Windswept piles of dust, or layers of ice? ESA’s Mars Categorical has revisited one in every of Mars’s most mysterious options to make clear its composition. Its findings recommend layers of water ice stretching a number of kilometers under floor—essentially the most water ever discovered on this a part of the planet.
Over 15 years in the past, Mars Categorical studied the Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF), revealing large deposits as much as 2.5 km deep. From these early observations, it was unclear what the deposits had been product of—however new analysis now has a solution.
“We have explored the MFF once more utilizing newer knowledge from Mars Categorical’s MARSIS radar, and located the deposits to be even thicker than we thought: as much as 3.7 km thick,” says Thomas Watters of the Smithsonian Establishment, U.S., lead writer of each the brand new analysis, revealed in Geophysical Analysis Letters, and the preliminary 2007 examine. “Excitingly, the radar alerts match what we might anticipate to see from layered ice, and are just like the alerts we see from Mars’s polar caps, which we all know to be very ice wealthy.”
If melted, the ice locked up within the MFF would cowl the complete planet in a layer of water 1.5 to 2.7 m deep: Probably the most water ever discovered on this a part of Mars, and sufficient to fill Earth’s Purple Sea.
Alternating layers of ice
The MFF consists of a number of wind-sculpted options measuring tons of of kilometers throughout and a number of other kilometers excessive. Discovered on the boundary between Mars’s highlands and lowlands, the options are presumably the most important single supply of dust on Mars, and one of the crucial in depth deposits on the planet.
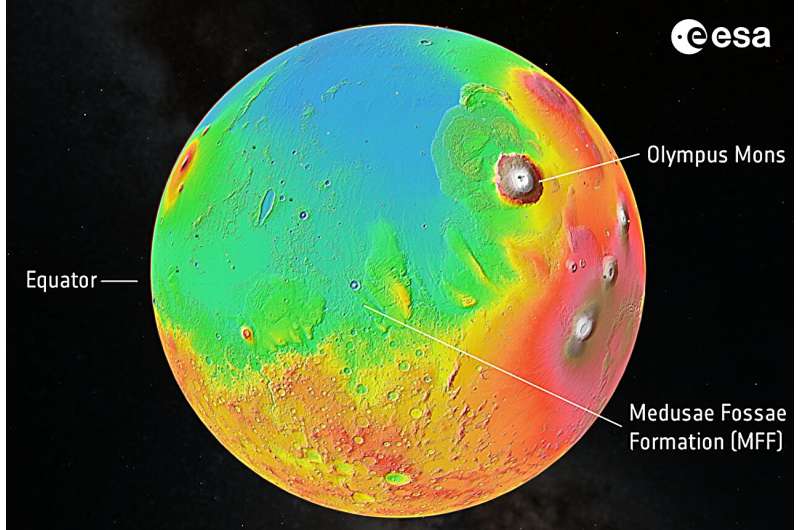
Preliminary observations from Mars Categorical confirmed the MFF to be comparatively clear to radar and low in density, each traits we might see from icy deposits. Nonetheless, scientists could not rule out a drier risk: that the options are literally big accumulations of windblown dust, volcanic ash or sediment.
“This is the place the brand new radar knowledge is available in. Given how deep it’s, if the MFF was merely an enormous pile of dust, we might anticipate it to change into compacted below its personal weight,” says co-author Andrea Cicchetti of the Nationwide Institute for Astrophysics, Italy. “This is able to create one thing far denser than what we really see with MARSIS. And after we modeled how completely different ice-free supplies would behave, nothing reproduced the properties of the MFF—we’d like ice.”
The brand new outcomes as a substitute recommend layers of dust and ice, all topped by a protecting layer of dry dust or ash a number of hundred meters thick.
Future exploration and collaboration
Though Mars now seems to be an arid world, the planet’s floor is filled with indicators that water was as soon as considerable, together with dried-up river channels, historical ocean and lake beds, and water-carved valleys. We have additionally discovered vital shops of water ice on Mars, reminiscent of the large polar caps, buried glaciers nearer the equator, and near-surface ice laced via Martian soil.
Large shops of ice close to the equator—reminiscent of these suspected to lurk under the dry floor of the MFF—could not have fashioned within the planet’s current local weather. They will need to have fashioned in a earlier local weather epoch.
“This newest evaluation challenges our understanding of the Medusae Fossae Formation, and raises as many questions as solutions,” says Colin Wilson, ESA challenge scientist for Mars Categorical and the ESA ExoMars Hint Gasoline Orbiter (TGO). “How way back did these ice deposits type, and what was Mars like at the moment? If confirmed to be water ice, these large deposits would change our understanding of Mars local weather historical past. Any reservoir of historical water can be an enchanting goal for human or robotic exploration.”
The extent and placement of those icy MFF deposits would additionally make them probably very helpful for our future exploration of Mars. Missions to Mars might want to land close to the planet’s equator, removed from the ice-rich polar caps or high-latitude glaciers. They usually’ll want water as a useful resource—so discovering ice on this area is sort of a necessity for human missions to the planet.
