Life and supernovae do not combine.
From a distance, supernovae explosions are fascinating. A star extra large than our sun runs out of hydrogen and turns into unstable. Ultimately, it explodes and releases a lot vitality it could possibly outshine its host galaxy for months.
However space is huge and largely empty, and supernovae are comparatively uncommon. And most planets do not help life, so most supernovae in all probability explode with out affecting dwelling issues.
However a brand new examine, accessible on the preprint server arXiv, reveals how one kind of supernova has a extra prolonged attain than thought. And it may have penalties for planets like ours.
Earth is not any stranger to supernovae. One hasn’t been shut sufficient to sterilize Earth, however there’s proof exhibiting supernovae have affected life on Earth.
A 2018 paper offered proof of a supernova exploding close to Earth about 2.6 million years in the past. It was about 160 light-years away. The authors of that paper tied the supernova to the Pliocene marine megafauna extinction. In that occasion, as much as a 3rd of Earth’s giant marine species had been worn out, however solely in shallow coastal waters.
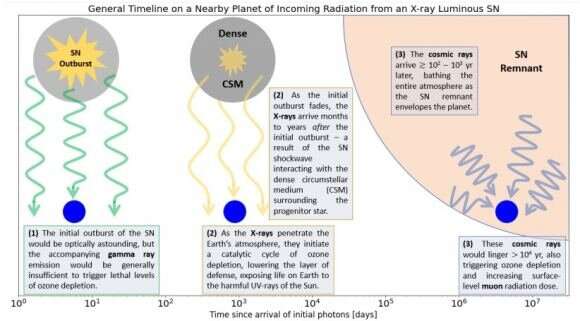
One other paper confirmed as much as 20 supernovae within the final 11 million years within the Scorpius-Centaurus OB affiliation. A few of these had been as shut as 130 light-years to Earth. The paper’s authors say that about 2 million years in the past, one of many supernovae exploded shut sufficient to our planet to break the ozone layer.
However there are various kinds of supernovae. A few of them have a for much longer attain and far higher period. Scientists have lengthy recognized in regards to the highly effective gamma rays that supernova launch through the explosion. Additionally they know in regards to the cosmic rays that may arrive a whole lot or 1000’s of years later. If this occurs shut sufficient to a planet like Earth, the cosmic rays can deplete the ozone layer and enhance muon radiation on the floor.
A sort IIn X-ray luminous supernova is totally different from different supernovae. When a supernova explodes, it emits gamma rays and different photons instantly. In an X-ray luminous supernova, gamma rays and photons are emitted, however among the radiation from the explosion interacts with a dense circumstellar medium surrounding the progenitor star. This creates X-rays that may be deadly as much as 160 light-years away.
In a situation the place an SN exploded near Earth, it could possibly take months or years following the preliminary explosion for the X-rays to reach. Interactions with the circumstellar particles trigger a delay. The X-rays can deplete Earth’s ozone layer, permitting dangerous UV radiation from the Solar to succeed in the planet’s floor.
After the X-rays arrive, the cosmic rays arrive, much like different SN. This can be a double whammy for Earth’s ozone layer.
Researchers aren’t positive in regards to the deadly distances of supernovae. There are lots of variables, each within the progenitor star and its setting. The progenitor star’s mass loss is very essential. However by characterizing the deadly X-ray dose for Earth’s stratosphere and the energy output of among the brightest SN, the authors calculated the deadly distance for some well-known supernovae.
SN 1987A exploded within the Giant Magellanic Cloud, and the sunshine reached Earth in 1987. Scientists noticed the explosion and confirmed the supply of vitality for the SN’s seen mild for the primary time. It proved that the long-duration glow after an SN explosion is radioactive.
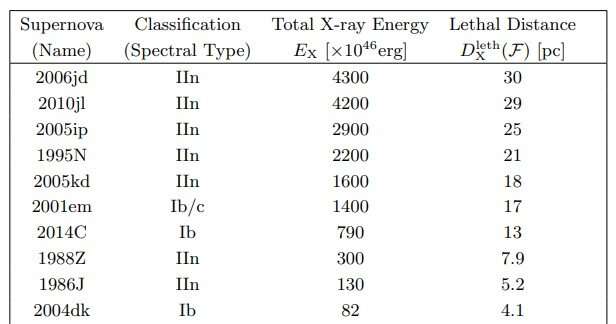
SN1987A wasn’t very deadly, based on the authors. They are saying the SN was solely lethal to a distance of lower than one light-year. It was the least harmful SN out of the 31 the workforce characterised.
Probably the most deadly of the 31 was SN2006jd. It exploded within the galaxy NGC 4179, about 57 million light-years away, and the sunshine reached Earth in 2006. In accordance with the researchers, SN2006jd was deadly to nearly 100 light-years.
