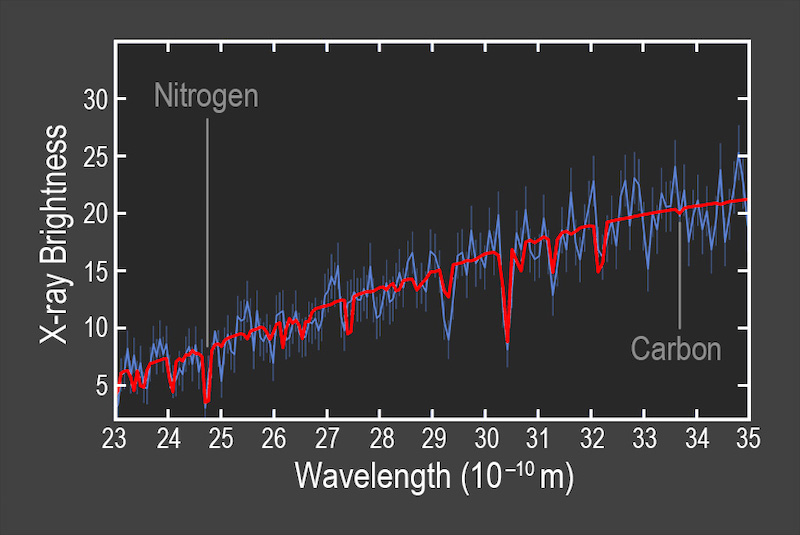
The occasion could have been first found nearly a decade in the past, however there’s nonetheless a lot that scientists can study from it. Miller and his colleagues used new theoretical fashions to make improved estimates, as in comparison with earlier research, of the quantity of nitrogen and carbon across the black hole. And certainly, the brand new evaluation has offered a wealth of knowledge concerning the occasion. Co-author Brenna Mockler of Carnegie Observatories and the College of California, Los Angeles stated:
These X-ray telescopes can be utilized as forensic instruments in space. The relative quantity of nitrogen to carbon that we discovered factors to materials from the inside of a doomed star weighing about thrice the mass of the sun.
The Hubble House Telescope beforehand noticed an enhanced quantity of nitrogen in comparison with carbon as nicely, however by a smaller quantity.
Some of the large stars destroyed by a black hole
Which means ASASSN-14li is likely one of the most large – if not probably the most large – stars that astronomers have discovered destroyed by a black hole. Co-author Enrico Ramirez-Ruiz of the College of California, Santa Cruz, added:
ASASSN-14li is thrilling as a result of one of many hardest issues with tidal disruptions is with the ability to measure the mass of the unfortunate star, as we now have performed right here. Observing the destruction of an enormous star by a supermassive black hole is spellbinding as a result of extra large stars are anticipated to be considerably much less frequent than lower-mass stars.
Future research
Astronomers may also take what they’ve realized about ASASSN-14li and apply it to future observations. For instance, there’s a supermassive black hole within the heart of our Milky Way galaxy. It resides inside a star cluster that additionally incorporates reasonably large stars just like the one which used to exist within the ASASSN-14li system. Since astronomers can estimate the stellar plenty of tidally disrupted stars, they will now detect star clusters round supermassive black holes within the facilities of different galaxies as nicely. Most galaxies are thought to have these big black holes, identical to the Milky Way does.
Astronomers have seen black holes destroy or devour stars a number of instances earlier than. You’ll be able to learn extra EarthSky tales here.
Backside line: Scientists have accomplished an in depth “forensic examine” of an enormous star destroyed by a large black hole. The black hole ripped out the insides of the star.
Source: Evidence of a Massive Stellar Disruption in the X-Ray Spectrum of ASASSN-14li
Read more: Astronomers see a star ‘spaghettified’ by a black hole
Read more: Cosmic ray originated in cataclysmic event