-
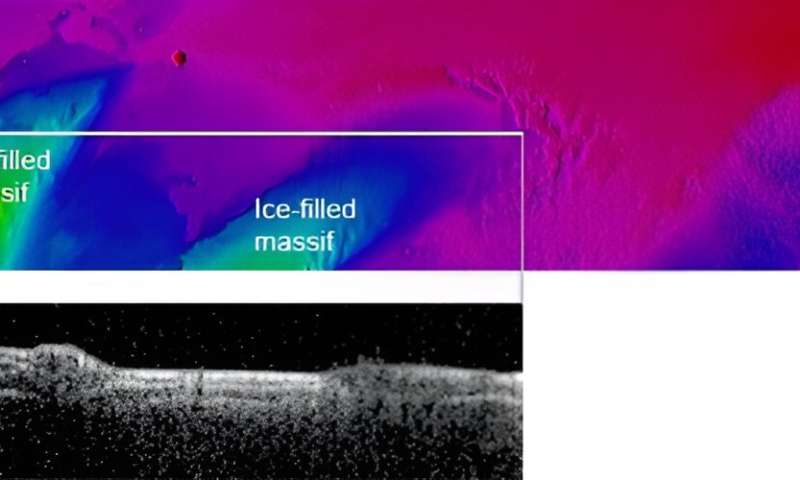
Near Mars’s equator lies the Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF), an enchanting wind-sculpted area which may be the most important single supply of dust on Mars. When Mars Categorical turned its MARSIS radar sounder instrument in direction of the MFF, it revealed a shock. The radar alerts that echoed again match what we’d anticipate to see from layered deposits wealthy in water ice. On this picture, the white horizontal line on the colored peak map of Mars’s floor (prime) exhibits a slim stretch of land that was scanned by MARSIS. The come out under exhibits the radar knowledge collected by the instrument that reveals the subsurface; the brighter the world, the stronger the radar echo obtained from that space. The white line covers two mounds separated by a valley. These mounds are clearly seen within the radar knowledge under. Evaluation of the radar knowledge means that beneath a thick layer of dry materials (possible dust or volcanic ash), the mounds are full of water ice. Credit score: CReSIS/KU/Smithsonian Establishment
-
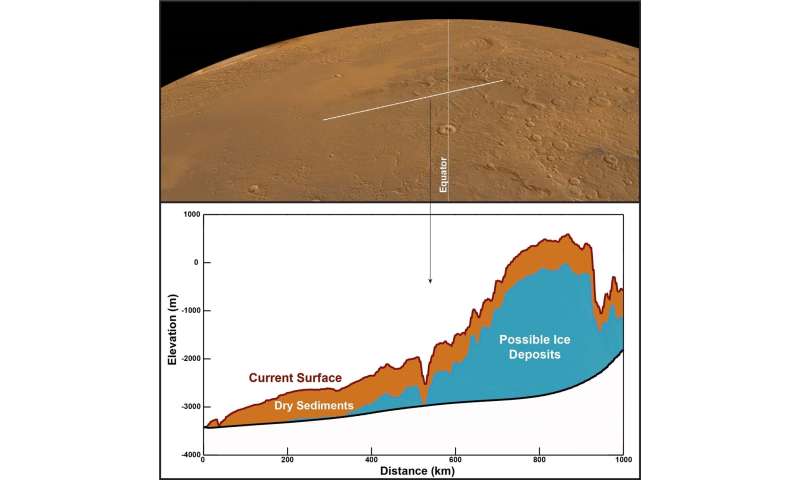
Near Mars’s equator lies the Medusae Fossae Formation (MFF), an enchanting collection of wind-sculpted deposits which may be the most important single supply of dust on Mars. When Mars Categorical turned its MARSIS radar sounder instrument in direction of the MFF, it revealed a shock. The radar alerts that echoed again from under the floor match what we’d anticipate to see from layered deposits wealthy in water ice. On this picture, the white line on Mars’s floor (prime) exhibits a stretch of land that was scanned by MARSIS. The graph under exhibits the form of the land and the construction of the subsurface, with the layer of dry sediments (possible dust or volcanic ash) in brown and the layer of suspected ice-rich deposits in blue. The graph exhibits that the ice deposit is 1000’s of metres excessive and tons of of kilometres large. If all of the suspected water ice within the MFF melted, it could cowl Mars in an ocean of water as much as 2.7 m deep. Credit score: CReSIS/KU/Smithsonian Establishment
“Sadly, these MFF deposits are lined by tons of of meters of dust, making them inaccessible for at the least the subsequent few many years. Nonetheless, each little bit of ice we discover helps us construct a greater image of the place Mars’s water has flowed earlier than, and the place it may be discovered at this time.”
Whereas Mars Categorical maps water ice to a depth of some kilometers, a view of near-surface water is offered by Mars orbiter TGO. This orbiter is carrying the FREND instrument, which is mapping hydrogen—an indicator of water ice—within the topmost meter of Martian soil. FREND noticed a hydrogen-rich space the dimensions of the Netherlands inside Mars’s Valles Marineris in 2021, and is at the moment mapping how shallow water deposits are distributed throughout the Purple Planet.
“Collectively, our Mars explorers are revealing increasingly more about our planetary neighbor,” provides Colin.
Extra info:
Thomas Watters et al, Proof of Ice-Wealthy Layered Deposits within the Medusae Fossae Formation of Mars, Geophysical Analysis Letters (2024).
Offered by
European Space Agency
Quotation:
Mars Categorical finds proof of enormous water deposit on the Medusae Fossae Formation (2024, January 19)
retrieved 19 January 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-01-mars-evidence-large-deposit-medusae.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




