Once you launch humanity’s strongest telescope, you anticipate outcomes. The JWST has delivered glorious outcomes by detecting historical galaxies, figuring out chemical compounds in exoplanet atmospheres, and peering into star-forming areas with extra element and readability than another telescope.
However each time a brand new telescope is about to enter service, astronomers inform us they’re excited not solely in regards to the anticipated outcomes but in addition in regards to the shocking outcomes. And like different telescopes, the JWST has additionally delivered some surprises. Whereas going about its enterprise, the JWST has found 21 brown dwarfs.
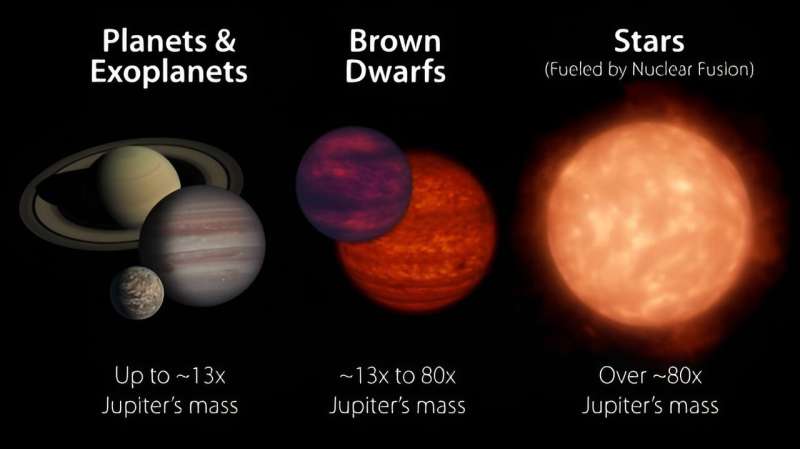
Brown dwarfs are “in-between” objects. They’re generally known as “failed stars.” They’re extra huge than a gas giant, however much less huge than a star. They by no means grew huge sufficient to set off hydrogen fusion, the hallmark of a primary sequence star.
Brown dwarfs won’t appear very attention-grabbing. They don’t seem to be planets, and so they’re not stars. However they’re a part of nature, so that they match into the grand scheme of issues in some way.
There are scientific causes to need to study extra about them. “Choosing and characterizing these sources is significant for exploring the stellar preliminary mass perform, understanding binary stellar evolution, and for growing the census of stars round which probably habitable planets might lie,” the authors of a brand new paper clarify.
The paper is “Brown Dwarf Candidates in the JADES and CEERS Extragalactic Surveys,” and it is obtainable on the arXiv preprint server. The lead writer is Kevin Hainline, an Assistant Analysis Professor at Steward Observatory.
Brown dwarfs emit most of their mild within the infrared, which the JWST makes a speciality of sensing. However brown dwarfs are nonetheless tough to detect, even for the mighty JWST. The 21 new brown dwarfs had been present in information from two completely different surveys carried out by the JWST that weren’t targeted on brown dwarfs: JADES and CEERS.
JADES is the JWST Superior Deep Extragalactic Survey, and CEERS is the Cosmic Evolution Early Launch Science Survey. Each surveys are targeted on distant, historical galaxies, one of many JWST’s major science targets. The brand new brown dwarfs had been hidden in all their information.
These findings are vital due to the placement of the brown dwarfs. A lot of the brown dwarfs we learn about are in our stellar neighborhood, as a result of that is the place they’re best to see. However that is an issue as a result of when astronomers need to research one thing, they want a great, consultant pattern. They cannot draw any strong conclusions from a pattern that is all from one area of a galaxy.
“It is important to increase on these samples, as brown dwarf stars at these distances assist us perceive the historical past of star formation within the Milky Way,” the authors write. A lot of the 21 newly found brown dwarfs are within the Milky Way’s thick disk and halo. They’re between between 0.1 and 4.2 kpc., about 360 lightyears to 13,700 lightyears away.
