When did people first arrive in East Asia?
A brand new examine has make clear the date of the traditional Liujiang skeleton – a major human fossil discover in a collapse China – altering our understanding of the migration of early trendy people (Homo sapiens) to East Asia. The brand new examine has positioned the skeleton’s age at 33,000 to 23,000 years outdated.
Beforehand, the age of this skeleton was a matter of debate. Some research had prompt it was as outdated as 227,000 years, however that age was debated. The brand new outcomes, published within the peer-reviewed journal Nature Communications on April 29, 2024, put the skeleton’s age in the identical vary as different historical trendy human stays in China. The authors wrote:
Populations of H. sapiens have been clearly current from north to south China throughout this era, ranging throughout latitudes extending from ~40 to 24 degrees north, and in several ecosystems ranging over a distance of ~1,800 km [1,100 miles]. The brand new relationship info signifies that the Liujiang stays are from a serious dispersal occasion of recent people in Eurasia round 40,000 to 30,000 years in the past.
Junyi Ge of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences is lead writer of the examine. He stated in a statement from Griffith College in Queensland, Australia:
This discovering holds vital implications for understanding human dispersals and variations within the area. It challenges earlier interpretations and offers insights into the occupation historical past of China.
Who was the Liujiang skeleton?
Scientists suppose, based mostly on skeletal options, that the Liujiang fossils belonged to an grownup male. He was about 40 years outdated on the time of loss of life. Employees digging for phosphorus fertilizer in Tongtianyan Collapse 1958 found his stays. That’s within the Liujiang District of Liuzhou Metropolis in southern China.
Little is thought in regards to the lifetime of this early trendy human, since no artifacts resembling instruments have been discovered with him. However in loss of life, he has change into probably the most necessary human fossils within the examine of early trendy human migration. That’s as a result of a good portion of his skeleton was preserved: many of the cranium, sections of spine, just a few ribs, a hip bone, sacrum, and higher leg bones.
The bones present priceless info on early trendy people’ options.
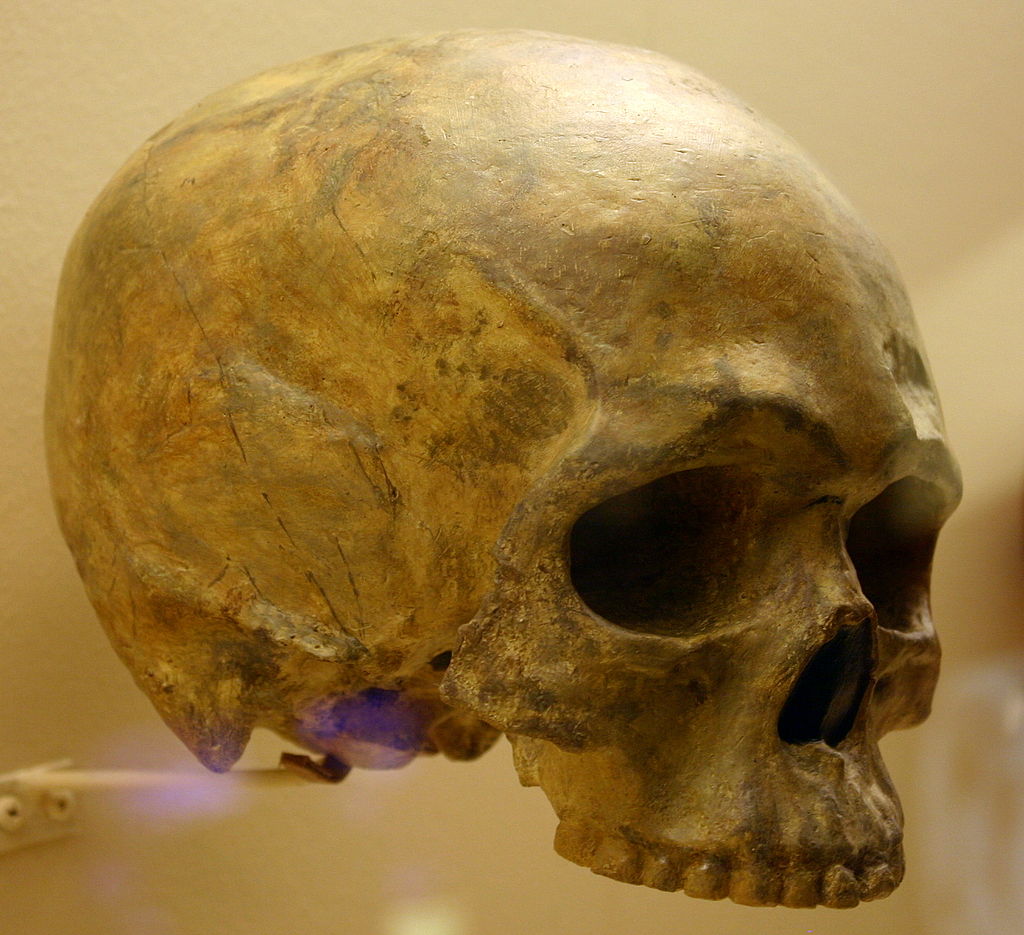
Getting a extra correct age on the Liujiang skeleton
Measurements, pictures, and sediment samples from a fossil’s location are helpful in serving to to find out a fossil’s age. However when these bones got here to gentle in 1958, scientists who visited the cave to examine the Liujiang skeleton discovered that the positioning had been fairly disturbed and priceless knowledge misplaced.
