Carbon = life’s constructing blocks
NASA said on June 26, 2023, that scientists have used the Webb space telescope to detect a brand new carbon compound in space, for the primary time. They discovered it in a younger star system, known as d203-506. It’s situated some 1,350 light-years away within the well-known Orion Nebula, one of many best to identify star-forming areas within the night time sky. What’s so nice about carbon? Solely that, with out it, life as we all know it couldn’t exist. So carbon compounds in space are key to the seek for life elsewhere.
The system d203-506 comprises a red dwarf star, a typical form of star, plus one among many planet-forming disks – aka protoplanetary disks – now recognized to exist in our dwelling galaxy, the Milky Way. At one time, our sun had a disk of gasoline and dust round it, much like what we discover on this system. And it was from that sun-centered disk that the planets, together with Earth with its wondrous assemblage of life, arose four-and-a-half billion years in the past.
The carbon compound is called methyl cation (pronounced cat-eye-on) or, to scientists, CH3+. And it’s necessary, as a result of it aids the formation of extra advanced carbon-based molecules, reminiscent of people who make up our human our bodies and the our bodies of different dwelling issues.
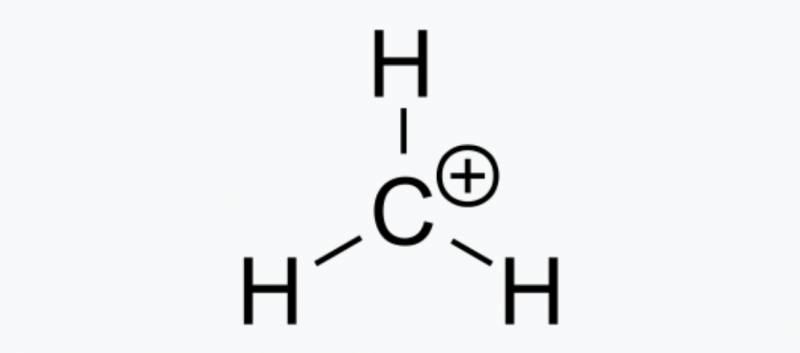
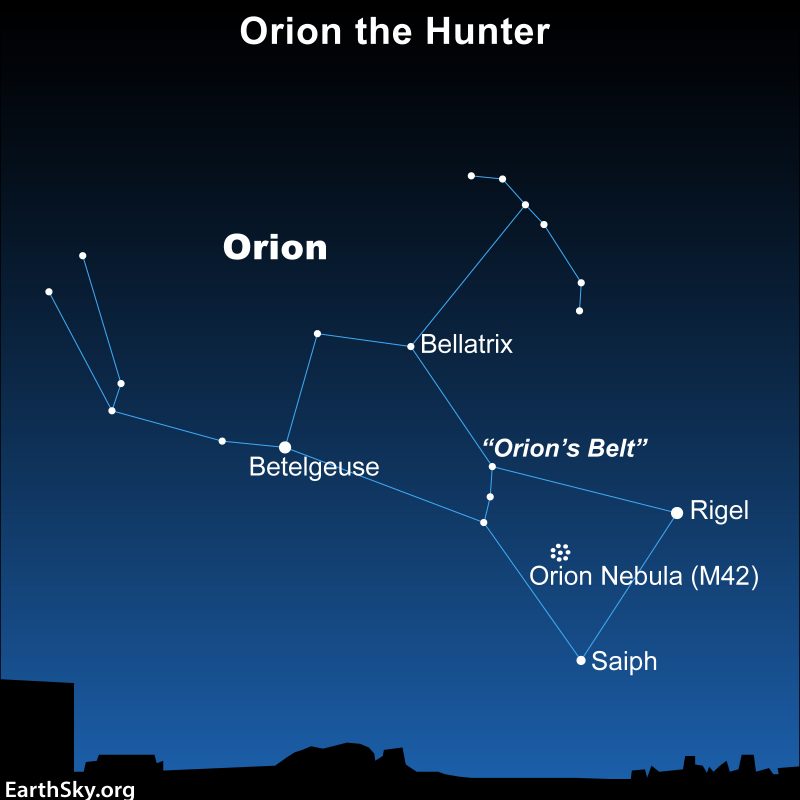
They discovered the carbon in a younger star system
The Orion Nebula has lengthy been referred to as a stellar nursery. It’s a spot the place new stars are forming. And it’s no shock that trendy astronomical devices are starting to seek out planet-forming disks round a few of these stars. Probing extra deeply, astronomers have now discovered carbon compounds in one among these disks.
