The Roman Coronagraph Instrument on NASA’s Nancy Grace Roman Area Telescope will assist pave the best way within the seek for liveable worlds outdoors our solar system by testing new instruments that block starlight, revealing planets hidden by the glare of their guardian stars. The expertise demonstration not too long ago shipped from NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California to the company’s Goddard Area Flight Middle in Greenbelt, Maryland, the place it has joined the remainder of the space observatory in preparation for launch by Could 2027.
Earlier than its cross-country journey, the Roman Coronagraph underwent probably the most full check of its starlight-blocking talents but—what engineers name “digging the darkish gap.” In space, this course of will allow astronomers to look at mild immediately from planets round different stars, or exoplanets. As soon as demonstrated on Roman, related applied sciences on a future mission might allow astronomers to make use of that mild to establish chemical compounds in an exoplanet’s ambiance, together with ones that probably point out the presence of life.
Let the testing start
For the darkish gap check, the staff positioned the coronagraph in a sealed chamber designed to simulate the chilly, darkish vacuum of space. Utilizing lasers and particular optics, they replicated the sunshine from a star as it could look when noticed by the Roman telescope. When the sunshine reaches the coronagraph, the instrument makes use of small round obscurations known as masks to successfully block out the star, like a automobile visor blocking the sun or the moon blocking the sun throughout a total solar eclipse. This makes fainter objects close to the star simpler to see.
Coronagraphs with masks are already flying in space, however they cannot detect an Earth-like exoplanet. From one other star system, our dwelling planet would seem roughly 10 billion occasions dimmer than the sun, and the 2 are comparatively shut to at least one one other. So attempting to immediately picture Earth could be like attempting to see a speck of bioluminescent algae subsequent to a lighthouse from 3,000 miles (about 5,000 kilometers) away. With earlier coronagraphic applied sciences, even a masked star’s glare overwhelms an Earth-like planet.
The Roman Coronagraph will show strategies that may take away extra undesirable starlight than previous space coronagraphs by utilizing a number of movable elements. These transferring components will make it the primary “energetic” coronagraph to fly in space. Its important instruments are two deformable mirrors, every solely 2 inches (5 centimeters) in diameter and backed by greater than 2,000 tiny pistons that transfer up and down. The pistons work collectively to alter the form of the deformable mirrors in order that they will compensate for the undesirable stray mild that spills across the edges of the masks.
The deformable mirrors additionally assist right for imperfections within the Roman telescope’s different optics. Though they’re too small to have an effect on Roman’s different extremely precise measurements, the imperfections can ship stray starlight into the darkish gap. Exact adjustments made to every deformable mirror’s form, imperceptible to the bare eye, compensate for these imperfections.
“The issues are so small and have such a minor impact that we needed to do over 100 iterations to get it proper,” mentioned Feng Zhao, deputy venture supervisor for the Roman Coronagraph at JPL. “It is sort of like while you go to see an optometrist they usually put totally different lenses up and ask you, ‘Is that this one higher? How about this one?’ And the coronagraph carried out even higher than we might hoped.”
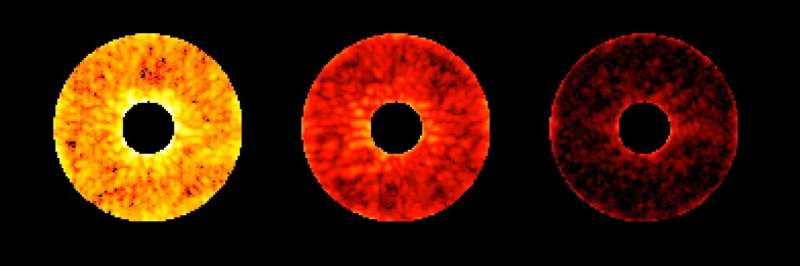
Through the check, the readouts from the coronagraph‘s digicam present a doughnut-shaped area across the central star that slowly will get darker because the staff directs extra starlight away from it—therefore the nickname “digging the darkish gap.” In space, an exoplanet lurking on this darkish area would slowly seem because the instrument does its work with its deformable mirrors.
Liveable worlds
Greater than 5,000 planets have been found and confirmed round different stars within the final 30 years, however most have been detected not directly, which means their presence is inferred primarily based on how they have an effect on their guardian star. Detecting these relative adjustments within the guardian star is way simpler than seeing the sign of the a lot fainter planet. In reality, fewer than 70 exoplanets have been immediately imaged.
The planets which were immediately imaged so far aren’t like Earth: Most are a lot larger, hotter, and usually farther from their stars. These options make them simpler to detect but in addition much less hospitable to life as we all know it.
To search for probably liveable worlds, scientists must picture planets that aren’t solely billions of occasions dimmer than their stars, but in addition orbit them on the proper distance for liquid water to exist on the planet’s floor—a precursor for the sort of life discovered on Earth.
Creating the capabilities to immediately picture Earth-like planets would require intermediate steps just like the Roman Coronagraph. At its most functionality, it might picture an exoplanet just like Jupiter round a star like our sun: a big, cool planet simply outdoors the star’s liveable zone.
What NASA learns from the Roman Coronagraph will assist blaze a path for future missions designed to immediately picture Earth-size planets orbiting within the liveable zones of sun-like stars. The company’s idea for a future telescope known as the Liveable Worlds Observatory goals to picture a minimum of 25 planets just like Earth utilizing an instrument that can construct on what the Roman Coronagraph Instrument demonstrates in space.
“The active components, like deformable mirrors, are important if you wish to obtain the objectives of a mission just like the Liveable Worlds Observatory,” mentioned JPL’s Ilya Poberezhskiy, the venture methods engineer for the Roman Coronagraph. “The energetic nature of the Roman Coronagraph Instrument permits you to take atypical optics to a special stage. It makes the entire system extra complicated, however we could not do these unimaginable issues with out it.”
Quotation:
NASA instrument prepares to picture faraway planets (2024, Could 21)
retrieved 21 Could 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-05-nasa-tool-image-faraway-planets.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




