The Apollo Program delivered 12 American astronauts to the floor of the moon. However that program led to 1972, and since then, no human beings have visited. However Artemis will change that. And as a substitute of simply visiting the moon, Artemis’ goal is to ascertain a longer-term presence on the moon. That requires extra complexity than Apollo did. Astronauts might want to switch between automobiles.
All of that exercise requires a dependable spacecraft docking system.
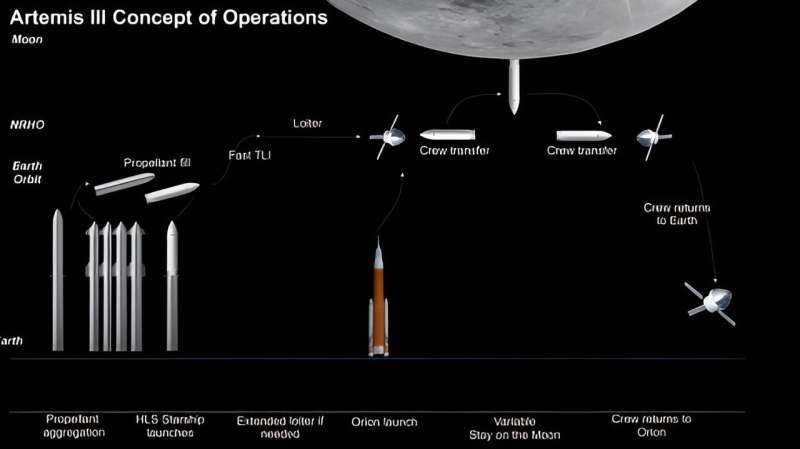
When Artemis astronauts blast off from Earth, they will be within the four-seat Orion spacecraft. Orion will take them to lunar orbit, the place two will switch into the Starship HLS, and two will stay in Orion. Starship HLS will ship them to the lunar floor. Sooner or later, the Lunar Gateway can be in orbit across the moon, and astronauts will transfer from Orion to the Gateway to the Starship HLS.
These transfers are sophisticated and dangerous maneuvers. The docking system that may make this work is named SpaceX’s Starship HLS docking system. It is based mostly on SpaceX’s profitable Dragon 2 docking system. The Dragon 2 system permits the Dragon 2 spacecraft to dock with the ISS so crew and gear may be transferred. It has been in use since 2020.
NASA and SpaceX are busy testing the brand new Starship HLS docking system. They not too long ago accomplished 10 days of testing on the Johnson Area Middle in Houston, Texas. They performed greater than 200 completely different docking eventualities involving completely different speeds and angles. The outcomes from this full-scale testing will feed into ongoing laptop fashions of the system, which is able to, in flip, feed into future testing and design.
The system has each an energetic and a passive mode. When two spacecraft dock, one is energetic, and the opposite is passive. The energetic one is named the chaser, and the opposite is the goal.
Throughout this spherical of exams, NASA and SpaceX demonstrated the mushy seize process. In passive seize, the chaser extends its mushy seize system (SCS) whereas the goal spacecraft’s system stays retracted. The chaser does all of the work, using latches and different mechanisms to seize the goal spacecraft and full the docking.
HLS necessities state that there should be redundancy in crew egress/ingress. The mushy seize process appears to deal with this if the docking system works whereas one docking system stays retracted.
That is simply the most recent spherical of exams. SpaceX has already reached a collection of necessary milestones for the Starship HLS. These milestones concerned energy technology, communications, steerage and navigation, propulsion, life support, and space environments safety.
Whereas watching highly effective rockets being examined and launched takes up a number of consideration, there’s much more to profitable missions than simply launch automobiles. In keeping with NASA, “the Human Touchdown System program is on the heart of Artemis, designed to yield groundbreaking science, develop and make the most of lunar surface sources and leverage what we study on the moon for future Mars missions.” Docking programs may not garner a lot consideration, however they’re clearly a crucial a part of success.
By that lens, any progress on Artemis is nice information as a result of, on different fronts, the information will not be at all times good. Artemis was initially scheduled to launch in 2025. However it’ll be no less than a 12 months late, and NASA says that SpaceX might want to carry out extra launches earlier than the Artemis mission is given the go-ahead.
Offered by
Universe Today
Quotation:
NASA exams the brand new Starship docking system (2024, March 4)
retrieved 4 March 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-03-nasa-starship-docking.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




