On July 7, 2024, NOAA’s GOES-U executed its last engine burn, inserting the satellite in geostationary orbit 22,236 miles above Earth’s equator. Upon reaching this milestone, GOES-U was renamed GOES-19. GOES satellites are designated with a letter previous to launch and a quantity as soon as they obtain geostationary orbit.
GOES-U launched on June 25, 2024, at 5:26 p.m. EDT, lifting off from Launch Complicated 39A at NASA’s Kennedy Area Heart in Florida, aboard a SpaceX Falcon Heavy rocket. The launch was managed by NASA’s Launch Companies Program, primarily based at Kennedy Area Heart.
GOES-U separated from the SpaceX Falcon Heavy second-stage rocket at 9.56 p.m. EDT on June 25. Mission managers confirmed first-stage deployment of the spacecraft’s solar array at 10:18 p.m., and the satellite started working by itself energy.
The Falcon Heavy rocket delivered GOES-U to a geostationary switch orbit, a extremely elliptical orbit the place the satellite is near the Earth throughout one a part of its orbit and much from the Earth on the alternative aspect. Inserting GOES-U in a geostationary switch orbit supplied the satellite a path to achieve its last geostationary orbit over the equator (see diagram under). After a sequence of orbit-raising maneuvers and engine burns, on July 7, GOES-U was delivered right into a round geostationary orbit. The satellite is now in place to orbit on the similar charge Earth rotates, so it could actually preserve fixed watch over the identical area.
Subsequent, GOES-19 will carry out the second-stage deployment of its solar array. The deployed solar panels will type a single solar array wing that can rotate as soon as per day to constantly level its photovoltaic (solar) cells towards the sun. The photovoltaic cells will convert power from the sun into electrical energy to energy the complete satellite, together with the devices, computer systems, knowledge processors, sensors and telecommunications gear.
-
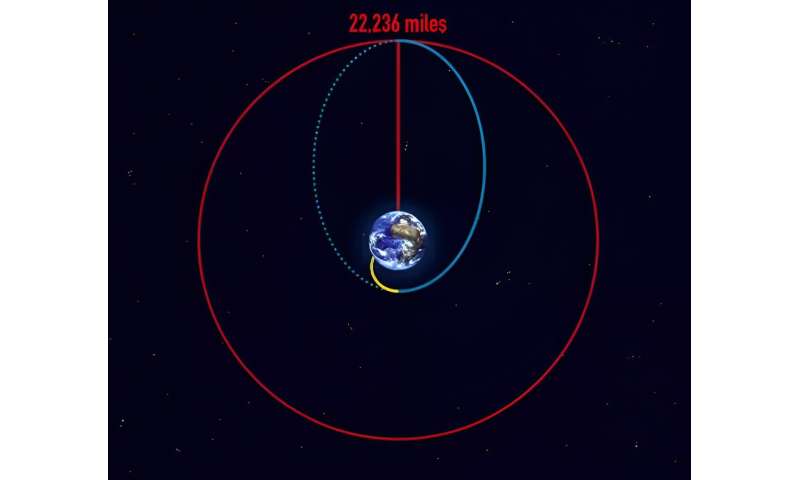
Geostationary switch orbit: After liftoff, the launch car makes its technique to space following a path proven by the yellow line. On the goal vacation spot, the rocket releases the payload which units it off on an elliptical orbit, following the blue line which sends the payload farther away from Earth. The purpose farthest away from the Earth on the blue elliptical orbit is named the apogee and the purpose closest is named the perigee. When the payload reaches the apogee on the geostationary altitude of twenty-two,236 miles, it fires its engines in such a approach that it enters onto the round geostationary orbit and stays there, proven by the crimson line within the diagram. The geostationary switch orbit is the blue path from the yellow orbit to the crimson orbit. Credit score: The European Area Company
-
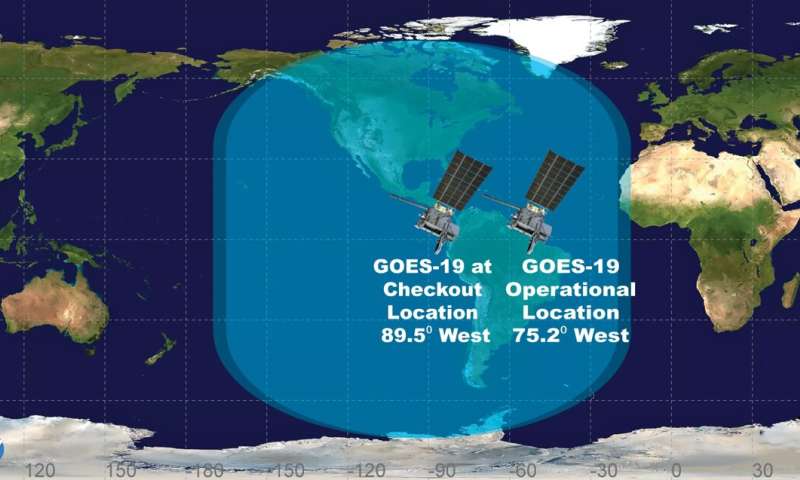
GOES-19’s place and think about over the Western Hemisphere at its checkout location and its operational location. Credit score: NOAA Headquarters
Within the days that observe, satellite operators will conduct a number of maneuvers to get GOES-19 to its 89.5 levels west longitude preliminary checkout place, between the operational GOES-East and GOES-West satellites. Then, the magnetometer growth will probably be deployed. The satellite will then start on-orbit checkout and validation of its devices and techniques.
NOAA expects to see the primary photos from GOES-19 in September. After finishing post-launch take a look at, NASA will hand GOES-19 over to NOAA, which can validate the satellite’s knowledge merchandise and drift GOES-19 to its operational place at 75.2 levels west longitude. NOAA plans for GOES-19 to take over because the operational GOES-East satellite in April 2025, changing GOES-16. GOES-16 will change into the on-orbit standby satellite.
GOES-19 will monitor severe storms, hurricanes, wildfires, lightning, fog and different hazards that threaten most of North America, together with the contiguous United States, Mexico, Central and South America and the Caribbean. The satellite may even monitor solar activity and space climate to offer early warnings of disruptions to energy grids, communications, and navigation techniques. Onboard GOES-19 is a brand new instrument, the Compact Coronagraph-1 (CCOR), which can help NOAA’s Area Climate Observe On (SWFO) mission.
CCOR-1 will picture the solar corona (the outer layer of the sun’s environment) and assist detect and characterize coronal mass ejections (CMEs), giant expulsions of plasma and accompanying magnetic field from the corona, that are the first explanation for geomagnetic storms. CCOR-1 would be the nation’s first operational coronagraph and can function the first supply for details about impending geomagnetic storm circumstances, permitting the Area Climate Prediction Heart to subject warnings one to 4 days upfront.
Offered by
NOAA Headquarters
Quotation:
GOES-U satellite reaches geostationary orbit, now designated GOES-19 (2024, July 10)
retrieved 10 July 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-07-satellite-geostationary-orbit.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




