The James Webb and Hubble telescopes on Thursday revealed their first pictures of a spacecraft intentionally smashing into an asteroid, as astronomers indicated that the affect appears to be like to have been a lot better than anticipated.
The world’s telescopes turned their gaze in the direction of the space rock Dimorphos earlier this week for a historic take a look at of Earth’s capacity to defend itself in opposition to a possible life-threatening asteroid sooner or later.
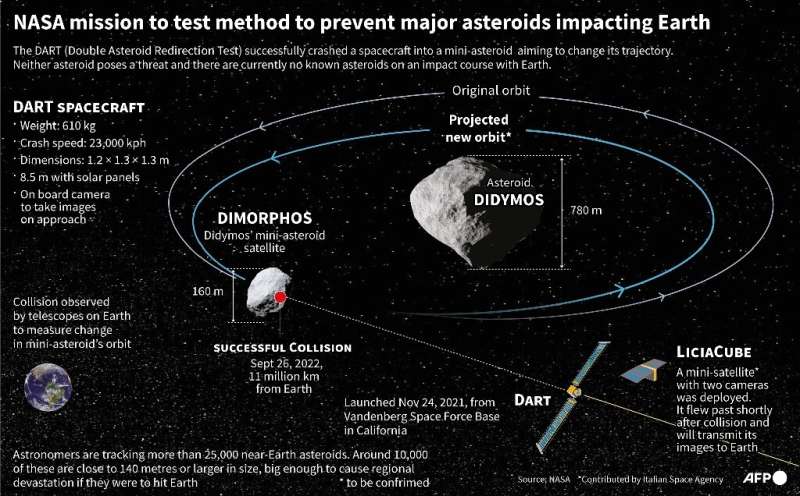
Astronomers rejoiced as NASA’s Double Asteroid Redirection Take a look at (DART) impactor slammed into its pyramid-sized, rugby ball-shaped goal 11 million kilometers (6.8 million miles) from Earth on Monday evening.
Pictures taken by Earth-bound telescopes confirmed an unlimited cloud of dust increasing out of Dimorphos—and its massive brother Didymos which it orbits—after the spaceship hit.
Whereas these pictures confirmed matter spraying out over hundreds of kilometers, the James Webb and Hubble pictures “zoom in a lot nearer”, mentioned Alan Fitzsimmons, an astronomer at Queen’s College Belfast concerned in observations with the ATLAS mission.
James Webb and Hubble can provide a view “inside only a few kilometers of the asteroids and you’ll actually clearly see how the fabric is flying out from that explosive affect by DART”, Fitzsimmons informed AFP.
“It actually is sort of spectacular,” he mentioned.
A picture taken by James Webb’s Close to-Infrared Digital camera (NIRCam) 4 hours after affect reveals “plumes of fabric showing as wisps streaming away from the middle of the place the affect came about”, based on a joint assertion from the European Area Company, James Webb and Hubble.
Hubble pictures from 22 minutes, 5 hours and eight hours after affect present the increasing spray of matter from the place DART hit.
‘Nervous there was nothing left’
Ian Carnelli of the European Area Company mentioned that the “actually spectacular” Webb and Hubble pictures had been remarkably just like these taken by the toaster-sized satellite LICIACube, which was simply 50 kilometers from the asteroid after separating from the DART spacecraft just a few weeks in the past.
The pictures depict an affect that appears “quite a bit larger than we anticipated,” mentioned Carnelli, the supervisor of the ESA’s Hera mission which intends to examine the harm in 4 years.

“I used to be actually frightened there was nothing left of Dimorphos” at first, Carnelli informed AFP.
The Hera mission, which is scheduled to launch in October 2024 and arrive on the asteroid in 2026, had anticipated to survey a crater round 10 meters (33 ft) in diameter.
It now appears to be like like it will likely be far larger, Carnelli mentioned, “if there’s a crater in any respect, possibly a bit of Dimorphos was simply chunked off.”
The true measure of DART’s success might be precisely how a lot it diverted the asteroid’s trajectory, so the world can begin getting ready to defend itself in opposition to larger asteroids that might head our approach sooner or later.
It’s going to doubtless take Earth-bound telescopes and radars no less than per week for a primary estimate of how a lot the asteroid’s orbit has been altered, and three or 4 weeks earlier than there’s a exact measurement, Carnelli mentioned.

‘Large implications’
“I’m anticipating a a lot larger deflection than we had deliberate,” he mentioned.
That might have “large implications in planetary protection as a result of it implies that this system could possibly be used for a lot bigger asteroids”, Carnelli added.
“Till as we speak, we thought that the one deflection method could be to ship a nuclear gadget.”
Fitzsimmons mentioned that even when no materials had been “flung off” Dimorphos, DART nonetheless would nonetheless have barely affected its orbit.
“However the extra materials and the sooner it is transferring, the extra of a deflection there can have been,” he mentioned.
The observations from James Webb and Hubble will assist reveal how a lot—and the way shortly—matter sprayed from the asteroid, in addition to the character of its floor.
The asteroid affect marked the primary time the 2 space telescopes noticed the identical celestial physique.
Since launching in December and releasing its first pictures in July, James Webb has taken the title of strongest space telescope from Hubble.
Fitzsimmons mentioned the photographs had been “an attractive demonstration of the additional science you may get by utilizing a couple of telescope concurrently”.
© 2022 AFP
Quotation:
New asteroid strike pictures present affect ‘quite a bit larger than anticipated’ (2022, September 29)
retrieved 30 September 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-09-images-asteroid-webb-hubble-telescopes.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