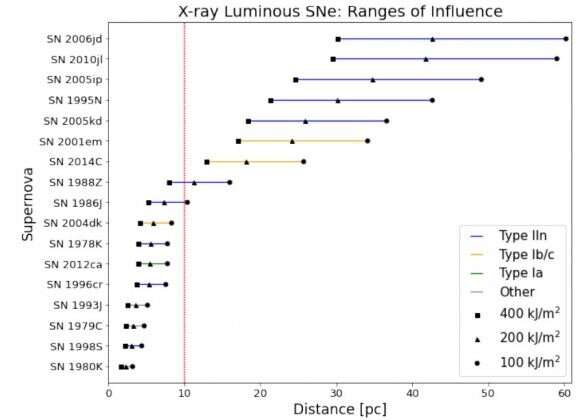
The 5 most deadly SNs on this examine are all Sort IIn supernovae, as are seven of the highest ten.
Sort IIn supernovae even have the best vary of affect. This reveals that these SN may considerably affect Earth’s biosphere from higher distances.
This analysis has some implications for Earth.
Our solar system is inside what’s often called the Native Bubble. It is a cavity carved out of the ISM within the Milky Way’s Orion Arm. A number of supernovae explosions created the bubble within the final 10 to twenty million years. Did these SN have an effect on Earth?
Advances in X-ray astronomy will shed extra mild on the implications for terrestrial planets, and the authors suppose there’s tons extra to uncover. However their observations present that “… the interacting X-ray phase of an SN’s evolution can entail vital penalties for terrestrial planets. We restrict any additional hypothesis till additional developments in X-ray astronomy are made; nevertheless, the proof offered right here actually factors to this course of as able to imposing deadly penalties for all times at formidable distances.”
Scientists know that supernovae have had some impact on Earth. The presence of the radioactive isotope 60Fe has a half-life of two.6 million years, but researchers discovered undecayed 60Fe in ocean samples relationship from 2 to three Myr in the past. It ought to’ve decayed into nickel way back. Supernovae can create 60Fe by way of nucleosynthesis after they explode.
However different issues can create 60Fe. Asymptomatic big department stars could make it, too, so by itself, it is not a smoking gun for a close-by supernova.
Researchers additionally discovered 53Mn in the identical samples of ferromanganese crust that maintain the 60Fe. It is also a radioactive isotope that ought to’ve decayed by now. Not like 60Fe, solely supernovae can create 53Mn. Its presence is particular proof of close by supernovae within the current geological previous.
It is not the presence of those radioactive isotopes that poses a risk to life. It is the radiation that should’ve struck Earth, and if the supernova that created the isotopes was shut sufficient to unfold them to Earth, then the radiation should’ve struck Earth, too.
Ionizing radiation from supernovae can alter Earth’s atmospheric chemistry from substantial distances. The preliminary burst of vitality from an SN poses one risk, and so do the cosmic rays that arrive a whole lot or 1000’s of years later and linger. However this analysis provides one other risk: X-rays that arrive months or years after the preliminary outburst. “Due to this fact, a corollary of the formidable risk discovered right here is that this alters the timeline by which we all know an SN can affect a close-by planet, including a further phase of antagonistic results.”

Precisely what impact did it have?
“Combining these findings with our risk evaluation right here, it’s attainable that a number of of those SNe had been interacting, and thus inflicted a excessive dosage of X-ray radiation on Earth’s ambiance. This is able to suggest that SN X-ray emission has had a notable influence on Earth and probably performed a task within the evolution of life itself,” they write.
SN outbursts have nearly actually struck our planet. The precise penalties are tough for scientists to untangle. But when the radiation weakened the ozone layer, permitting extra UV radiation to succeed in the Earth’s floor, it could’ve prompted mutations. It is referred to as UV mutagenesis, which can have pushed molecular evolution and been vital within the origin of intercourse. The truth is, mutation is evolution’s major driver.
The truth that supernovae can result in mutations is the backdrop for the authors’ concluding remarks.
“We thus conclude with the remark that additional analysis into SN X-ray emission has worth not only for stellar astrophysics but additionally for astrobiology, paleontology, and the Earth and planetary sciences as an entire.”

This analysis has implications for habitability all through the galaxy, too. The Galactic Liveable Zone (GHZ) is a area in a galaxy the place habitability is almost certainly. Since supernovae may be deadly for all times if shut sufficient, areas with many stars that may probably explode as supernovae are much less liveable. If this analysis is right, then supernovae may be deadly at higher distances than thought and may be deadly within the interval of some months or years after the preliminary outburst as a result of X-rays. That alters the form and placement of a galaxy’s GHZ.
The researchers urge extra long-term examine of supernovae for months and years after an outburst and plea for extra developments in X-ray statement to help the examine. “These observations and improvements will make clear the bodily nature of SN X-ray emission and can make clear the hazard that these occasions pose for all times in our galaxy and different star-forming areas,” they write.
Ian R. Brunton, Connor O’Mahoney, Brian D. Fields, Adrian L. Melott, Brian C. Thomas, X-Ray Luminous Supernovae: Threats to Terrestrial Biospheres. arXiv:2210.11622v1 [astro-ph.HE], arxiv.org/abs/2210.11622
Quotation:
How harmful are close by supernovae to life on Earth? (2022, October 27)
retrieved 27 October 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-10-dangerous-nearby-supernovae-life-earth.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




