A crew of worldwide scientists led by researchers at Newcastle College, have used the James Webb House Telescope (JWST) to disclose a hidden veil of dust in a galaxy 70 million gentle years away.
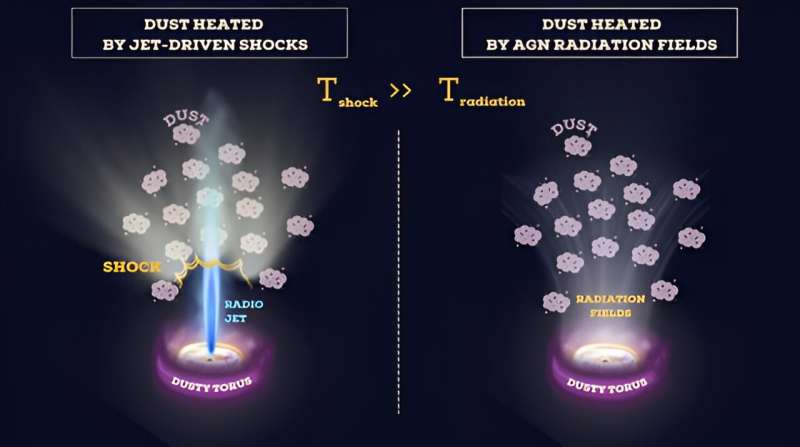
This analysis has proven that, unexpectedly, the vitality that heats the dust comes from collisions of gasoline flowing near the pace of sunshine (shocks), quite than by radiation from the supermassive black hole within the galaxy.
The analysis, led by Houda Haidar, a Ph.D. scholar within the College of Arithmetic, Statistics and Physics, has been published within the Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Houda and her crew are members of the Galactic Exercise, Torus, and Outflow Survey (GATOS), an international collaboration finding out the facilities of close by galaxies utilizing JWST. The crew at Newcastle College has been working with a number of the first devoted JWST observations ever taken.
“Having the chance to work with unique JWST information and entry these beautiful photographs earlier than anybody else is past thrilling,” mentioned Houda. “I really feel extremely fortunate to be a part of the GATOS crew. Working intently with main consultants within the subject is really a privilege.”‘
Mud close to supermassive black holes
Astronomers outline an active galactic nucleus (AGN) as a supermassive black hole, tens of millions to billions the mass of the sun, that grows by feeding on gasoline. In lots of AGN, the thick clouds of dust and gasoline that feed the nucleus additionally block its view from observers on Earth.
JWST’s infrared imaginative and prescient appears via this dust to disclose the hidden core. On the similar time, the telescope’s sharp eye permits us for the primary time to resolve the detailed construction of this dust throughout a whole lot of sunshine years.
The brand new JWST photographs of ESO 428-G14 reveal that a lot of the dust close to the supermassive black hole is unfold out alongside the radio jet. Unexpectedly, the analysis discovered an in depth relationship between the dust and the radio jet, suggesting that the jet itself could also be liable for heating and shaping the noticed dust.
Dr. David Rosario, senior lecturer at Newcastle College, and co-author of the examine, mentioned, “There may be quite a lot of debate as to how AGN switch vitality into their environment. We didn’t anticipate to see radio jets do that kind of injury. And but right here it’s.”‘
By finding out dust near supermassive black holes, we’re studying how galaxies recycle their materials, which finally helps us perceive the processes by which supermassive black holes affect galaxies, together with our personal.
Extra data:
Houda Haidar et al, Mud past the torus: revealing the mid-infrared coronary heart of native Seyfert ESO 428-G14 with JWST/MIRI, Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2024). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stae1596
Supplied by
Newcastle University
Quotation:
JWST unveils the construction of dust close to a supermassive black hole (2024, August 6)
retrieved 6 August 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-08-jwst-unveils-supermassive-black-hole.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




