The rising inhabitants of communication satellites equivalent to Starlink and OneWeb is posing challenges for Earth-based astronomy amenities. Since such constellations won’t be going away quickly, astronomers wish to discover methods to work across the challenge.
It isn’t going to be straightforward, contemplating that hundreds and hundreds of low-Earth satellites (LEOsats) might doubtlessly be positioned in low-Earth orbit within the subsequent few years. So, what are the options?
Satellite tv for pc streaks, and what will be performed
LEOsats are notably seen from Earth as a result of they replicate daylight. That is notably noticeable at twilight. As they transfer throughout the sky, they go away streaks in telescope pictures. Folks from the astronomy and satellite operators communities are working collectively to resolve the advanced drawback. Folks have steered the concept of “portray the satellites darkish” to be able to restrict their visibility. And, SpaceX has applied this.
The LSST Consortium has identified that if they might all could possibly be darkened to seventh magnitude, they might be far under the saturation in ensuing pictures. However, that does not utterly clear up the issue if operators don’t agree to do that.
Different solutions embody “masking out” the streaks from astronomical pictures. Or, perhaps observatories might “program round” the intrusions. Each of those final two options are doable, however they’ve challenges. Specifically, to work across the look of satellites throughout observations, amenities want extraordinarily correct orbital parts for them. Based on astronomer Peter Yoachim (College of Washington), who co-authored a current paper about satellite mitigation, information of these orbits is necessary. “I do not know the way effectively corporations will do sharing TLEs (two-line parts),” he mentioned, noting that or his crew’s work on avoidance algorithms, he generated his personal TLEs.
Vera Rubin Observatory and the LSST
So, can observatories program their method round these passes? Possibly. Let’s take a look at a real-world instance. The Vera Rubin Observatory is among the newest amenities coming on-line. It is a state-of-the-art telescope about to undertake an enormous challenge. That program is named the Legacy Survey of Area and Time (LSST) and it’ll survey the complete southern sky over a interval of ten years. Its outcomes ought to give astronomers distinctive perception into the construction and evolution of the universe. Sadly, the rising panoply of LEOsats on the LSST challenge might threaten its discoveries.
VRO scientists estimate from simulations that satellites will closely have an effect on the LSST observations. They base this on the observing cadence and assuming a full deployment of 42,000 SpaceX satellites. As many as 30% of all LSST pictures would comprise at the least one streak. Now, extrapolate that to constellations of 400,000 LEOsats. Most pictures may have seen streaks, a few of them shiny.
Yoachim identified that it isn’t essentially the brightnesses that concern them first. It is extra about discovering methods to keep away from streaks as a lot as potential. “Principally so long as they’re faint sufficient that they do not saturate our pixels it should not be too powerful to masks them out,” he mentioned. “In idea, brighter satellites would possibly want barely bigger masks (or trigger extra cross-talk that must be corrected), however that is not an enormous distinction.”
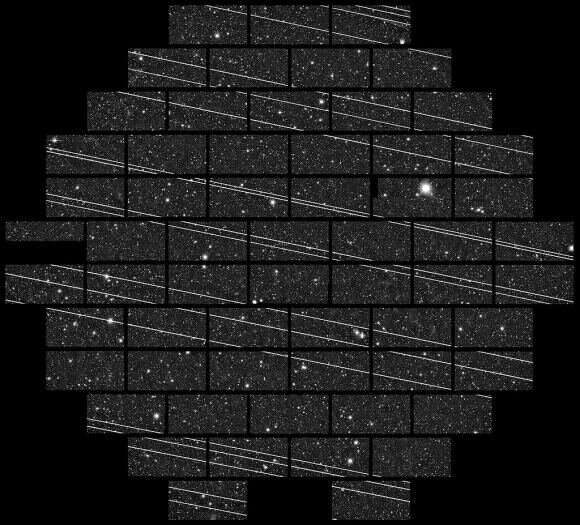
Streak removing to the rescue?
Now, in lots of circumstances, astronomers can take away streaks. Nonetheless, that additionally reduces the sign to noise within the remaining pixels. Significantly shiny ones equivalent to these created by the BlueWalker 3 check platform, can really saturate detector pixels. These streaks bleed into different pixels, wipe out complete columns, and truly “burn in” a persistent picture.
Nonetheless, masking is not very environment friendly when astronomers must masks tens of hundreds of them. There’s additionally a chance that masking out streaks might introduce different errors that have an effect on the standard of the science.
Can we ‘not look’ at satellites?
So, what about programming the observatory to easily keep away from trying on the sky throughout satellite passes? It is advanced. Yoachim is a part of the crew that simulated orbits of at the moment deliberate Starlink and OneWeb constellations (about 40,000 of them) to check a proposed Rubin scheduling program. The concept is to one way or the other “schedule round” the streaky incursions.
This does not come with out its issues, based on Yoachim. Not all constellations orbit in the identical locations. “That’s doubtlessly problematic as a result of OneWeb has been utilizing increased altitude orbits, which leaves their satellites illuminated by the Solar longer into the evening,” he mentioned. He additionally famous that dimmer satellites equivalent to Starlink do not pose the identical issues. “For Starlink, even when they make an enormous constellation, all the possibly seen satellites will likely be in Earth’s shadow 64% of our nominal observing time. Being increased up, OneWeb is all in shadow solely 30% of the time.”
The rise of very shiny orbiting platforms equivalent to BlueWalker 3, brings up the issue of pixel saturation. The excellent news is that scheduling observations round a BlueWalker 3 move is a potential workaround. BlueWeb’s mother or father firm AST Spacemobile can also be working with astronomers to mitigate the consequences of this technique on each optical and radio telescopes.
Shifting ahead regardless of satellites
The results of the crew’s simulations exhibits some promise in avoiding many incursions for VRO. Including in a weighted time period within the observatory’s scheduler for illuminated satellites can scale back the variety of streaks in observations, however does not clear up issues of knowledge loss. And, there are different technical challenges. However, the concept of including brightness weighting permits astronomers to decide on a brightness threshold and add in solely people who exceed it.
The authors conclude: “It could be potential to compute optimum beginning places for a sequence of observations primarily based on satellite forecasts to additional optimize satellite avoidance. Lastly, since faint path detection and masking is just not good, no satellite avoidance technique will successfully mitigate faint glints and the ensuing bogus alerts.”
Lastly, any avoidance programming goes to want good orbital information. Though VRO continues to be a while away from being “on the sky,” Yoachim identified the necessity for correct TLEs. “Our scheme will solely work in actual life if we’ve got good TLEs from the operators,” he mentioned.
Extra info:
Jinghan Alina Hu et al, Satellite tv for pc Constellation Avoidance with the Rubin Observatory Legacy Survey of Area and Time, arXiv (2022). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2211.15908
Journal info:
arXiv
Supplied by
Universe Today
Quotation:
Floor telescopes can adapt to satellite megaconstellations in the event that they get correct telemetry information (2022, December 6)
retrieved 6 December 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-12-ground-telescopes-satellite-megaconstellations-accurate.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




