Utilizing NASA’s Chandra X-ray Observatory, astronomers have positioned an exhaust vent hooked up to a “chimney” of sizzling gasoline blowing away from the middle of the Milky Way galaxy. Their paper describing these outcomes is published in The Astrophysical Journal.
Eruptions from the supermassive black hole on the Milky Way’s heart referred to as Sagittarius A* (Sgr A* for brief) could have created this chimney and exhaust vent.
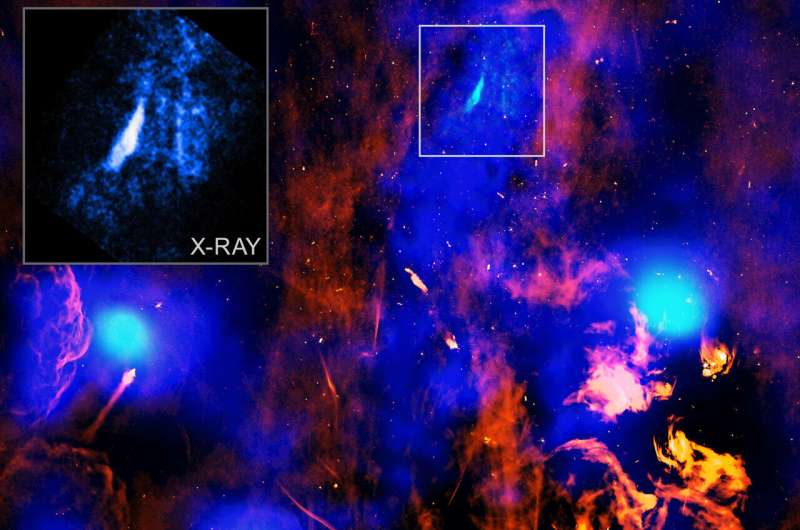
The chimney and vent are about 26,000 light-years from Earth. The chimney begins on the heart of the galaxy and stands perpendicular to the Milky Way’s spiral disk. Astronomers had beforehand recognized the chimney utilizing X-ray knowledge from Chandra and XMM-Newton, an ESA (European Area Company) mission with NASA contributions. Radio emission detected by the MeerKAT radio telescope exhibits the impact of magnetic fields enclosing the gasoline within the chimney.
The most recent Chandra knowledge reveals a number of X-ray ridges roughly perpendicular to the airplane of the galaxy. Researchers suppose these are the partitions of a tunnel, formed like a cylinder, which helps funnel sizzling gasoline because it strikes upwards alongside the chimney and away from the Galactic Middle. The newly found vent is positioned close to the highest of the chimney about 700 light-years from the middle of the galaxy.
“We suspected that magnetic fields are performing because the partitions of the chimney and that sizzling gasoline is touring up via them, like smoke,” stated Scott Mackey of the College of Chicago, who led the research. “Now we have found an exhaust vent close to the highest of the chimney.”
The workforce thinks the exhaust vent fashioned when sizzling gasoline rising via the chimney struck cooler gasoline mendacity in its path. The brightness of the exhaust vent partitions in X-rays is attributable to shock waves—just like sonic booms from supersonic planes—generated by this collision. The left aspect of the exhaust vent is probably going significantly shiny as a result of the gasoline flowing upwards is hanging the tunnel wall at a extra direct angle and with extra drive than different areas.
The authors of the research suppose that the new gasoline is most definitely coming from a sequence of occasions involving materials falling into Sgr A* after which eruptions from the black hole driving the gasoline upwards alongside the chimney, and out via the exhaust vent. Nonetheless, they have no idea precisely how typically the black hole is being fed.
Earlier research have indicated that dramatic X-ray flares happen each few hundred years at or close to the placement of the central black hole, so these might play necessary roles in driving the new gasoline upwards via the exhaust vent. Astronomers additionally estimate that the galactic black hole rips aside and swallows a star each 20,000 years or so. Such occasions would result in highly effective, explosive releases of power, a lot of which might be destined to rise via the chimney vents.
“We’re undecided if this power and warmth are stoked by a considerable amount of materials being dumped onto Sgr A* directly, like a bunch of logs being dumped on a fireplace,” stated co-author Mark Morris of the College of California, Los Angeles. “Or it would come from a number of small hundreds being fed into the black hole just like kindling being often tossed in.”
The particles and power within the vent present clues concerning the origin of two mysterious and far bigger buildings across the heart of the Milky Way: the Fermi Bubbles seen in gamma-rays by NASA’s Fermi Gamma-ray Area Telescope and the eROSITA Bubbles, detected by ESA’s latest X-ray telescope. Each of those are pairs of buildings extending hundreds of light-years away from the middle of the galaxy. They supply necessary details about previous explosive exercise close to the middle of the galaxy.
The Fermi and eROSITA bubbles are each aligned with the path of the chimney and a second X-ray chimney that begins on the galaxy’s heart and factors in the wrong way. The funneling results of the exhaust vent close to the highest of the chimney could preserve the new gasoline targeted because it travels upwards, aiding within the formation of the coherent construction of the bubbles.
“The origin of the Fermi Bubbles and the eROSITA bubbles are among the greatest mysteries confronted by research of the excessive power radiation from our galaxy,” stated co-author Gabriele Ponti of the Italian Nationwide Institute of Astrophysics in Merate. “We have found a small construction which may play a big position within the creation of those gigantic bubbles.”
Extra info:
Scott C. Mackey et al, X-Rays from a Central “Exhaust Vent” of the Galactic Middle Chimney, The Astrophysical Journal Letters (2024). DOI: 10.3847/2041-8213/ad3248
Supplied by
Chandra X-ray Center
Quotation:
NASA’s Chandra notices the galactic heart is venting (2024, Might 10)
retrieved 10 Might 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-05-nasa-chandra-galactic-center-venting.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




