The Japan-led XRISM (X-ray Imaging and Spectroscopy Mission) observatory has launched a primary have a look at the unprecedented information it can acquire when science operations start later this yr.
The satellite’s science staff launched a snapshot of a cluster of a whole bunch of galaxies and a spectrum of stellar wreckage in a neighboring galaxy, which provides scientists an in depth have a look at its chemical make-up.
“XRISM will present the worldwide science group with a brand new glimpse of the hidden X-ray sky,” mentioned Richard Kelley, the U.S. principal investigator for XRISM at NASA’s Goddard House Flight Middle in Greenbelt, Maryland. “We’ll not solely see X-ray photos of those sources, but additionally research their compositions, motions, and bodily states.”
XRISM (pronounced “crism”) is led by JAXA (Japan Aerospace Exploration Company) in collaboration with NASA, together with contributions from ESA (European House Company). It launched on Sept. 6, 2023.
It is designed to detect X-rays with energies as much as 12,000 electron volts and can research the universe’s hottest areas, largest constructions, and objects with the strongest gravity. For comparability, the vitality of seen mild is 2 to three electron volts.
The mission has two devices, Resolve and Xtend, every on the focus of an X-ray Mirror Meeting designed and constructed at Goddard.

Resolve is a microcalorimeter spectrometer developed by NASA and JAXA. It operates at only a fraction of a level above absolute zero inside a refrigerator-sized container of liquid helium.
When an X-ray hits Resolve’s 6-by-6-pixel detector, it warms the machine by an quantity associated to its vitality. By measuring every X-ray’s vitality, the instrument supplies beforehand unavailable details about the supply.
The mission staff used Resolve to review N132D, a supernova remnant and one of many brightest X-ray sources within the Giant Magellanic Cloud, a dwarf galaxy round 160,000 light-years away within the southern constellation Dorado. The increasing wreckage is estimated to be about 3,000 years outdated and was created when a star roughly 15 instances the sun’s mass ran out of gasoline, collapsed, and exploded.
The Resolve spectrum reveals peaks related to silicon, sulfur, calcium, argon, and iron. That is probably the most detailed X-ray spectrum of the item ever obtained and demonstrates the unimaginable science the mission will do when common operations start later in 2024.
“These parts had been cast within the unique star after which blasted away when it exploded as a supernova,” mentioned Brian Williams, NASA’s XRISM challenge scientist at Goddard.
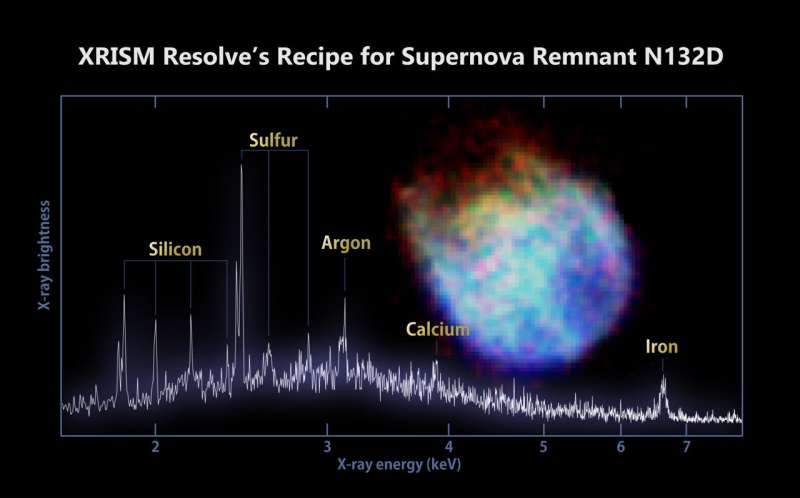
“Resolve will enable us to see the shapes of those traces in a method by no means potential earlier than, letting us decide not solely the abundances of the assorted parts current, but additionally their temperatures, densities, and instructions of movement at unprecedented ranges of precision. From there, we will piece collectively details about the unique star and the explosion.”
XRISM’s second instrument, Xtend, is an X-ray imager developed by JAXA. It offers XRISM a big area of view, permitting it to watch an space about 60% bigger than the common obvious measurement of the full moon.
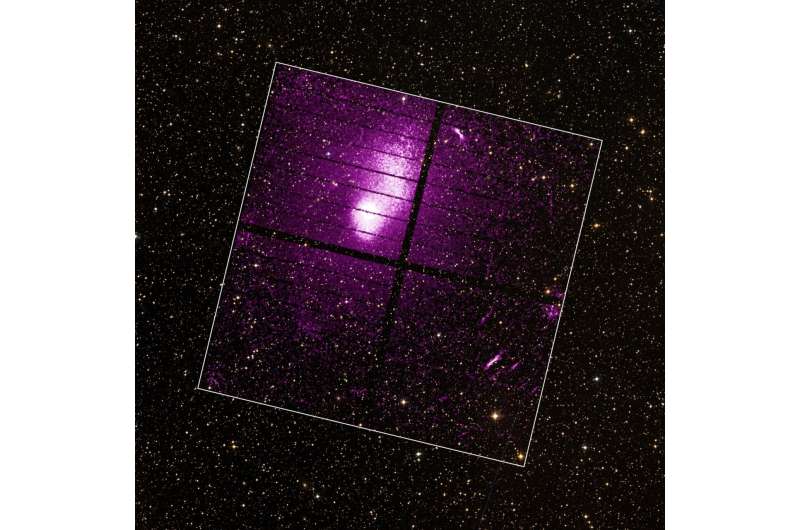
Xtend captured an X-ray picture of Abell 2319, a wealthy galaxy cluster about 770 million light-years away within the northern constellation Cygnus. It is the fifth brightest X-ray cluster within the sky and is presently present process a serious merger occasion.
The cluster is 3 million light-years throughout and highlights Xtend’s broad area of view.
“Even earlier than the tip of the commissioning course of, Resolve is already exceeding our expectations,” mentioned Lillian Reichenthal, NASA’s XRISM challenge supervisor at Goddard. “Our objective was to realize a spectral decision of seven electron volts with the instrument, however now that it is in orbit, we’re reaching 5. What meaning is we’ll get much more detailed chemical maps with every spectrum XRISM captures.”
Resolve is performing exceptionally and already conducting thrilling science regardless of a problem with the aperture door protecting its detector. The door, designed to guard the detector earlier than launch, has not opened as deliberate after a number of makes an attempt. The door blocks lower-energy X-rays, successfully slicing the mission off at 1,700 electron volts in comparison with the deliberate 300.
The XRISM staff will proceed to discover the anomaly and is investigating completely different approaches to opening the door. The Xtend instrument is unaffected.
Offered by
NASA’s Goddard Space Flight Center
Quotation:
NASA/JAXA XRISM mission reveals its first have a look at X-ray cosmos (2024, January 5)
retrieved 5 January 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-01-nasajaxa-xrism-mission-reveals-ray.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




