On Earth, shifting tectonic plates reshuffle the planet’s floor and make for a dynamic inside, so the absence of such processes on Mars led many to consider it as a lifeless planet, the place not a lot occurred previously 3 billion years.
Within the present challenge of Nature Astronomy, scientists from the College of Arizona problem present views of Martian geodynamic evolution with a report on the invention of an lively mantle plume pushing the floor upward and inflicting earthquakes and volcanic eruptions. The discovering means that the planet’s deceptively quiet floor might conceal a extra tumultuous inside than beforehand thought.
“Our research presents a number of strains of proof that reveal the presence of a large lively mantle plume on present-day Mars,” stated Adrien Broquet, a postdoctoral analysis affiliate within the UArizona Lunar and Planetary Laboratory and co-author of the research with Jeff Andrews-Hanna, an affiliate professor of planetary science on the LPL.
Mantle plumes are giant blobs of heat and buoyant rock that rise from deep inside a planet and push by way of its intermediate layer—the mantle—to achieve the bottom of its crust, inflicting earthquakes, faulting and volcanic eruptions. The island chain of Hawaii, for instance, shaped because the Pacific plate slowly drifted over a mantle plume.
“We’ve robust proof for mantle plumes being lively on Earth and Venus, however this is not anticipated on a small and supposedly chilly world like Mars,” Andrews-Hanna stated. “Mars was most lively 3 to 4 billion years in the past, and the prevailing view is that the planet is actually lifeless in the present day.”
“An amazing quantity of volcanic exercise early within the planet’s historical past constructed the tallest volcanoes within the solar system and blanketed many of the northern hemisphere in volcanic deposits,” Broquet stated. “What little exercise has occurred in latest historical past is often attributed to passive processes on a cooling planet.”
The researchers have been drawn to a stunning quantity of exercise in an in any other case nondescript area of Mars known as Elysium Planitia, a plain inside Mars’ northern lowlands near the equator. Not like different volcanic areas on Mars, which have not seen main exercise for billions of years, Elysium Planitia skilled giant eruptions over the previous 200 million years.
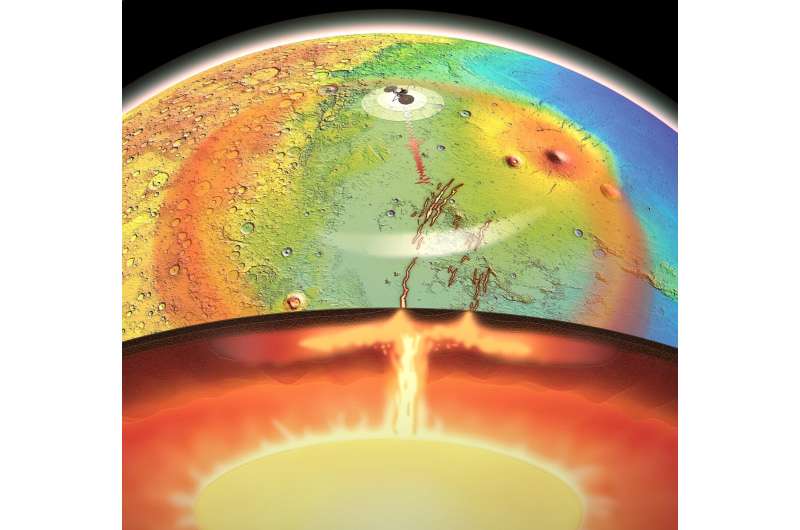
“Earlier work by our group discovered proof in Elysium Planitia for the youngest volcanic eruption recognized on Mars,” Andrews-Hanna stated. “It created a small explosion of volcanic ash round 53,000 years in the past, which in geologic time is actually yesterday.”
