The examine of how particular person stars are born and die in galaxies, how new stars are born from remnants of previous stars, and the way galaxies themselves develop are necessary themes in astronomy, as they supply perception into our roots within the universe. Galaxy clusters, one of many largest buildings within the universe, are the meeting of greater than 100 galaxies that are certain collectively by means of mutual gravitational pressure.
Observations of close by galaxies have proven that the expansion of a galaxy depends upon its surroundings within the sense that mature stellar populations are generally seen in areas the place galaxies are densely collected. That is known as the “surroundings impact.” Though the surroundings impact has been thought-about an necessary piece to grasp galaxy formation and evolution, it’s not well-known when the impact initiated within the historical past of the universe.
One of many keys to understanding that is to look at the ancestors of galaxy clusters shortly after the beginning of the universe; generally known as galaxy protoclusters (hereafter protoclusters), these are assemblies of about 10 distant galaxies. Luckily, astronomy permits us to look at the distant universe because it was prior to now. For instance, gentle from a galaxy 13 billion light-years away takes 13 billion years to achieve Earth, so what we observe now’s what that galaxy seemed like 13 billion years in the past.
Nonetheless, gentle that travels 13 billion light-years turns into fainter, so the telescopes that observe it should have excessive sensitivity and spatial decision.
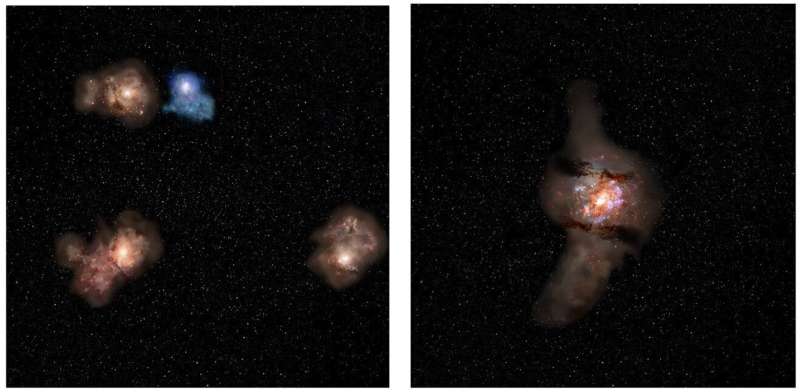
A global analysis workforce led by Assistant Professor Takuya Hashimoto (College of Tsukuba, Japan) and researcher Javier Álvarez-Márquez (Spanish Heart for Astrobiology) has used the James Webb Area Telescope (JWST, observing seen and infrared light) and the Atacama Giant Millimeter/submillimeter Array (ALMA, observing radio waves) to review the “core area” of the protocluster A2744z7p9OD.
The protocluster A2744z7p9OD had been introduced as probably the most distant proto-cluster at 13.14 billion light-years away primarily based on observations with JWST by one other analysis group. “Nonetheless, we now have not been capable of observe all the core area, the metropolitan space, with the biggest variety of galaxy candidates on this protocluster. It was unclear whether or not the environmental results of galaxies had begun on this protocluster. So we determined to focus our analysis on the core area,” says Hashimoto.
The analysis workforce first noticed the core area of this protocluster utilizing JWST. Utilizing NIRSpec, an instrument that observes spectra at wavelengths starting from seen to near-infrared, the workforce made integral subject spectroscopy observations that may concurrently purchase spectra from all areas throughout the subject of view.
The workforce has efficiently detected ionized oxygen-ion gentle ([OIII] 5008 Å) from 4 galaxies in a quadrangle area measuring 36,000 light-years alongside a facet, which is equal to half the radius of the Milky Way galaxy. Primarily based on the redshift of this gentle (the elongation of the wavelength because of the cosmic growth), the gap of the 4 galaxies from the Earth was recognized as 13.14 billion gentle years.