The astronomers’ June 26 statement stated they’re:
… working to know each how life developed on Earth, and the way it may doubtlessly develop elsewhere in our universe. The research of interstellar natural (carbon-containing) chemistry, which Webb is opening in new methods, is an space of eager fascination to many astronomers.
The distinctive capabilities of Webb made it a super observatory to seek for this significant molecule. Webb’s beautiful spatial and spectral decision [Ed note: its ability to see clearly], in addition to its sensitivity, all contributed to the group’s success.
Particularly, Webb’s detection of a collection of key emission lines from CH3+ cemented the invention.
A member of the science group, Marie-Aline Martin-Drumel of the College of Paris-Saclay in France, commented:
This detection not solely validates the unbelievable sensitivity of Webb but in addition confirms the postulated central significance of CH3+ in interstellar chemistry.
UV bombardment
It’s price noting that the star within the d203-506 system and its planet-forming disk are being bombarded by sturdy ultraviolet (UV) gentle from close by scorching, younger, huge stars.
Scientists imagine that almost all planet-forming disks undergo a interval of such intense UV radiation, as a result of stars are likely to type in teams that always embody huge, UV-producing stars.
Usually, NASA said, UV radiation is anticipated to destroy advanced natural molecules, during which case the invention of CH3+ may appear to be a shock.
However, on this case, the group predicts that UV radiation may present the required supply of power for CH3+ to type within the first place.
As soon as shaped, it then promotes extra chemical reactions to construct extra advanced carbon molecules.
The scientists’ statement additionally famous that the molecules astronomers see in d203-506 are fairly totally different from these they’ve seen earlier than in planet-forming disk. Particularly, they couldn’t detect any indicators of water. Olivier Berné of the French Nationwide Centre for Scientific Analysis in Toulouse, lead creator of the research, defined:
This clearly exhibits that ultraviolet radiation can fully change the chemistry of a protoplanetary disk. It’d truly play a important position within the early chemical phases of the origins of life.
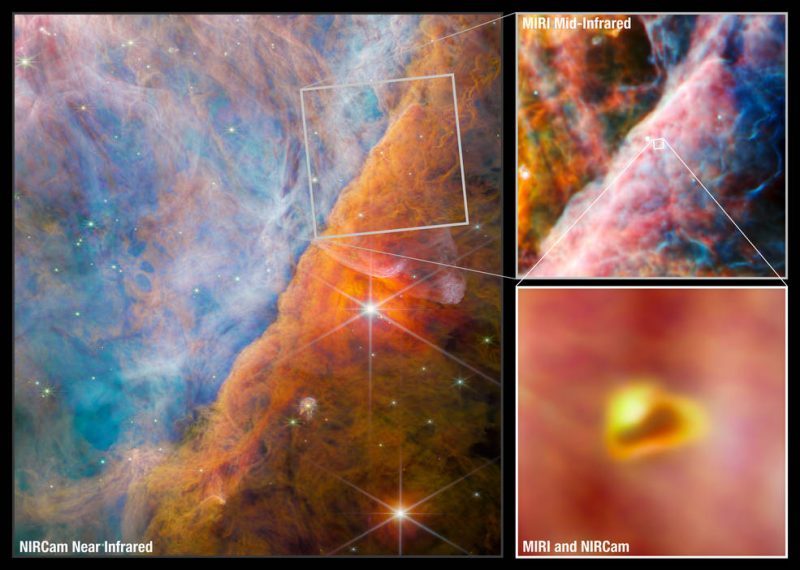

Backside line: Scientists have discovered carbon compounds – life’s constructing blocks – in a planet-forming disk, encircling a star within the well-known Orion Nebula.
Source: Formation of the Methyl Cation by Photochemistry in a Protoplanetary Disk




