If you hear astronomers converse of liveable worlds – or worlds within the liveable zone of their stars – do you consider alien civilizations? Or do you consider worlds the place people would possibly sometime stay? What do astronomers imply by liveable? Maybe not what you assume.
To an astronomer, the phrase liveable merely means a planet whose bodily circumstances would possibly permit life – any type of life, maybe microbial life – to exist there. Right here’s what NASA says concerning the phrase liveable:
The usual definition for a liveable planet is one that may maintain life for a major interval. Primarily based on our solar system, life requires liquid water, vitality and vitamins. A ‘liveable zone’ is the area round a star the place planets can obtain the proper quantity of warmth to take care of liquid water on their surfaces.
So our Earth, for instance, is liveable. It’s the one planet within the liveable zone of our star, that’s, the one one in all our sun’s planets the place liquid water can exist on the floor. So Earth has the precise circumstances for all times: liquid water, vitality, vitamins. Different worlds orbiting distant stars additionally lie within the liveable zones of their stars. However have they got liquid water … sufficient vitality reaching the floor for dwelling issues to develop, thrive and produce vitamins? We don’t know for certain but of any worlds like that, past Earth.
Liveable doesn’t imply inhabited
So it goes with out saying that – to date – Earth is the solely planet we all know that’s inhabited. And it’s additionally the solely planet we all know, to date, the place human life can stroll round on the floor with out spacesuits, respiration the air, ingesting the water, consuming the vegetation.
Then once more, exoplanets – or planets orbiting distant sun – aren’t simple to seek out. As of late January 2024, we all know solely 5,572 confirmed exoplanets in 4,145 planetary programs, with 942 programs having multiple planet. In the meantime, there are an estimated 100 to 400 billion stars in our dwelling galaxy, the Milky Way.
So after we within the science media point out liveable exoplanets, please don’t assume it means we’re suggesting that world is perhaps an alternate Earth, or a world we would sometime colonize. Removed from it! Likewise, liveable doesn’t imply that astronomers imagine alien life exists on this or that distant planet.
So why talk about habitability in any respect? The phrase has educational curiosity, definitely; skilled astronomers are curious. And plenty of within the public are curious additionally! We at EarthSky are curious. Aren’t you? Is Earth alone within the Milky Way galaxy, or are different worlds able to supporting life as we all know it? These are large and weighty questions, and it’s thrilling that astronomers are ferreting out the clues that may allow us to start to reply them.
And certain. Perhaps sometime people will enterprise to a liveable exoplanet. And possibly sometime we will discover life on a world orbiting the liveable zone of its star. However will this occur in our lifetimes? Will it ever occur?
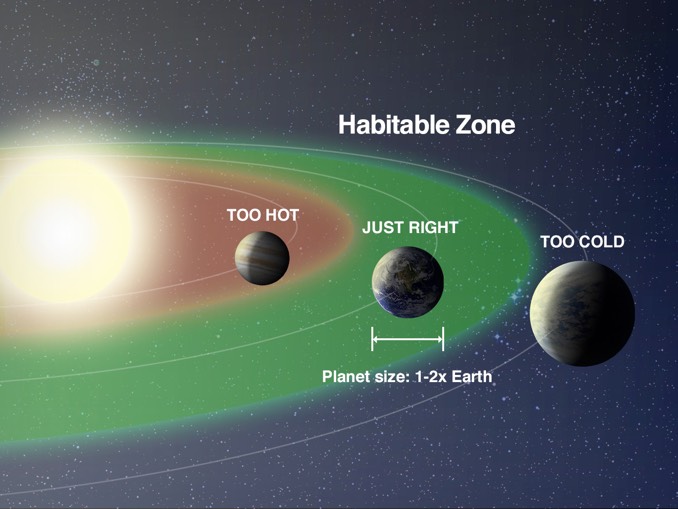
Habitability in our solar system
Let’s have a look at our personal solar system. We all know Earth is liveable. However what concerning the different planets and moons? Some scientists assume Venus might have been habitable in the past, however local weather change turned it into the scorching furnace we all know at the moment. It additionally seems that Mars might have been extra liveable prior to now, when an ocean lined a lot of its floor. Even Mercury might have liveable spots, equivalent to in its salt glaciers.
Farther out within the solar system, Saturn’s moon Enceladus is an thrilling prospect for habitability. It’s lined in a world ocean hiding beneath an icy crust. Jupiter’s moon Europa may additionally have an ocean that could possibly be liveable.
Liveable exoplanets
Many scientists are researching simply what elements, abundances and combinations we needs to be on the lookout for to seek out liveable exoplanets.
A few of the different key issues scientists search for are terrestrial planets with the potential for water on their surfaces. A few of the candidate exoplanets for habitability embody K2-18 b, which can have a deep hydrogen environment and international water ocean. One other is Wolf 1069 b, an Earth-size and Earth-mass exoplanet orbiting within the liveable zone of its star simply 31 light-years away.
Plans for a devoted observatory
A proposed mission, known as the Habitable Worlds Observatory, would assist astronomers examine exoplanets in liveable zones. In August 2023, scientists and engineers gathered at Caltech to debate the longer term mission, which might launch within the late 2030s or early 2040s. The Nationwide Academy of Sciences’ Decadal Survey on Astronomy and Astrophysics – a roadmap of upcoming astronomy targets – picked the Liveable Worlds Observatory as their prime precedence in 2020. The observatory can be second in energy solely to the James Webb Space Telescope.
Backside line: When astronomers say a distant world is ‘liveable,’ what do they imply? Do they imply people might stay there? Do they imply we’ve found alien life? No to each. They merely imply that – on that distant world – the circumstances are proper for all times, probably simply microbial life, to exist.




