Numerous meteorites have struck Earth up to now and formed the historical past of our planet. It’s assumed, for instance, that meteorites introduced with them a big a part of its water. The extinction of the dinosaurs may also have been triggered by the impression of a really giant meteorite.
Meteorite craters that are nonetheless seen in the present day are uncommon as a result of most traces of the celestial our bodies have lengthy since disappeared once more. This is because of erosion and shifting processes in Earth’s crust, referred to as plate tectonics.
The “Earth Impression Database” lists simply 190 such craters worldwide. In the entire of Western Europe, solely three had been beforehand recognized: Rochechouart in Aquitaine, France, the Nördlinger Ries between the Swabian Alb and the Franconian Jura, and the Steinheim Basin close to Heidenheim in Baden-Württemberg (each in Germany). Due to tens of millions of years of abrasion, nonetheless, for laypersons the three impression craters are hardly recognizable as such.
Geologist and cosmochemist Professor Frank Brenker from Goethe College Frankfurt is satisfied the brand new meteorite crater will now lengthen the record. Whereas on vacation, the “Domaine du Météore” vineyard caught his consideration. One in every of its vineyards lies in a spherical despair about 220 meters in diameter and 30 meters deep, and the proprietors use the scientific speculation that it’s the impression crater of a meteorite—seemingly lengthy disproved—as a advertising gag for his or her wine.
Though this speculation was proposed by a number of geologists within the Nineteen Fifties, it was dismissed by acclaimed colleagues a number of years later.
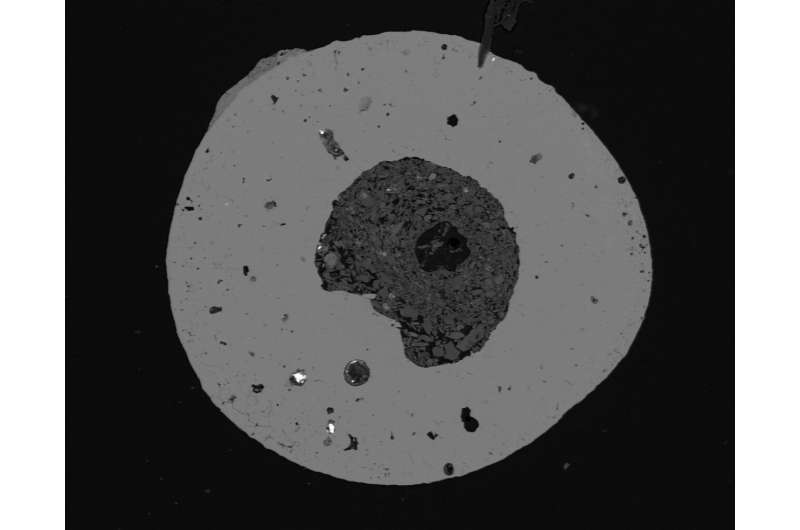
Frank Brenker explains, “Craters can kind in some ways, and meteorite craters are certainly very uncommon. Nonetheless, I discovered the assorted different interpretations of how this despair may have shaped unconvincing from a geological perspective.” That’s the reason he and his spouse collected rock samples for evaluation within the labs at Goethe College Frankfurt—and certainly discovered the primary indicators of an impression crater.
Brenker says, “The microanalysis confirmed that dark-colored layers in one of many shists, which often merely comprise a bigger share of mica, is perhaps shock veins produced by the grinding and fracturing of the rock, which in flip may have been attributable to an impression.” He additionally discovered proof of breccia, angular rock particles held collectively by a sort of “cement”, which might additionally happen throughout a meteorite impression.
The next 12 months, Brenker took his colleague Andreas Junge, Professor of Utilized Geophysics at Goethe College Frankfurt, and a bunch of scholars with him to Southern France to look at the crater intimately. They found that Earth’s magnetic area is barely weaker within the crater than within the surrounding space. That is typical for impression craters as a result of the impression shatters and even melts the rock, which might thus contribute much less to Earth’s magnetic area.
With the assistance of robust magnets connected to a plate, the researchers additionally discovered tiny iron oxide spherules of as much as one millimeter in diameter. Such spherules had already been present in different impact craters. Later laboratory evaluation confirmed that those right here additionally contained nickel-bearing iron and encased a core of minerals typical for the crater atmosphere. As well as, the researchers found quite a few shock microdiamonds produced by means of the excessive stress in the course of the meteorite’s impression.
Frank Brenker explains, “Such microspheres kind both by means of abrasion of the meteorite within the ambiance or solely upon impression, when a big a part of the iron meteorite melts after which reacts with the oxygen within the air. On impression, materials shattered on the level of impression may then even be encased. This, along with the decrease magnetic area and the opposite geological and mineralogical finds, permits us to attract hardly every other conclusion: a meteorite did certainly strike right here.”
This makes the crater very thrilling for geological laypeople too, says Brenker, as a result of “each customer can expertise right here the immense energies launched upon such an impression.”
Extra info:
LPSC Houston 2023 Summary #1910: Impact origin of the “Domaine du Meteore”-crater, France. Compelling mineralogical and geophysical evidence for an unrecognized destructive event in the heart of Europe.
Offered by
Goethe University Frankfurt am Main
Quotation:
Meteorite crater found in French vineyard (2023, February 22)
retrieved 22 February 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-02-meteorite-crater-french-winery.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




