4 thousand Martian days after setting its wheels in Gale Crater on Aug. 5, 2012, NASA’s Curiosity rover stays busy conducting thrilling science. The rover lately drilled its thirty ninth pattern, then dropped the pulverized rock into its stomach for detailed evaluation.
To check whether or not historical Mars had the circumstances to assist microbial life, the rover has been steadily ascending the bottom of 3-mile-tall (5-kilometer-tall) Mount Sharp, whose layers fashioned in several durations of Martian historical past and supply a report of how the planet’s local weather modified over time.
The newest pattern was collected from a goal nicknamed “Sequoia” (all the mission’s present science targets are named after areas in California’s Sierra Nevada). Scientists hope the pattern will reveal extra about how the local weather and habitability of Mars developed as this area turned enriched in sulfates—minerals that doubtless fashioned in salty water that was evaporating as Mars first started drying up billions of years in the past. Finally, Mars’s liquid water disappeared for good.
“The kinds of sulfate and carbonate minerals that Curiosity’s devices have recognized within the final yr assist us perceive what Mars was like so way back. We have been anticipating these outcomes for many years, and now Sequoia will inform us much more,” stated Ashwin Vasavada, Curiosity’s undertaking scientist at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory in Southern California, which leads the mission.
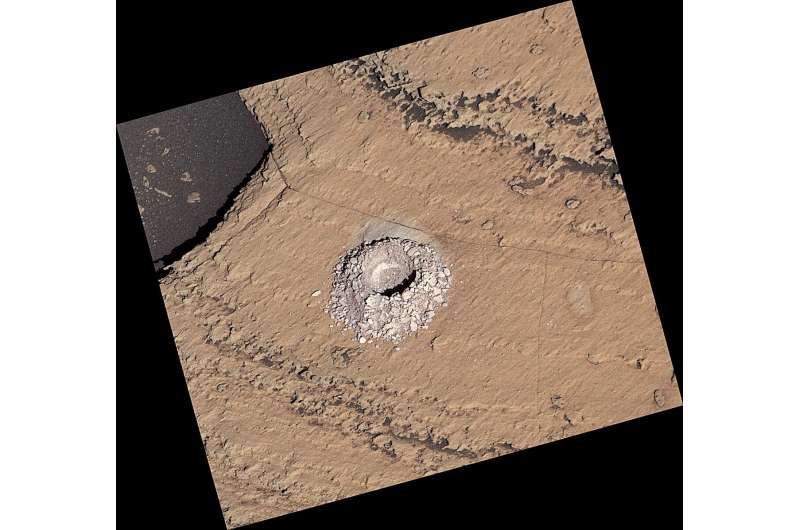

Deciphering the clues to Mars’ historical local weather requires detective work. In a recent paper revealed within the Journal of Geophysical Analysis: Planets, team members used information from Curiosity’s Chemistry and Mineralogy (CheMin) instrument to find a magnesium sulfate mineral referred to as starkeyite, which is related to particularly dry climates like Mars’s trendy local weather.
The group believes that after sulfate minerals first fashioned in salty water that was evaporating billions of years in the past, these minerals remodeled into starkeyite because the local weather continued drying to its current state. Findings like this refine scientists’ understanding of how the Mars of at present got here to be.
Time-tested rover
Regardless of having pushed nearly 20 miles (32 kilometers) by means of a punishingly chilly atmosphere bathed in dust and radiation since 2012, Curiosity stays robust. Engineers are presently working to resolve a difficulty with one of many rover’s most important “eyes”—the 34 mm focal length left digicam of the Mast Digicam (Mastcam) instrument. Along with offering shade pictures of the rover’s environment, every of Mastcam’s two cameras helps scientists decide from afar the composition of rocks by the wavelengths of sunshine, or spectra, they replicate in several colours.
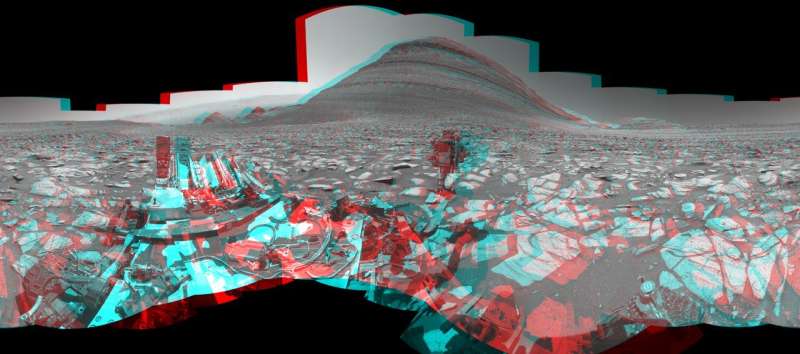
To try this, Mastcam depends on filters organized on a wheel that rotates underneath every digicam’s lens. Since Sept. 19, the left digicam’s filter wheel has been caught between filter positions, the results of which could be seen on the mission’s uncooked (unprocessed) pictures. The mission continues to steadily nudge the filter wheel again towards its normal setting.
If unable to nudge it again all the way in which, the mission would depend on the higher-resolution 100 mm-focal size proper Mastcam as the first color-imaging system. In consequence, how the group scouts for science targets and rover routes can be affected: The precise digicam must take 9 occasions extra pictures than the left to cowl the identical space. The groups additionally would have a degraded capacity to watch the detailed shade spectra of rocks from afar.
Together with efforts to nudge the filter again, mission engineers proceed to carefully monitor the efficiency of the rover’s nuclear energy supply and anticipate it’ll present sufficient power to function for a lot of extra years. They’ve additionally discovered methods to beat challenges from put on on the rover’s drill system and robotic-arm joints. Software program updates have mounted bugs and added new capabilities to Curiosity, too, making lengthy drives simpler for the rover and lowering wheel put on that comes from steering (an earlier addition of a traction-control algorithm additionally helps cut back wheel put on from driving over sharp rocks).
In the meantime, the group is making ready for a break of a number of weeks in November. Mars is about to vanish behind the sun, a phenomenon generally known as solar conjunction. Plasma from the sun can work together with radio waves, doubtlessly interfering with instructions throughout this time. Engineers are leaving Curiosity with a to-do listing from Nov. 6 to twenty-eight, after which interval communications can safely resume.
Extra info:
S. J. Chipera et al, Mineralogical Investigation of Mg‐Sulfate on the Canaima Drill Web site, Gale Crater, Mars, Journal of Geophysical Analysis: Planets (2023). DOI: 10.1029/2023JE008041
Quotation:
NASA’s Curiosity rover clocks 4,000 days on Mars (2023, November 6)
retrieved 6 November 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-11-nasa-curiosity-rover-clocks-days.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




