Earlier this yr, astronomers have been protecting tabs on knowledge from the Zwicky Transient Facility, an all-sky survey based mostly on the Palomar Observatory in California, once they detected a unprecedented flash in part of the sky the place no such gentle had been noticed the evening earlier than. From a tough calculation, the flash appeared to present off extra gentle than 1,000 trillion suns.
The group, led by researchers at NASA, Caltech, and elsewhere, posted their discovery to an astronomy publication, the place the sign drew the eye of astronomers around the globe, together with scientists at MIT. Over the subsequent few days, a number of telescopes targeted in on the sign to assemble extra knowledge throughout a number of wavelengths within the X-ray, ultraviolet, optical, and radio bands, to see what might presumably produce such an infinite quantity of sunshine.
Now, the MIT astronomers together with their collaborators have decided a possible supply for the sign. In a research showing in Nature Astronomy, the scientists report that the sign, named AT 2022cmc, possible comes from a relativistic jet of matter streaking out from a supermassive black hole at near the pace of sunshine. They imagine the jet is the product of a black hole that immediately started devouring a close-by star, releasing an enormous quantity of vitality within the course of.
Astronomers have noticed different such “tidal disruption occasions,” or TDEs, by which a passing star is torn aside by a black hole’s tidal forces. AT 2022cmc is brighter than any TDE found to this point. The supply can be the farthest TDE ever detected, at some 8.5 billion lights years away—greater than midway throughout the universe.
How might such a distant occasion seem so vibrant in our sky? The group says the black hole’s jet could also be pointing immediately towards Earth, making the sign seem brighter than if the jet have been pointing in another route. The impact is “Doppler boosting” and is much like the amped-up sound of a passing siren.
AT 2022cmc is the fourth Doppler-boosted TDE ever detected and the primary such occasion that has been noticed since 2011. It’s also the primary TDE found utilizing an optical sky survey.
As extra highly effective telescopes begin up within the coming years, they may reveal extra TDEs, which may make clear how supermassive black holes develop and form the galaxies round them.
“We all know there’s one supermassive black hole per galaxy, and so they shaped in a short time within the universe’s first million years,” says co-author Matteo Lucchini, a postdoc in MIT’s Kavli Institute for Astrophysics and Area Analysis. “That tells us they feed very quick, although we do not understand how that feeding course of works. So, sources like a TDE can truly be a extremely good probe for a way that course of occurs.”
Lucchini’s MIT co-authors embody first writer Dheeraj “DJ” Pasham, Peter Kosec, Erin Kara, and Ronald Remillard, together with collaborators at universities and establishments around the globe.
Feeding frenzy
Following AT 2022cmc’s preliminary discovery, Pasham and Lucchini targeted in on the sign utilizing the Neutron star Inside Composition ExploreR (NICER), an X-ray telescope that operates aboard the Worldwide Area Station.
“Issues regarded fairly regular the primary three days,” Pasham remembers. “Then we checked out it with an X-ray telescope, and what we discovered was, the supply was too vibrant.”
Sometimes, such vibrant flashes within the sky are gamma-ray bursts—excessive jets of X-ray emissions that spew from the collapse of large stars.
“This explicit occasion was 100 instances extra highly effective than essentially the most highly effective gamma-ray burst afterglow,” Pasham says. “It was one thing extraordinary.”
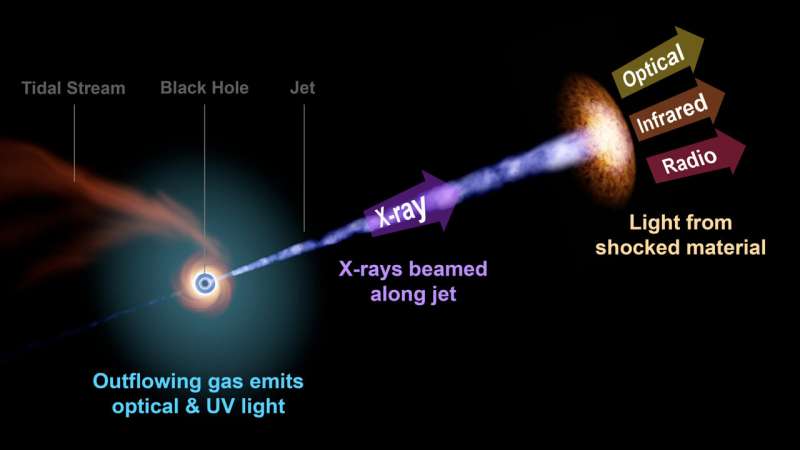
The group then gathered observations from different X-ray, radio, optical, and UV telescopes and tracked the sign’s exercise over the subsequent few weeks. Essentially the most outstanding property they noticed was the sign’s excessive luminosity within the X-ray band. They discovered that X-ray emissions from AT 2022cmc swung broadly by an element of 500 over a couple of weeks,
They suspected that such excessive X-ray exercise have to be powered by an “excessive accretion episode”—an occasion that generates an enormous churning disk, similar to from a tidal disruption occasion, by which a shredded star creates a whirlpool of particles because it falls right into a black hole.
Certainly, the group discovered that AT 2022cmc’s X-ray luminosity was corresponding to, although brighter than, three beforehand detected TDEs. These vibrant occasions occurred to generate jets of matter pointing straight towards Earth. The researchers puzzled: If AT 2022cmc’s luminosity is the results of an identical Earth-targeting jet, how briskly should the jet be shifting to generate such a vibrant sign? To reply this, Lucchini modeled the sign’s knowledge, assuming the occasion concerned a jet headed straight towards Earth.
“We discovered that the jet pace is 99.99% the pace of sunshine,” Lucchini says.”
To provide such an intense jet, the black hole have to be in a particularly lively phase—what Pasham describes as a “hyper-feeding frenzy.”
“It is in all probability swallowing the star on the charge of half the mass of the sun per yr,” Pasham estimates. “Lots of this tidal disruption occurs early on, and we have been in a position to catch this occasion proper at the start, inside one week of the black hole beginning to feed on the star.”
“We anticipate many extra of those TDEs sooner or later,” Lucchini provides. “Then we’d be capable to say, lastly, how precisely black holes launch these extraordinarily highly effective jets.”
Extra data:
The Delivery of a Relativistic Jet Following the Disruption of a Star by a Cosmological Black Gap, Nature Astronomy (2022). DOI: 10.1038/s41550-022-01820-x , www.nature.com/articles/s41550-022-01820-x
Supplied by
Massachusetts Institute of Technology
Quotation:
Mysteriously vibrant flash is a black hole jet pointing straight towards Earth, astronomers say (2022, November 30)
retrieved 30 November 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-11-mysteriously-bright-black-hole-jet.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