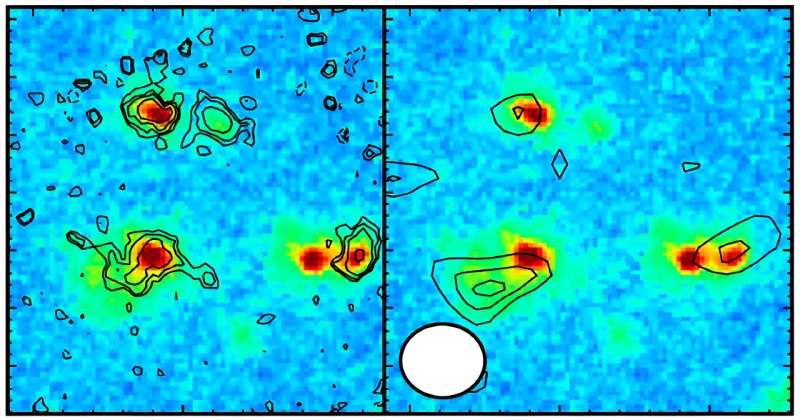
“I used to be shocked once we recognized 4 galaxies by detecting oxygen-ion emission at nearly the identical distance. The ‘candidate galaxies’ within the core area have been certainly members of probably the most distant protocluster,” says Yuma Sugahara (Waseda/NAOJ), who led the JWST information evaluation.
As well as, the analysis workforce paid consideration to the archival ALMA information, which had already been acquired for this area. The information captures radio emission from cosmic dust in these distant galaxies. On account of analyses, they detected dust emissions from three of the 4 galaxies.
That is the primary detection of dust emission in member galaxies of a protocluster this far again in time. Cosmic dust in galaxies is regarded as provided by supernova explosions on the finish of the evolution of large stars within the galaxies, which give the fabric for brand new stars.
Due to this fact, the presence of enormous quantities of dust in a galaxy signifies that lots of the first-generation stars within the galaxy have already accomplished their lives and that the galaxy is rising. Professor Luis Colina (El Centro de Astrobiología (CAB, CSIC-INTA)) describes the importance of the outcomes: “Emission from cosmic dust was not detected in member galaxies of the protocluster exterior the core area. The outcomes point out that many galaxies are clustered in a small area and that galaxy development is accelerated, suggesting that environmental results existed solely ~700 million years after the Large Bang.”
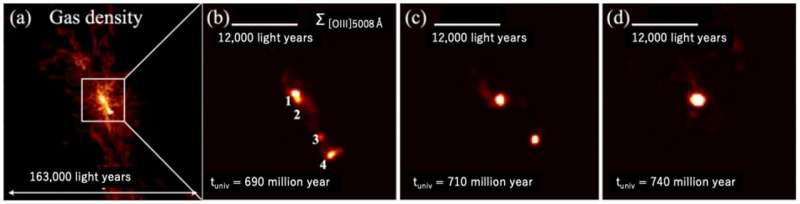
Moreover, the analysis workforce performed a galaxy formation simulation to theoretically take a look at how the 4 galaxies within the core area shaped and developed. The outcomes confirmed {that a} area of dense fuel particles existed round 680 million years after the Large Bang. Within the center 4 galaxies are shaped, just like the noticed core area. To observe the evolution of those 4 galaxies, the simulation calculated bodily processes such because the kinematics of stars and fuel, chemical reactions, star formation, and supernovae.
The simulations confirmed that the 4 galaxies merge and evolve right into a single bigger galaxy inside a couple of tens of tens of millions of years, which is a short while scale within the evolution of the universe.
“We efficiently reproduced the properties of the galaxies within the core area owing to the excessive spatial decision of our simulations and the massive variety of galaxy samples we now have. Sooner or later, we want to discover the formation mechanism of the core area and its dynamical properties in additional element,” says Yurina Nakazato, a graduate pupil on the College of Tokyo, who analyzed the simulation information.
Javier Álvarez-Márquez (Spanish Heart for Astrobiology) says, “We’ll conduct extra delicate observations of the proto-cluster A2744z7p9OD with ALMA to see if there are any galaxies that weren’t seen with the earlier sensitivity. We may also apply the JWST and ALMA observations, which have confirmed to be very highly effective, to extra protoclusters to elucidate the expansion mechanism of galaxies, and to discover our roots within the universe.”
The work is revealed in The Astrophysical Journal Letters.
Extra data:
T. Hashimoto et al, Reionization and the ISM/Stellar Origins with JWST and ALMA (RIOJA): The Core of the Highest-redshift Galaxy Overdensity at z = 7.88 Confirmed by NIRSpec/JWST, The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2023). DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/acf57c
Supplied by
University of Tsukuba
Quotation:
James Webb Area Telescope and ALMA seize the core of probably the most distant galaxy protocluster (2023, September 20)
retrieved 20 September 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-09-james-webb-space-telescope-alma.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




