Scientists from the Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam (AIP) have found a brand new plasma instability that guarantees to revolutionize our understanding of the origin of cosmic rays and their dynamic influence on galaxies.
In the beginning of the final century, Victor Hess found a brand new phenomenon known as cosmic rays that in a while earned him the Nobel prize. He performed high-altitude balloon flights to search out that the Earth’s ambiance will not be ionized by the radioactivity of the bottom. As an alternative, he confirmed that the origin of ionization was extra-terrestrial. Subsequently, it was decided that cosmic “rays” include charged particles from outer space flying near the velocity of sunshine somewhat than radiation. Nevertheless, the identify “cosmic rays” outlasted these findings.
Within the new study, Dr. Mohamad Shalaby, scientists at AIP and the primary creator of this examine, and his collaborators have carried out numerical simulations to observe the trajectories of many cosmic ray particles and examine how these work together with the encircling plasma consisting of electrons and protons. The paper seems on the pre-print server arXiv.
When the researchers studied cosmic rays flying from one facet of the simulation to the opposite, they found a brand new phenomenon that excites electromagnetic waves within the background plasma. These waves exert a power on the cosmic rays, which modifications their winding paths.
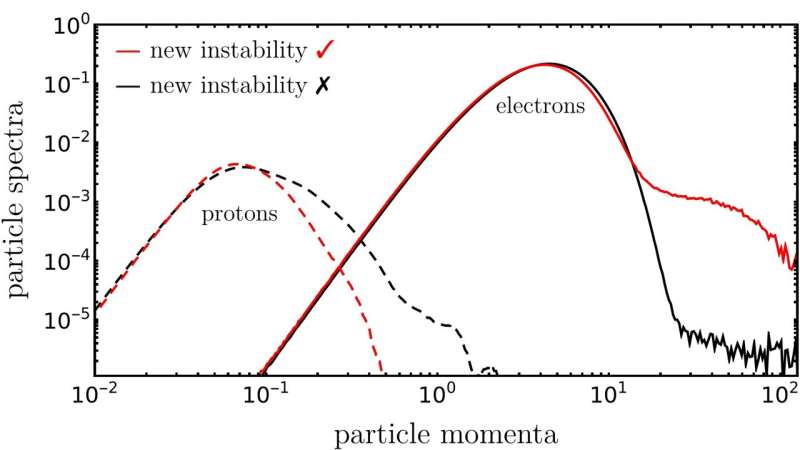
Most significantly, this new phenomenon may be finest understood if we take into account the cosmic rays to not act as particular person particles however as an alternative to assist a collective electromagnetic wave. As this wave interacts with the basic waves within the background, these are strongly amplified and a switch of power takes place.
“This perception permits us to contemplate cosmic rays as behaving like radiation and never particular person particles on this context, simply because it has been initially believed by Victor Hess,” remarks Professor Christoph Pfrommer, head of the Cosmology and Excessive-Vitality Astrophysics part at AIP. analogy for this conduct is particular person water molecules collectively forming a wave that breaks on the shore.
“This progress solely took place by contemplating smaller scales which have beforehand been neglected and that query the usage of efficient hydrodynamic theories when finding out plasma processes,” explains Dr. Mohamad Shalaby.
There are various purposes of this newly found plasma instability, together with a primary clarification of how electrons from the thermal interstellar plasma may be accelerated to excessive energies at supernova remnants.
“This newly discovered plasma instability represents a big leap in our understanding of the acceleration course of and eventually explains why these supernova remnants shine within the radio and gamma rays,” studies Mohamad Shalaby. Furthermore, this groundbreaking discovery opens the door to a deeper understanding of the basic processes of the transport of cosmic rays in galaxies, which represents the best thriller in our understanding of the processes that form galaxies throughout their cosmic evolution.
Extra data:
Mohamad Shalaby et al, Deciphering the bodily foundation of the intermediate-scale instability, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2305.18050
Journal data:
arXiv
Supplied by
Leibniz Institute for Astrophysics Potsdam
Quotation:
New plasma instability sheds gentle on the character of cosmic rays (2023, December 12)
retrieved 12 December 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-12-plasma-instability-nature-cosmic-rays.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