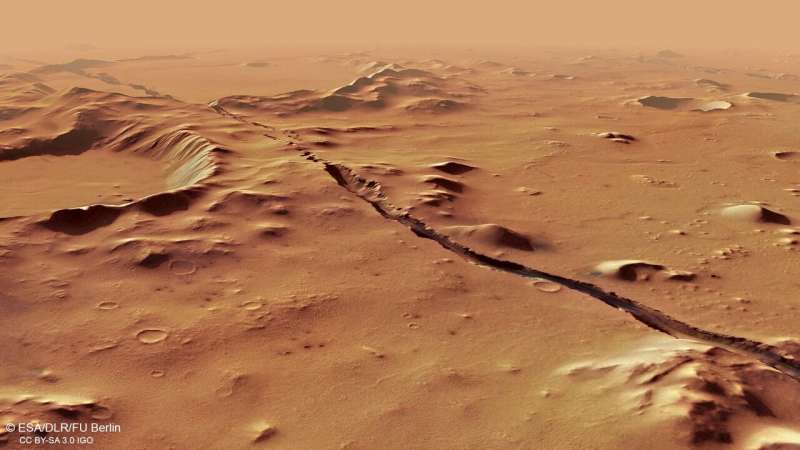
Volcanism at Elysium Planitia originates from the Cerberus Fossae, a set of younger fissures that stretch for greater than 800 miles throughout the Martian floor. Not too long ago, NASA’s InSight crew discovered that just about all Martian quakes, or marsquakes, emanate from this one area. Though this younger volcanic and tectonic exercise had been documented, the underlying trigger remained unknown.
On Earth, volcanism and earthquakes are typically related to both mantle plumes or plate tectonics, the worldwide cycle of drifting continents that frequently recycles the crust.
“We all know that Mars doesn’t have plate tectonics, so we investigated whether or not the exercise we see within the Cerberus Fossae area could possibly be the results of a mantle plume,” Broquet stated.
Mantle plumes, which may be seen as analogous to scorching blobs of wax rising in lava lamps. give away their presence on Earth by way of a classical sequence of occasions. Heat plume materials pushes in opposition to the floor, uplifting and stretching the crust. Molten rock from the plume then erupts as flood basalts that create huge volcanic plains.
When the crew studied the options of Elysium Planitia, they discovered proof of the identical sequence of occasions on Mars. The floor has been uplifted by greater than a mile, making it one of many highest areas in Mars’ huge northern lowlands. Analyses of delicate variations within the gravity subject indicated that this uplift is supported from deep throughout the planet, according to the presence of a mantle plume.
Different measurements confirmed that the ground of influence craters is tilted within the course of the plume, additional supporting the concept one thing pushed the floor up after the craters shaped. Lastly, when researchers utilized a tectonic mannequin to the world, they discovered that the presence of a large plume, 2,500 miles extensive, was the one technique to clarify the extension answerable for forming the Cerberus Fossae.

“By way of what you count on to see with an lively mantle plume, Elysium Planitia is checking all the proper bins,” Broquet stated, including that the discovering poses a problem for fashions utilized by planetary scientists to check the thermal evolution of planets. “This mantle plume has affected an space of Mars roughly equal to that of the continental United States. Future research must discover a technique to account for a really giant mantle plume that wasn’t anticipated to be there.
“We used to assume that InSight landed in one of the vital geologically boring areas on Mars—a pleasant flat floor that ought to be roughly consultant of the planet’s lowlands,” Broquet added. “As a substitute, our research demonstrates that InSight landed proper on high of an lively plume head.”
The presence of an lively plume will have an effect on interpretations of the seismic knowledge recorded by InSight, which should now keep in mind the truth that this area is way from regular for Mars.
“Having an lively mantle plume on Mars in the present day is a paradigm shift for our understanding of the planet’s geologic evolution,” Broquet stated, “just like when analyses of seismic measurements recorded throughout the Apollo period demonstrated the moon’s core to be molten.”
Their findings may even have implications for all times on Mars, the authors say. The studied area skilled floods of liquid water in its latest geologic previous, although the trigger has remained a thriller. The identical warmth from the plume that’s fueling ongoing volcanic and seismic exercise may additionally soften ice to make the floods—and drive chemical reactions that would maintain life deep underground.
“Microbes on Earth flourish in environments like this, and that could possibly be true on Mars, as effectively,” Andrews-Hanna stated, including that the invention goes past explaining the enigmatic seismic exercise and resurgence in volcanic exercise. “Realizing that there’s an lively big mantle plume beneath the Martian floor raises vital questions concerning how the planet has developed over time. We’re satisfied that the long run has extra surprises in retailer.”
Extra data:
Adrien Broquet & J. C. Andrews-Hanna, Geophysical proof for an lively mantle plume beneath Elysium Planitia on Mars, Nature Astronomy (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41550-022-01836-3. www.nature.com/articles/s41550-022-01836-3
Supplied by
University of Arizona
Quotation:
Big mantle plume reveals Mars is extra lively than beforehand thought (2022, December 5)
retrieved 5 December 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-12-giant-mantle-plume-reveals-mars.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




