The close by radio galaxy M87, situated 55 million light-years from the Earth and harboring a black hole 6.5 billion occasions extra huge than the sun, displays an oscillating jet that swings up and down with an amplitude of about 10 levels, confirming the black hole’s spin.
The examine, which was headed by Chinese language researcher Dr. Cui Yuzhu and revealed in Nature on Sept. 27, was carried out by a global staff utilizing a world community of radio telescopes.
By means of intensive evaluation of telescope information from 2000–2022, the analysis staff revealed a recurring 11-year cycle within the precessional movement of the jet base, as predicted by Einstein’s Common Idea of Relativity. The examine hyperlinks the dynamics of the jet with the central supermassive black hole, providing proof that M87’s black hole spins.
Supermassive black holes on the middle of energetic galaxies—essentially the most disruptive celestial objects in our universe—can accrete super quantities of fabric as a result of extraordinary gravitational drive and energy of plasma outflows, generally known as jets, that method the velocity of sunshine and prolong hundreds of light-years away.
The vitality switch mechanism amongst supermassive black holes and their accretion disks and relativistic jets has puzzled physicists and astronomers for over a century.
A prevailing concept means that vitality may be extracted from a spinning black hole, permitting some materials surrounding the supermassive black hole to be ejected with nice vitality. Nonetheless, the spin of supermassive black holes, an important issue on this course of and essentially the most basic parameter aside from black hole mass, had not been immediately noticed.
On this examine, the analysis staff targeted on M87, the place the primary observational astrophysical jet was noticed in 1918. Due to its proximity, the jet formation areas near the black hole may be resolved intimately with Very Lengthy Baseline Interferometry (VLBI), as represented by current black hole shadow imaging with the Occasion Horizon Telescope (EHT). By analyzing VLBI information from M87 obtained over the past 23 years, the staff detected the periodic precessional jet at its base, providing perception into the standing of the central black hole.
On the coronary heart of this discovery lies the important query: What drive within the universe can alter the path of such a robust jet? The reply might be hidden within the habits of the accretion disk, a configuration associated to the central supermassive black hole.
As infalling supplies orbit the black hole as a consequence of their angular momenta, they type a disk-like construction earlier than steadily spiraling inwards till they’re fatefully drawn into the black hole. Nonetheless, if the black hole is spinning, it exerts a major affect on surrounding spacetime, inflicting close by objects to be dragged alongside its axis of rotation, a phenomenon generally known as “frame-dragging,” which was predicted by Einstein’s basic concept of relativity.
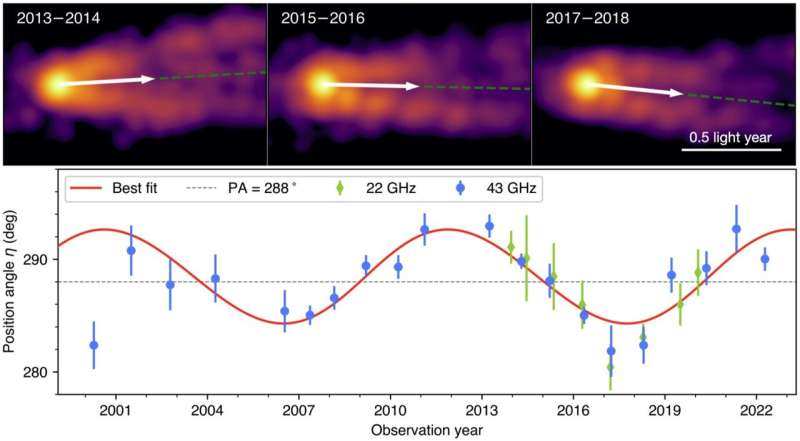
The analysis staff’s intensive evaluation signifies that the rotational axis of the accretion disk misaligns with the black hole’s spin axis, resulting in a precessional jet. Detecting this precession offers unequivocal proof that the supermassive black hole in M87 is certainly spinning, thus enhancing our understanding of the character of supermassive black holes.
“We’re thrilled by this important discovering,” mentioned Cui Yuzhu, a postdoctoral researcher at Zhejiang Lab, a analysis establishment in Hangzhou, and lead and corresponding creator of the paper. “Because the misalignment between the black hole and the disk is comparatively small and the precession interval is round 11 years, accumulating high-resolution information tracing M87’s construction over twenty years and thorough evaluation are important to acquire this achievement.”
“After the success of black hole imaging on this galaxy with the EHT, whether or not this black hole is spinning or not has been a central concern amongst scientists,” added Dr. Kazuhiro Hada from the Nationwide Astronomical Observatory of Japan. “Now anticipation has become certainty. This monster black hole is certainly spinning.”
This work made use of a total of 170 epochs of observations obtained by the East Asian VLBI Community (EAVN), the Very Lengthy Baseline Array (VLBA), the joint array of KVN and VERA (KaVA), and the East Asia to Italy Almost World (EATING) community. In total, greater than 20 telescopes throughout the globe contributed to this examine.
Radio telescopes in China additionally made contribution to this mission, together with China’s Tianma 65-meter radio telescope with its enormous dish and excessive sensitivity at millimeter wavelengths. As well as, Xinjiang 26-meter radio telescope enhances the angular decision of EAVN observations. The great high quality information with each excessive sensitivity and excessive angular decision are important to acquire this achievement.
“The in-building Shigatse 40-meter radio telescope by Shanghai Astronomical Observatory, will additional enhance the imaging functionality of EAVN at millimeters. Particularly, the Tibetan Plateau, the place the telescope is situated, owns probably the most wonderful website circumstances for (sub-)millimeter wavelength observations. It fulfills our expectations to advertise home sub-millimeter amenities for astronomical observations,” mentioned Prof. Shen Zhiqiang, Director of the Shanghai Astronomical Observatory of the Chinese language Academy of Sciences.
Whereas this examine sheds gentle on the mysterious world of supermassive black holes, it additionally presents formidable challenges. The accretion disk’s construction and the precise worth of the M87 supermassive black hole’s spin are nonetheless extremely unsure. This work additionally predicts that there shall be extra sources with this configuration, thus difficult scientists to find them.
Extra data:
Yuzhu Cui, Precessing jet nozzle connecting to a spinning black hole in M87, Nature (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41586-023-06479-6. www.nature.com/articles/s41586-023-06479-6
Supplied by
Chinese Academy of Sciences
Quotation:
Monitoring of radio galaxy M87 confirms black hole spin (2023, September 27)
retrieved 28 September 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-09-radio-galaxy-m87-black-hole.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




