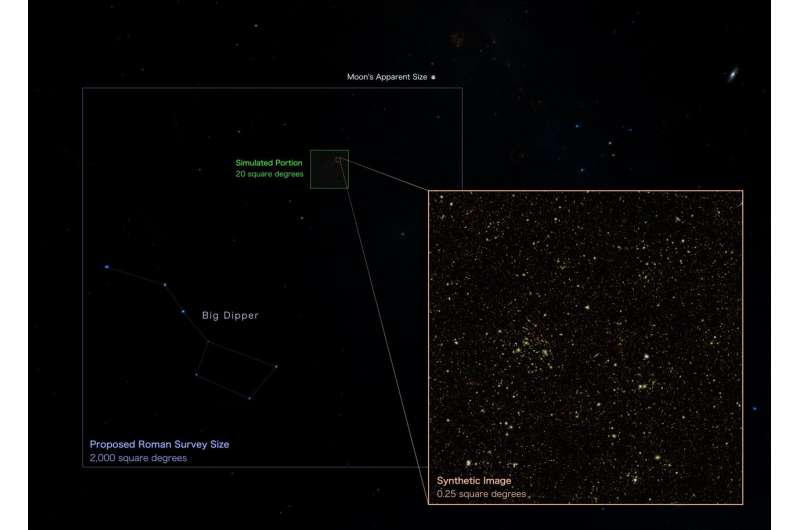
Scientists have created a gargantuan artificial survey that reveals what we are able to anticipate from the Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope’s future observations. Although it represents only a small chunk of the true future survey, this simulated model comprises a staggering variety of galaxies—33 million of them, together with 200,000 foreground stars in our house galaxy.
The simulation will assist scientists plan the very best observing methods, take a look at alternative ways to mine the mission’s huge portions of knowledge, and discover what we are able to study from tandem observations with different telescopes.
“The amount of knowledge Roman will return is unprecedented for a space telescope,” mentioned Michael Troxel, an assistant professor of physics at Duke College in Durham, North Carolina. “Our simulation is a testing floor we are able to use to ensure we’ll get probably the most out of the mission’s observations.”
The workforce drew information from a mock universe initially developed to help science planning with the Vera C. Rubin Observatory, which is situated in Chile and set to start full operations in 2024. As a result of the Roman and Rubin simulations use the identical supply, astronomers can examine them and see what they will anticipate to study from pairing the telescopes’ observations as soon as they’re each actively scanning the universe.
A paper describing the outcomes, led by Troxel, has been accepted for publication in The Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society.
Cosmic building
Roman’s Excessive Latitude Large Space Survey will encompass each imaging—the main target of the brand new simulation—and spectroscopy throughout the identical monumental swath of the universe. Spectroscopy entails measuring the depth of sunshine from cosmic objects at totally different wavelengths, whereas Roman’s imaging will reveal exact positions and shapes of lots of of hundreds of thousands of faint galaxies that will likely be used to map dark matter. Though this mysterious substance is invisible, astronomers can infer its presence by observing its results on common matter.
Something with mass warps the material of space-time. The larger the mass, the higher the warp. This creates an impact known as gravitational lensing, which occurs when gentle from a distant supply turns into distorted because it travels previous intervening objects. When these lensing objects are huge galaxies or galaxy clusters, background sources will be smeared or seem as a number of photographs.
Much less huge objects can create extra delicate results known as weak lensing. Roman will likely be delicate sufficient to make use of weak lensing to see how clumps of dark matter warp the looks of distant galaxies. By observing these lensing results, scientists will be capable to fill in additional of the gaps in our understanding of dark matter.
“Theories of cosmic construction formation make predictions for the way the seed fluctuations within the early universe develop into the distribution of matter that may be seen via gravitational lensing,” mentioned Chris Hirata, a physics professor at Ohio State College in Columbus, and a co-author of the paper.
“However the predictions are statistical in nature, so we take a look at them by observing huge areas of the cosmos. Roman, with its huge area of view, will likely be optimized to effectively survey the sky, complementing observatories such because the James Webb House Telescope which can be designed for deeper investigation of particular person objects.”
Floor and space
The artificial Roman survey covers 20 sq. levels of the sky, which is roughly equal to 95 full moons. The precise survey will likely be 100 instances bigger, unveiling greater than a billion galaxies. Rubin will scan a fair higher space—18,000 sq. levels, almost half of all the sky—however with decrease decision because it must peer via Earth’s turbulent ambiance.
Pairing the Roman and Rubin simulations gives the primary alternative for scientists to attempt to detect the identical objects in each units of photographs. That is vital as a result of ground-based observations aren’t all the time sharp sufficient to tell apart a number of, shut sources as separate objects. Generally they blur collectively, which impacts weak lensing measurements. Now, scientists can decide the difficulties and advantages of “deblending” such objects in Rubin photographs by evaluating them with Roman ones.
With Roman’s colossal cosmic view, astronomers will be capable to accomplish excess of the survey’s major targets, that are to review the construction and evolution of the universe, map dark matter, and discern between the main theories that try to clarify why the enlargement of the universe is dashing up. Scientists can comb via the brand new simulated Roman information to get a style of the bonus science that may come from seeing a lot of the universe in such beautiful element.
“With Roman’s gigantic area of view, we anticipate many various scientific alternatives, however we may also need to study to anticipate the sudden,” mentioned Julie McEnery, the senior venture scientist for the Roman mission at NASA’s Goddard House Flight Heart in Greenbelt, Maryland. “The mission will assist reply vital questions in cosmology whereas probably revealing model new mysteries for us to resolve.”
Extra info:
Michael Troxel et al, A Joint Roman House Telescope and Rubin Observatory Artificial Large-Subject Imaging Survey, The Month-to-month Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society (2023). DOI: 10.1093/mnras/stad664. On arXiv:
doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2209.06829
Offered by
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Quotation:
Thousands and thousands of galaxies emerge in new simulated photographs from NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman House Telescope (2023, March 8)
retrieved 8 March 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-03-millions-galaxies-emerge-simulated-images.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




