NASA switched off one in every of its oldest devices finding out Mars on April 3, a step that is been deliberate since final 12 months. Driving aboard NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter, CRISM, or the Compact Reconnaissance Imaging Spectrometer for Mars, revealed minerals similar to clays, hematite (in any other case referred to as iron oxide), and sulfates throughout the Purple Planet’s floor for 17 years.
Led by Johns Hopkins College’s Utilized Physics Laboratory (APL) in Laurel, Maryland, CRISM produced high-resolution mineral maps essential in serving to scientists perceive how lakes, streams, and groundwater formed the planet billions of years in the past. The instrument’s two detectors noticed in seen and infrared gentle, recognizing the chemical fingerprints, or spectra, of minerals that type within the presence of water.
“Shutting down CRISM marks the top of an period for us,” mentioned Wealthy Zurek, MRO’s undertaking scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory, which manages the mission. “It is revealed the place and the way water reworked historical Mars. The CRISM information merchandise will likely be mined by scientists for years to return.”
NASA has additionally relied on CRISM maps to determine the place probably the most scientifically fascinating touchdown websites are, as with Gale Crater, which Curiosity has been exploring since 2012, and Jezero Crater, the place NASA’s Perseverance rover lately collected its nineteenth pattern.
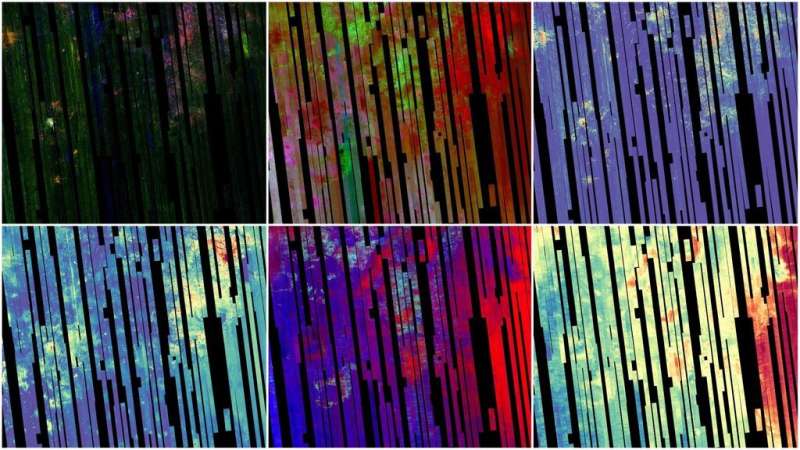
With the intention to research infrared gentle, which is radiated by heat objects and is invisible to the human eye, CRISM relied on cryocoolers to isolate one in every of its spectrometers from the heat of the spacecraft. Three cryocoolers have been utilized in succession, and the final accomplished its lifecycle in 2017.
The CRISM group then seemed for tactics to proceed producing information with out using cryocoolers, deciding to create two new, almost world maps. The primary of those relied on information beforehand collected by the infrared spectrometer and by the second spectrometer on the instrument, which considered a extra restricted vary of minerals in seen and near-infrared gentle. This primary map of water-related minerals, containing 5.6 gigapixels, has a spatial decision of 600 ft (180 meters) per pixel and covers 86% of Mars. Scientists started releasing it in sections final 12 months.
For the second map, CRISM’s remaining spectrometer gathered information at a good increased spatial decision (300 ft, or 90 meters per pixel). This map is slated for launch in September.
“With these new maps, researchers can simply tie mineral deposits noticed in high-resolution photographs to regional scale traits, panorama options, and geology,” mentioned Kim Seelos, CRISM’s deputy principal investigator at APL. “Although the CRISM investigation is formally coming to an in depth, I hope and count on to see many future scientists benefiting from CRISM information for his or her analysis.”
Quotation:
NASA retires mineral mapping instrument on Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (2023, April 25)
retrieved 25 April 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-04-nasa-mineral-instrument-mars-reconnaissance.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




