Researchers led by Dr. Xin Liping from the House-based Multi-band Astronomical Variable Objects Monitor (SVOM) analysis group, Nationwide Astronomical Observatories of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences (NAOC), have detected the immediate optical emission and its transition to the early afterglow of a gamma-ray burst (GRB 201223A), utilizing the Floor Extensive Angle Digicam Array (GWAC) situated at Xinglong Observatory of NAOC. The examine was revealed in Nature Astronomy on April 10.
Gamma-ray bursts (GRBs) are produced by the collapse of huge stars or the merger of binary neutron stars. They’re accompanied by excessive relativistic jets emitting monumental quantities of vitality inside a number of seconds of the bursts. This phenomenon contains the immediate emission brought on by the shock within the jet and the afterglow produced by interplay between the jet and exterior medium.
Typical high-energy emission lasts just a few milliseconds to tens of seconds, and it’s tough to observe up in actual time when ground-based optical telescopes obtain alerts triggered by space-based high-energy devices. Till now, just a few instances of optical emission have been detected earlier than the tip of immediate high-energy emission. These GRBs have longer length of high-energy emission (>30 seconds). Moreover, all these measurements had been contaminated with reverse shock, making it tough to obviously evaluate the transition from immediate emission to afterglow.
GWAC, proposed and led by Prof. Wei Jianyan, principal investigator of the SVOM mission, is likely one of the key ground-based telescopes for the SVOM challenge. It may well cowl an ultra-large sky space with a temporal resolution of 15 seconds and a detection functionality of magnitude 16. Its scientific goal is to conduct systematic analysis on the immediate optical emission of GRBs found by the SVOM mission.
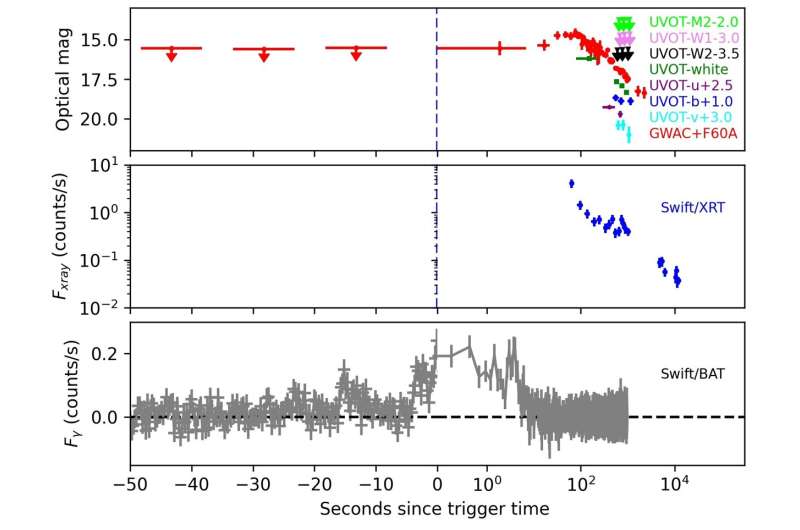
On this examine, GWAC recorded your complete course of—earlier than, throughout and after the set off time of the burst. The length of the high-energy emission was 29 seconds. The emergence of optical and gamma-ray emissions was detected concurrently.
“The immediate optical emission is much brighter than anticipated by about 4 orders of magnitude, if solely gamma-ray emission is analyzed, which requires a particular bodily interpretation for these measurements,” mentioned by Dr. Xin.
In keeping with joint evaluation utilizing the follow-up observations by F60A, an optical telescope collectively operated by NAOC and Guangxi College, the whole transition from immediate optical emission to afterglow was clearly achieved with none contamination from reverse shock.
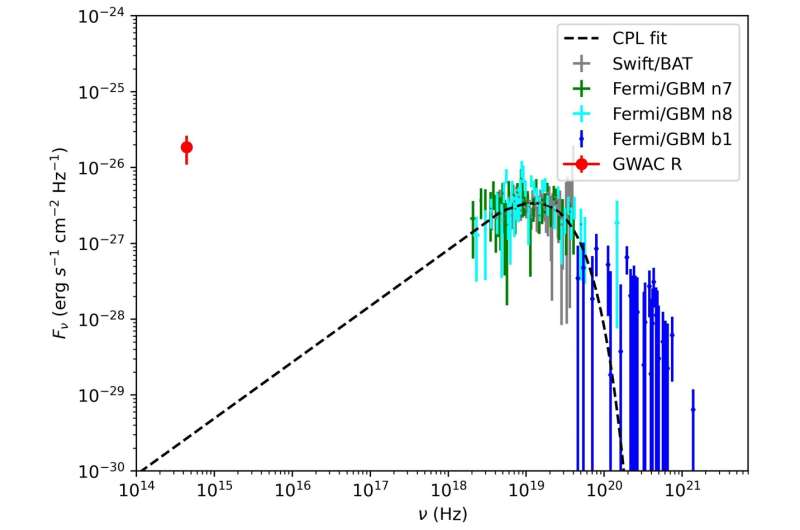
The extraordinarily early distinctive information offered by GWAC place a wonderful constraint on the traits of the progenitor. Scientists anticipate sturdy stellar winds round a large star, which is regarded as the best progenitor of a gamma-ray burst. Nevertheless, the stellar wind is kind of small for this occasion, even at a really shut distance from the burst, thus suggesting the progenitor has a small stellar mass.
After the launch of SVOM, simultaneous observations by GWAC and SVOM space-based devices may have the potential to offer important information for GRB research, and at last a big pattern with immediate optical observations might be constructed throughout the SVOM mission.
Extra data:
Liping Xin et al, Immediate-to-afterglow transition of optical emission in an extended gamma-ray burst according to a fireball, Nature Astronomy (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41550-023-01930-0
Supplied by
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Quotation:
Floor large angle digicam array detects immediate optical emission of gamma-ray burst (2023, April 28)
retrieved 29 April 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-04-ground-wide-angle-camera-array.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