Among the outcomes of this analysis present how a lot we’ve got but to find out about brown dwarfs. Our lack of expertise should not come as a shock. Brown dwarfs had been first theorized to exist within the Nineteen Sixties, however the first unambiguous detections weren’t till the mid-Nineteen Nineties. Astrophysicists are nonetheless determining the place they slot in.
The areas of among the brown dwarfs, particularly those within the galactic halo, are at odds with what form we expect galaxies take. “Whereas nearly all of the sources are within the thick disk, we do discover 4 sources which are probably within the Milky Way halo,” the researchers write. “These sources are poorly match with galaxy template fashions.” Their atmospheric spectra additionally aren’t a great match with present fashions.
The crew of researchers discovered these brown dwarfs in simply the primary 12 months of information from each JADES and CEERS. So they may possible discover extra sooner or later, particularly since this work reveals how completely different JWST filters make the brown dwarfs discoverable. However the actual enjoyable would possibly start sooner or later. “These sources present an thrilling alternative for follow-up observations with focused JWST NIRSpec spectroscopy, contemplating their positions inside the Milky Way,” the authors clarify.
Solely just lately, a research in The Astrophysical Journal Letters introduced the very first focused observations of a brown dwarf with the JWST. That research is titled “The First JWST Spectral Energy Distribution of a Y Dwarf.” (Brown dwarfs are of spectral sorts M, L, T, and Y.) These observations introduced some outcomes that conflicted with idea.
“This supply introduced a problem to theoretical fashions, demonstrating the significance of accelerating the variety of these sources explored spectroscopically,” the authors write. So it is important to look at extra brown dwarfs with the JWST’s NIRSpec and MIRI devices.
Brown dwarfs are nonetheless elusive targets. They’re very faint and really low-mass in comparison with primary sequence stars. Some might be as massive as 80 instances extra huge than Jupiter, regardless that they’re all about the identical radius as Jupiter. That is tiny for a star. Nonetheless, discovering extra of them and finding out them in higher element is crucial to understanding how stars and planets type. Thankfully, astronomers are about to search out many extra of them and can start to fill within the gaps of their information.
These 21 brown dwarfs had been present in surveys which are extragalactic. These surveys are designed to detect objects exterior the Milky Way and to keep away from stellar contamination. That is led us to a contented accident.
“Whereas extragalactic deep fields are designed to level exterior the aircraft of our galaxy to reduce stellar contamination, the utilization of JWST deep observations to gather these sources has implications for the inhabitants of objects exterior of the thick disk, which can be among the many most metal-poor and oldest stars at these temperatures within the galaxy,” the paper states.
There are a bunch of unanswered questions surrounding brown dwarfs. When one types, it types in a disk identical to another star. It is affordable to imagine that planets type within the disk identical to round different stars. However a brown dwarf’s disk has a lot much less mass than the disk round different stars, in addition to having a lot smaller radii. That ought to favor the formation of terrestrial planets like Earth quite than gasoline giants. However solely observations can conclude if that is the case.
Brown dwarfs are neither stars nor planets, and their evolution may very well be very unusual. Astrophysicists suppose that as a brown dwarf cools, about 100 million to 500 million years after formation, unusual issues occur in its ambiance. It is attainable that dusty clouds of quartz and different minerals might type.
The authors of this paper are clearly trying ahead to what could be a coming glut of brown dwarf detections. Some estimates say there are between 25 billion and 100 billion brown dwarfs within the Milky Way. We’re solely within the early days of finishing a census of brown dwarfs, and as astronomers detect an increasing number of of them and topic them to review, we’ll perceive the place they slot in nature.
“We anticipate that the massive bounty of brown dwarf candidates discovered over the subsequent a number of years will make clear the historical past of star and planet formation in our galaxy.”
Extra data:
Kevin N. Hainline et al, Brown Dwarf Candidates within the JADES and CEERS Extragalactic Surveys, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2309.03250
Samuel A. Beiler et al, The First JWST Spectral Vitality Distribution of a Y Dwarf, The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2023). DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ace32c
Offered by
Universe Today
Quotation:
JWST by accident discovers 21 brown dwarfs (2023, September 12)
retrieved 12 September 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-09-jwst-accidentally-brown-dwarfs.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




