The define of the Hyades open star cluster in Taurus is likely one of the finest naked-eye landmarks within the winter sky. It’s brightest stars type right into a ‘V’- or wedge-shaped-asterism, or star sample that’s a simple spot round 25 levels to the upper-right (north-west) of Orion’s well-known ‘Belt’.
First-magnitude Aldebaran, a Ok-class big star that exudes a noticeably orange-red hue, dominates the asterism although it lies too near us (65 gentle years) to be a member of the open cluster. It’s blissful line-of-sight coincidence offers observers a terrific celestial signpost to the Hyades ought to or not it’s wanted.
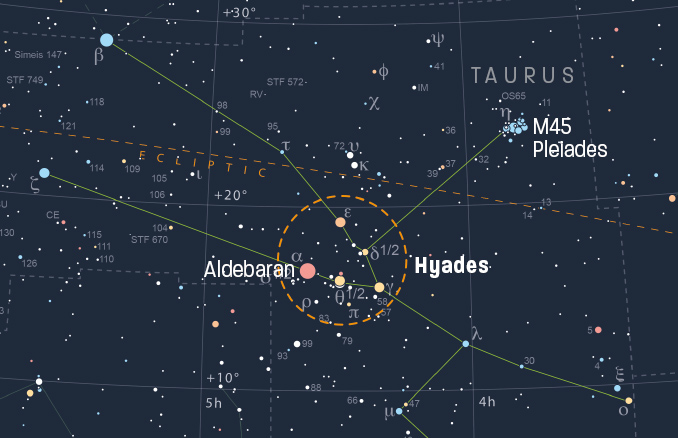
The Hyades, additionally catalogued as Caldwell 41, Melotte 25 and Collinder 50, is the closest open cluster to our Photo voltaic System at a distance of 153 gentle years, close to sufficient to be precisely measured by parallax. Round 200 stars are believed to populate the Hyades, which shaped about 625 million years in the past.

In the end, the Hyades will over the eons lose its stars to gravitational interplay inside the cluster itself and dissipate into interstellar space. Current observations by the Gaia spacecraft means that this course of is being accelerated the gravitational affect of a large and unseen construction in our Galaxy, which astronomers suspect may very well be a dark matter sub-halo.
The Hyades’ brightest stars are 5 of these within the ‘V’formation, specifically specifically gamma (γ, magnitude +3.65), epsilon (ε, +3.53), delta¹ (δ¹, +3.77), and at last, theta (θ) Tauri, a double star of parts + 3.84 (θ¹) and +3.40 (θ¹) separated by 5.62 arcminutes. The Hyades spans 4 x 3 levels, making it good for framing in a humble pair of binoculars binoculars.





