Planetary scientists have lengthy recognized that Mercury has been shrinking for billions of years. Regardless of being the closest planet to the sun, its inside has been cooling down as inside warmth leaks away. Which means the rock (and, inside that, the steel) of which it’s composed will need to have contracted barely in quantity.
It’s unknown, nevertheless, to what extent the planet continues to be shrinking at present—and, in that case, for the way lengthy that’s prone to proceed. Now our new paper, printed in Nature Geoscience, affords recent perception.
As a result of Mercury’s inside is shrinking, its surface (crust) has progressively much less space to cowl. It responds to this by creating “thrust faults”—the place one tract of terrain will get pushed over the adjoining terrain (see picture under). That is just like the wrinkles that type on an apple because it ages, besides that an apple shrinks as a result of it’s drying out whereas Mercury shrinks due to thermal contraction of its inside.
The primary proof of Mercury’s shrinkage got here in 1974 when the Mariner 10 mission transmitted photos of kilometers-high scarps (ramp-like slopes) snaking their manner for a whole lot of kilometers throughout the terrain. Messenger, which orbited Mercury from 2011 to 2015, confirmed many extra “lobate scarps” (as they’d change into recognized) in all components of the globe.
From such observations, it was doable to infer that lightly dipping geological faults, referred to as thrusts, method the floor under every scarp and are a response to Mercury having shrunk in radius by a total of about 7km.
However when did this occur? The accepted approach to work out the age of Mercury’s floor is to rely the density of influence craters. The older the floor, the extra craters. However this technique is difficult, as a result of the speed of impacts that produce craters was a lot higher within the deep previous.
Nonetheless, it was at all times clear that Mercury’s scarps have to be pretty historical, as a result of though they reduce via some older craters, fairly a couple of youthful craters are superimposed upon the scarps and so the scarps have to be older than these.
When did that scarp final transfer?
The consensus view is that Mercury’s scarps are largely about 3 billion years outdated. However are all of them that outdated? And did the older ones stop shifting way back or are they nonetheless energetic at present?
We must always not count on that the thrust fault under every scarp has moved solely as soon as. The largest earthquake on Earth in recent times, the magnitude 9 Tohoku earthquake offshore of Japan in 2011 which prompted the Fukushima catastrophe, was the results of a sudden bounce by 20 meters alongside a 100km size of the accountable thrust fault.
Mercury’s greatest “earthquakes” are most likely smaller. To build up the two–3km of total shortening that may be measured throughout a typical scarp on Mercury would take a whole lot of magnitude 9 “earthquakes,” or extra seemingly hundreds of thousands of smaller occasions, which may have been unfold out over billions of years.
Getting a deal with on the size and period of fault actions on Mercury is necessary, as a result of we’d not count on Mercury’s thermal contraction to have solely completed, though this ought to be slowing down.
Cracking up
Till now, proof has been sparse. However our staff discovered unambiguous indicators that many scarps have continued to maneuver in geologically latest instances, even when they have been initiated billions of years in the past.
This work was triggered when a Ph.D. pupil at Open College within the U.Ok., Ben Man, seen that some scarps have small fractures piggy-backing on their stretched higher surfaces. He interpreted these as “grabens,” the geological phrase to explain a strip of floor dropped down between two parallel faults.
This usually occurs when the crust is stretched. Stretching could appear shocking on Mercury, the place general the crust is being compressed, however Man realized that these grabens would happen if a thrust slice of crust has been bent as it’s pushed over the adjoining terrain. Should you attempt to bend a chunk of toast, it might crack in an analogous manner.
The grabens are lower than 1km vast and fewer than about 100 meters deep. Such comparatively small options have to be a lot youthful than the traditional construction on which they sit, in any other case they might have already been erased from view by impacts tossing materials throughout the floor in a course of aptly named “impact gardening.”
Primarily based on the speed of blurring ensuing from influence gardening, we calculated that almost all of grabens are lower than about 300 million years outdated. This means that the newest motion will need to have occurred equally “lately.”
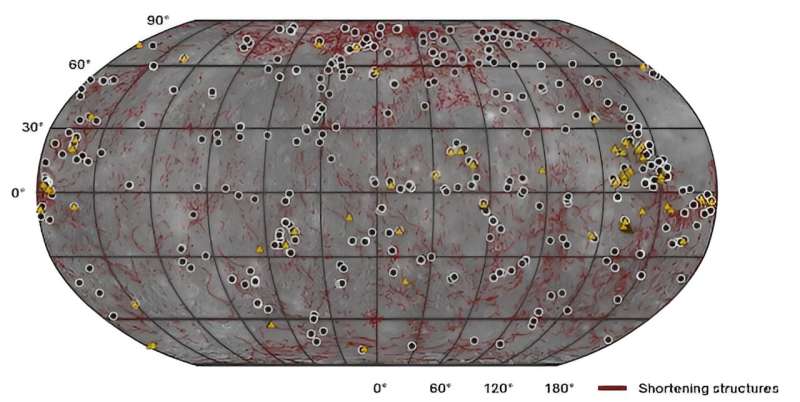
Working with essentially the most detailed pictures supplied by MESSENGER, Man discovered 48 massive lobate scarps that undoubtedly have small grabens. An extra 244 have been topped by “possible” grabens—which are not seen fairly clearly sufficient on one of the best MESSENGER pictures.
These at the moment are prime targets for affirmation by the imaging system of the joint European/Japanese BepiColombo mission, which ought to begin working in orbit round Mercury early in 2026.
Classes from the moon
The moon has additionally cooled and contracted. Its lobate scarps are significantly smaller and fewer spectacular than these on Mercury, however on the moon we all know for certain that in addition to being geologically latest, some are energetic at present.
It is because latest reanalysis of the places of moonquakes recorded by seismometers (vibration detectors) left on the moon’s floor by a number of Apollo missions exhibits that moonquakes are clustered near lobate scarps.
Additionally, essentially the most detailed pictures of the moon’s floor from orbit reveal the tracks made by boulders bouncing down scarp faces, presumably after being dislodged by moonquakes. A lot smaller in scale than Mercury’s grabens, comparable logic applies to those boulder tracks: they might change into erased from visibility after just a few million years, so that they have to be younger.
BepiColombo will not be touchdown and so we have now no prospect of gathering any seismic knowledge on Mercury. Nonetheless, in addition to exhibiting small grabens extra clearly, its most detailed pictures would possibly reveal boulder tracks that could possibly be further proof of latest quakes. I’m wanting ahead to discovering out.
Extra data:
Benjamin Man et al, Widespread small grabens in step with latest tectonism on Mercury, Nature Geoscience (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41561-023-01281-5
Supplied by
The Conversation
This text is republished from The Conversation underneath a Artistic Commons license. Learn the original article.![]()
Quotation:
Mercury: Shrinking planet continues to be getting smaller, in line with new analysis (2023, October 3)
retrieved 3 October 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-10-mercury-planet-smaller.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