For the current examine, scientists used the newest obtainable relationship methods to reevaluate its age. They’d two objectives:
- First, they needed to seek out and decide the age of the possible cave sediment layer that after held the skeleton.
- Second, they needed thus far the skeleton immediately.
To help of their first aim, researchers recovered bits of yellowish-brown clay caught to the fossils. They evaluated the traits of this clay and have been capable of finding a probable match in one of many cave’s sediment layers. Within the lab, they then dated that layer, utilizing three completely different relationship methods, to between 32,500 to 22,600 years outdated.
Subsequent, they subjected samples of bone and enamel on to one more relationship approach. These outcomes yielded an approximate burial age of 23,900 years. Mixed with the outcomes from sediment evaluation, scientists have been in a position to age the Liujiang skeleton at 33,000 and 23,000 years outdated.
The puzzle of historical human migration
The Liujian skeleton is a crucial a part of understanding the bigger story of early modern human migration. Trendy people, in response to many researchers, possible first emerged in Africa about 300,000 years in the past. They subsequently migrated out of Africa to occupy different components of the world.
And that’s the place the story will get much more advanced.
That’s, as a result of historical human stays are scarce, it’s laborious for scientists to establish when people arrived at completely different geographical areas, utilizing fossil proof alone. No matter historical human stays have been discovered are sometimes not properly preserved.
So, these scientists say, understanding the actions of historical peoples requires a multi-disciplinary approach. That features learning the consequences of local weather and surroundings. The event of cultures, know-how, and language are additionally priceless clues.
Relationship migration with DNA
Scientists additionally use genetic studies in learning human migration. One discipline of DNA analysis, often called genetic anthropology, research genetic markers in hundreds of present-day individuals to look into historical migration patterns of their ancestors.
It’s additionally doable, in well-preserved fossils, to immediately extract DNA samples. That’s how we all know that historical trendy people interbred with now-extinct Neanderthals and Denisovans. Many people right now proceed to hold the DNA of those long-gone human species.
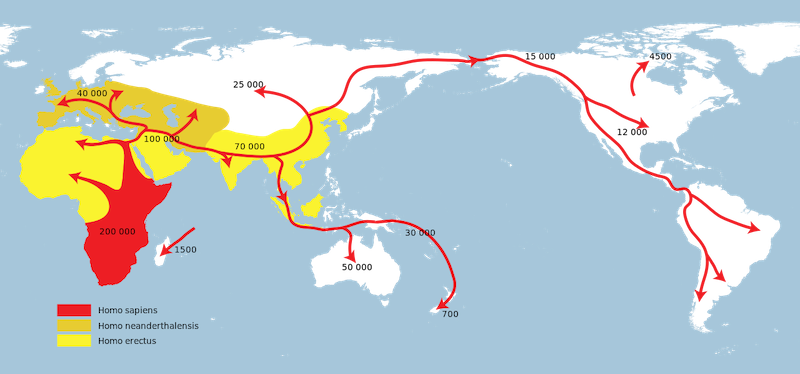
Backside line: A brand new examine dates the Liujiang skeleton, a fossil crucial to understanding early trendy human migration in Jap Asia, to between 33,000 and 23,000 years outdated.
Source: New Late Pleistocene age for the Homo sapiens skeleton from Liujiang southern China




