Steady analysis is being performed globally on utilizing the moon as a sophisticated base for deep space exploration, and Korea is not any exception in these efforts. The Korea Institute of Civil Engineering and Constructing Expertise (KICT) efficiently applied an electrostatic surroundings that simulates the moon’s floor situations, not in space however on Earth. The researchers additionally assessed its efficiency and effectiveness.
Among the many most critical threats in executing lunar missions is the moon‘s floor surroundings, which is electrostatically charged. On account of its extraordinarily skinny environment, the moon is instantly uncovered to solar ultraviolet rays, X-rays, solar wind, Earth plasma, and so forth. Thus, clouds of dust on the moon exhibit robust static electrical energy. The moon’s electrostatic surroundings is positively charged throughout the day and negatively charged throughout the night time.
On condition that the moon has almost no environment, dust may be simply blown away even by small impacts because of the minimal air resistance. Electrostatically charged regolith particles might trigger extreme injury to space exploration gadgets once they turn out to be caught on them.
For instance, when caught on PV cells, these particles degrade electrical energy technology effectivity. In manned missions, they will injury space suits that defend astronauts or penetrate the respiratory system, leading to life-threatening penalties.
KICT’s analysis group, led by Dr. Shin Hyusoung (together with senior researcher Chung Taeil and Dr. Park Seungsoo), developed a chamber designed to simulate electrically charged situations. The purpose is to implement an electrostatic surroundings that resembles the moon’s floor.
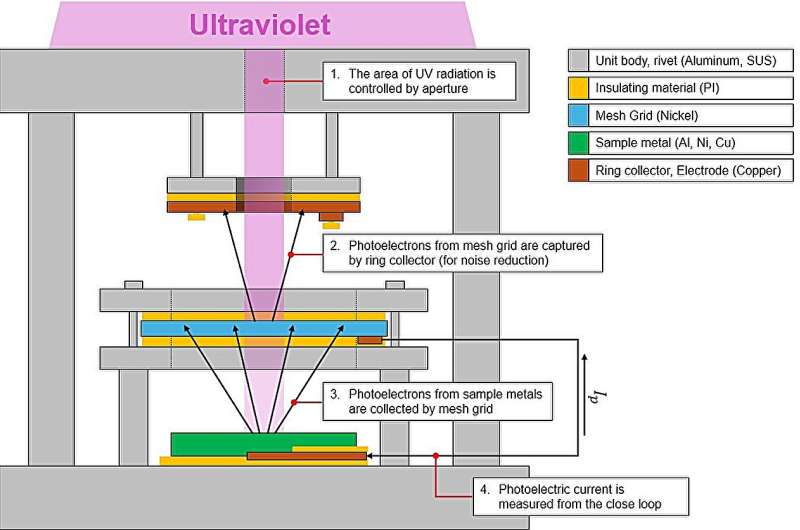
The chamber developed by KICT incorporates ultraviolet lamps, digital beams, and plasma turbines to positively or negatively cost the surfaces of check objects. Going ahead, this tools can be utilized to electrostatically cost a reproduction of lunar soil utilizing ultraviolet radiation and electron beams. It’ll assist to find out how a lot materials adheres to rovers and to anticipate potential issues.
This know-how goes past merely conducting electrostatic charging to simulate the moon’s electrically charged surroundings below numerous situations, comparable to day or night time environments whereas being influenced by Earth plasma.
The best achievement of this analysis work lies within the developed tools’s means to measure, in a quantitative and unbiased method, the quantity of photoelectric present generated, which has essentially the most vital impact on the charging of lunar dust throughout the day of the moon. The error between the experimental measurement obtained on this analysis and the corresponding theoretical worth was inside roughly 5%, demonstrating the reliability of the developed know-how.
As such, KICT’s makes an attempt have been profitable not solely in reproducing a moon-like surroundings the place soil dust stays electrostatically charged but in addition in creating evaluation know-how for it. This analysis work has laid the groundwork for equipping a large-scale soiled thermal vacuum chamber (DTVC) with the developed tools to implement an electrostatically charged surroundings and additional assess its efficiency.
Dr. Shin, Hyusoung, who led this undertaking, mentioned, “Our analysis presents the potential for successfully integrating the full-size DTVC, developed by Korea for the primary time on this planet, with lunar dust charging technology. This resolution will function a check mattress for a sequence of applied sciences to implement in-situ useful resource utilization (ISRU) on the moon sooner or later, addressing and responding to a variety of potential technological challenges posed by electrically charged lunar dust.”
The work is published within the journal Aerospace.
Extra data:
Seungsoo Park et al, Design and Validation of a Photoelectric Present Measuring Unit for Lunar Daytime Simulation Chamber, Aerospace (2024). DOI: 10.3390/aerospace11010069
Quotation:
Korean researchers create an electrostatic surroundings that simulates the moon’s floor (2024, February 27)
retrieved 27 February 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-02-korean-electrostatic-environment-simulates-moon.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




