Ganymede is Jupiter’s largest moon, and it’s additionally the most important moon within the solar system. Like a number of different icy moons, scientists assume that Ganymede has a deep ocean of liquid water beneath its outer ice crust. Now, NASA’s Juno spacecraft has discovered mineral salts and natural compounds on Ganymede’s floor. The findings recommend that briny water has made its option to the moon’s floor. NASA said on October 30, 2023, that the invention will assist scientists study extra concerning the composition of the ocean and the way the moon itself first shaped.
Researchers within the U.S. and Italy published their peer-reviewed ends in Nature Astronomy on October 30.
The 2024 lunar calendars are here! Best Christmas gifts in the universe! Check ’em out here.
A detailed flyby of Ganymede
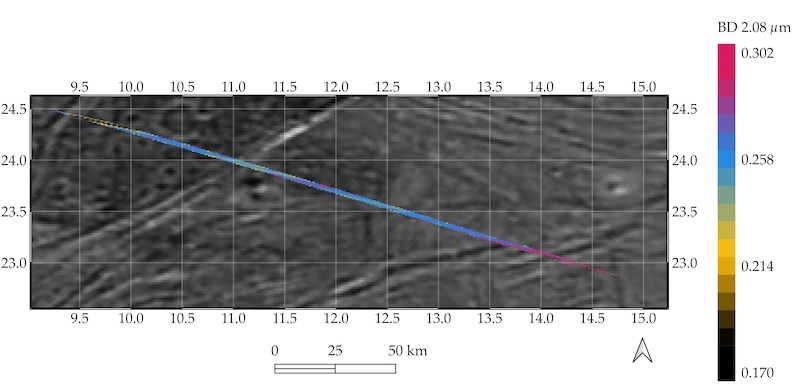
Juno carried out a detailed flyby of Ganymede on June 7, 2021, coming inside 650 miles (1,046 km) of the icy floor. Juno’s Jovian InfraRed Auroral Mapper (JIRAM) spectrometer acquired infrared photographs and infrared spectra. Usually, mission scientists primarily use JIRAM to see deep into Jupiter’s environment. They’ve additionally used it, nonetheless, to review the surfaces of Io, Europa, Ganymede and Callisto.
And, the truth is, the decision of the infrared spectroscopy throughout the flyby was spectacular, higher than 0.62 miles (1 km) per pixel. Juno discovered a wide range of floor supplies, together with hydrated sodium chloride, ammonium chloride, sodium bicarbonate and perhaps additionally aliphatic aldehydes.
Federico Tosi is a Juno co-investigator on the Nationwide Institute for Astrophysics in Rome, Italy, and lead writer of the brand new paper. He said:
The presence of ammoniated salts means that Ganymede might have accrued supplies chilly sufficient to condense ammonia throughout its formation. The carbonate salts may very well be remnants of carbon dioxide-rich ices.
Watery brines
Because the paper defined, the composition and distribution of the salts and organics means that they originated from inside Ganymede (making them endogenous, or endogenic). In reality, they most probably got here to the floor in watery brines:
The composition and spatial distribution of those salts and organics recommend that their origin is endogenic, ensuing from the extrusion of subsurface brines, whose chemistry displays the water–rock interplay inside Ganymede.
As well as, this result’s paying homage to one other examine that was revealed final month, displaying that carbon-dioxide ice on the floor of Europa came from inside the moon as an alternative of from an exterior supply (exogenous).
Magnetic area protects brines
So, how do the scientists know that the salts and organics got here from beneath as brines, as an alternative of being created on the floor by some means? One large clue comes from Ganymede’s magnetic area. The magnetic area shields the moon’s floor alongside the equator as much as about 40 levels latitude. Extra particularly, the magnetic area blocks electrons and ions that come from Jupiter’s personal and extra highly effective magnetic area. These electrons and ions can simply injury the mineral salts and organics.
In 2021, throughout the flyby, Juno’s JIRAM instrument studied Ganymede’s floor from latitudes 10 levels north to 30 levels north and longitudes -35 levels east to 40 levels east. These areas embody the moon’s attribute darkish and brilliant areas. These latitudes are protected by the magnetic area. And – shock – that’s the place the salts and organics had been primarily discovered. Scott Bolton, Juno’s principal investigator on the Southwest Analysis Institute in San Antonio, Texas, stated:
We discovered the best abundance of salts and organics in the dead of night and brilliant terrains at latitudes protected by the magnetic area. This implies we’re seeing the remnants of a deep ocean brine that reached the floor of this frozen world.
Initially, proof for Ganymede’s magnetic area first got here when the Hubble Space Telescope noticed the moon in ultraviolet (UV) gentle in 1998 and 2010. Pictures from each observations revealed an aurora zone on Ganymede. This was an indication that the big moon has a everlasting magnetic area, produced by an iron core.
Water vapor on Ganymede
Additionally, in 2021, astronomers utilizing archival knowledge from Hubble discovered the primary proof of water vapor on Ganymede. Utilizing the previous knowledge together with new knowledge, the researchers measured the quantity of atomic oxygen within the moon’s tenuous environment. What they discovered was that the moon Ganymede has hardly any atomic oxygen. In essence, this discovering appeared to upend their clarification for variations within the UV auroras.
However then, they regarded extra carefully at the place the UV auroral shows had been on Ganymede. Because it turned out, the areas of Ganymede’s auroras correlated with the place they’d look forward to finding water in Ganymede’s environment, if the moon was releasing water vapor.
Backside line: NASA’s Juno spacecraft has discovered salts and organics on Jupiter’s largest moon, Ganymede. They recommend that watery brines got here as much as the floor from deep beneath.
Source: Salts and organics on Ganymede’s surface observed by the JIRAM spectrometer onboard Juno
Learn more about the Juno mission
Read more: See 1st new images of Ganymede in over 20 years
Read more: Webb telescope provides unique view of 2 Jupiter moons




