Wayward asteroids current an actual collision hazard to Earth. Scientists estimate that an asteroid measuring a number of miles throughout smashed into Earth 65 million years in the past and worn out the dinosaurs, amongst different types of life, in a mass extinction. In contrast to the dinosaurs, humanity can keep away from this destiny if we start working towards the best way to knock an Earth-approaching asteroid off target.
That is trickier than the way it has been depicted in science fiction motion pictures like Deep Impression. Planetary scientists first have to understand how asteroids had been assembled. Are they flying rubble piles of loosely agglomerated rocks, or one thing extra substantial? This info would assist present methods on the best way to efficiently deflect a menacing asteroid.
As a primary step, NASA did an experiment to smash into an asteroid to see how it’s perturbed. The DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Take a look at) spacecraft impression on asteroid Dimorphos occurred on September 26, 2022. Astronomers utilizing the Hubble Area Telescope proceed following the aftermath of the cosmic collision.
A shock is the invention of a number of dozen boulders lifted off the asteroid after the smashup. In Hubble photos they seem like a swarm of bees very slowly transferring away from the asteroid. This may imply that smacking an Earth-approaching asteroid may end in a cluster of threatening boulders heading in our course.
The favored 1954 rock music “Shake, Rattle and Roll,” could possibly be the theme music for the Hubble Area Telescope’s newest discovery about what is occurring to the asteroid Dimorphos within the aftermath of NASA’s DART (Double Asteroid Redirection Take a look at) experiment. DART deliberately impacted Dimorphos on September 26, 2022, barely altering the trajectory of its orbit across the bigger asteroid Didymos.
Astronomers utilizing Hubble’s extraordinary sensitivity have found a swarm of boulders that had been probably shaken off the asteroid when NASA intentionally slammed the half-ton DART impactor spacecraft into Dimorphos at roughly 14,000 miles per hour.
The 37 free-flung boulders vary in measurement from three toes to 22 toes throughout, primarily based on Hubble photometry. They’re drifting away from the asteroid at little greater than a half-mile per hour—roughly the strolling velocity of a large tortoise. The total mass in these detected boulders is about 0.1% the mass of Dimorphos.
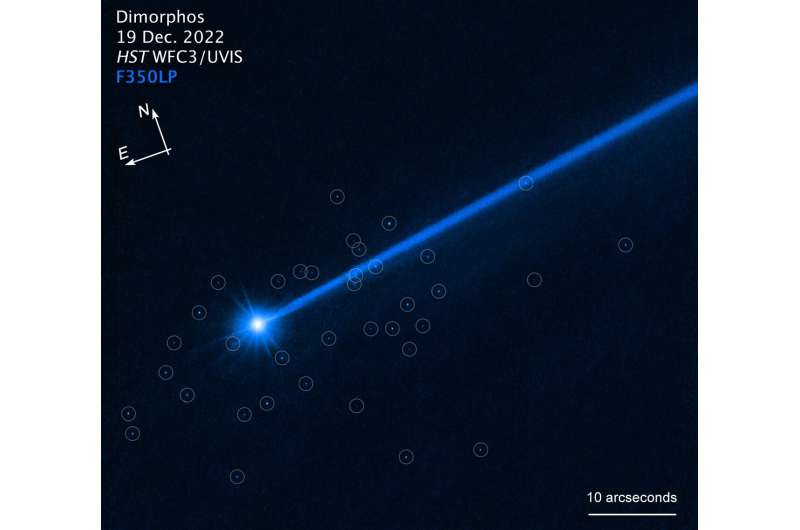
“This can be a spectacular remark—a lot better than I anticipated. We see a cloud of boulders carrying mass and power away from the impression goal. The numbers, sizes, and shapes of the boulders are according to them having been knocked off the floor of Dimorphos by the impression,” mentioned David Jewitt of the College of California at Los Angeles, a planetary scientist who has been utilizing Hubble to trace adjustments within the asteroid throughout and after the DART impression.
“This tells us for the primary time what occurs while you hit an asteroid and see materials popping out as much as the biggest sizes. The boulders are among the faintest issues ever imaged inside our solar system.”
Jewitt says that this opens up a brand new dimension for finding out the aftermath of the DART experiment utilizing the European Area Company’s upcoming Hera spacecraft, which can arrive on the binary asteroid in late 2026. Hera will carry out an in depth post-impact survey of the focused asteroid.
“The boulder cloud will nonetheless be dispersing when Hera arrives,” mentioned Jewitt. “It is like a really slowly increasing swarm of bees that finally will unfold alongside the binary pair’s orbit across the sun.”
The boulders are almost certainly not shattered items of the diminutive asteroid attributable to the impression. They had been already scattered throughout the asteroid’s floor, as evident within the final close-up image taken by the DART spacecraft simply two seconds earlier than collision, when it was solely seven miles above the floor.
Jewitt estimates that the impression shook off two p.c of the boulders on the asteroid’s floor. He says the boulder observations by Hubble additionally give an estimate for the dimensions of the DART impression crater. “The boulders may have been excavated from a circle of about 160 toes throughout (the width of a soccer area) on the floor of Dimorphos,” he mentioned. Hera will finally decide the precise crater measurement.
Way back, Dimorphos could have shaped from materials shed into space by the bigger asteroid Didymos. The mum or dad physique could have spun up too shortly or may have misplaced materials from a glancing collision with one other object, amongst different situations. The ejected materials shaped a hoop that gravitationally coalesced to kind Dimorphos. This may make it a flying rubble pile of rocky particles loosely held collectively by a comparatively weak pull of gravity. Due to this fact, the inside might be not strong, however has a construction extra like a bunch of grapes.
It isn’t clear how the boulders had been lifted off the asteroid’s floor. They could possibly be a part of an ejecta plume that was photographed by Hubble and different observatories. Or a seismic wave from the impression could have rattled by the asteroid—like hitting a bell with a hammer—shaking lose the floor rubble.
“If we comply with the boulders in future Hubble observations, then we could have sufficient knowledge to pin down the boulders‘ exact trajectories. After which we’ll see wherein instructions they had been launched from the floor,” mentioned Jewitt.
The findings are revealed in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Extra info:
David Jewitt et al, The Dimorphos Boulder Swarm, The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2023). DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ace1ec
Offered by
ESA/Hubble Information Centre
Quotation:
Hubble sees boulders escaping from asteroid Dimorphos (2023, July 20)
retrieved 20 July 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-07-hubble-boulders-asteroid-dimorphos.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




