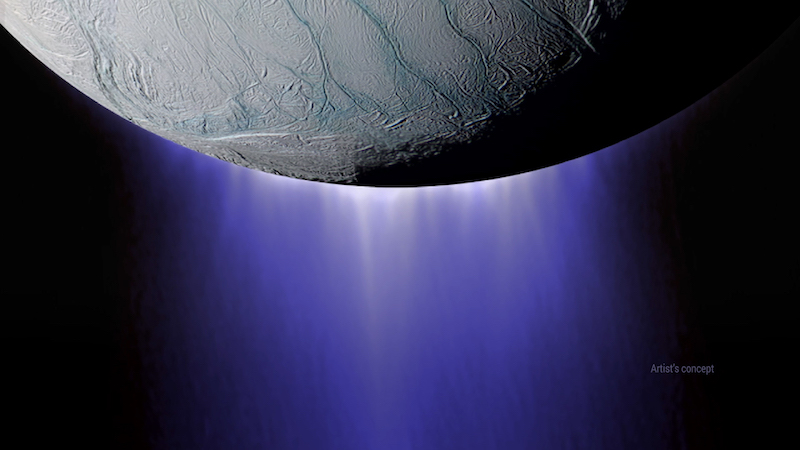
Saturn’s moon Enceladus is known for its big, lively plumes of water vapor. They erupt like geysers at this little moon’s south pole. NASA’s Cassini spacecraft found them in 2005. And scientists rapidly surmised that the plumes originate from a world ocean under the floor of Saturn’s moon. That subsurface ocean may be inhabited by residing issues. So the plumes may comprise evidence of life. In Could 2023, we started to listen to that the James Webb Area Telescope (JWST) has now taken a brand new shut take a look at Enceladus. Webb has noticed a brand new, a lot bigger plume.
The water vapor plumes on Enceladus may be big, usually talking. They tower above the moon’s icy floor. Contemplate that Enceladus itself is barely about 314 miles (505 km) huge. The plumes noticed by Cassini had been identified to be at the least as tall because the moon’s diameter. However this new plume – noticed by Webb – is the largest one ever seen, many instances the diameter of Enceladus itself. As Sara Faggi, a planetary astronomer at NASA’s Goddard Area Flight Middle, said:
It’s immense.
Largest water plume on Enceladus ever seen
We haven’t seen an announcement from scientists concerning the new plume. And we haven’t seen the Webb picture. It apparently hasn’t been launched but.
However Alexandra Witze wrote concerning the new plume in Nature on Could 18, 2023.
And Faggi talked about the plume and the Webb observations at a convention on the Area Telescope Science Institute in Baltimore, Maryland, on Could 17.
Whereas few particulars had been offered on the convention, Faggi mentioned {that a} new paper will likely be popping out quickly.
Many instances Enceladus’ diameter
The water vapor erupts by means of massive cracks in Enceladus’ icy floor. Scientists name these cracks tiger stripes.
The venting was identified for sending the water vapor and different particles it incorporates a great distance from Enceladus, out into space. However this latest eruption despatched spray from the moon’s inside even farther out, as much as many instances Enceladus’ diameter of 314 miles (505 km).
Webb was in a position to observe this plume on November 22, 2022, and scientists have been finding out the info despatched again ever since.
Cassini analyzed particles within the plume that had been comparatively near Enceladus itself. However Webb has the benefit of with the ability to take a look at plume particles that journey a lot farther away from the little moon. The flexibility to check each will assist scientists higher perceive the plumes and the wealthy number of substances they comprise.
New evaluation of Enceladus’ plumes
The evaluation of the plume materials, to be offered within the forthcoming paper, ought to be fairly attention-grabbing. Cassini beforehand discovered that the plumes comprise water vapor, ice particles, salts, silica, carbon dioxide, ammonia, methane and natural molecules.
Webb noticed the plume for under 4.5 minutes, however that was ample time to acquire the info wanted. The evaluation will present extra particulars about how a lot water vapor the plume contained and the temperature. This plume, nonetheless, since it’s so unfold out away from Enceladus, is probably going way more diffuse than the plumes Cassini noticed (and truly flew by means of!). Which will make it harder to find out what sorts of natural molecules had been within the plume. Cassini did discover a wide range of each easy and sophisticated natural molecules throughout its mission, nonetheless. As Witze wrote:
However the plume is more likely to be of low density, extra like a diffuse, chilly cloud than a humid spray. That’s not nice information for anybody trying to seize samples from the plume and hoping to seek out life, as a result of the indicators of life may be too sparse to detect. Ice grains seen by Cassini a lot nearer to Enceladus usually tend to have excessive concentrations of natural particles, says Shannon MacKenzie, a planetary scientist on the Johns Hopkins College Utilized Physics Laboratory in Laurel, Maryland.
With that in thoughts, Webb did discover an abundance of intriguing chemical substances within the plume. Witze wrote:
JWST additionally analyzed the spectrum of daylight reflecting off Enceladus and located proof of many chemical substances, together with water and probably different compounds that would trace at geological or organic exercise within the moon’s ocean.
What are they? We’ll have to attend to seek out out, however as Faggi famous:
Now we have many extra surprises.
Life on Enceladus?
The plumes are of particular curiosity to science as a result of they may comprise clues about attainable life in Enceladus’ subsurface ocean. The substances discovered thus far are tantalizing, though not proof but that the ocean harbors residing organisms.
Cassini did additionally discover proof suggesting that there are hydrothermal vents on the ocean ground. In that case, they might probably be a supply of warmth and vitamins, simply as they’re in oceans on Earth.
Future missions
As of now, there aren’t any confirmed missions going again to Enceladus. However there are ideas on the drawing boards, similar to a mixture of orbiter and lander referred to as Orbilander. Learn the idea research here. A return mission will likely be important to seek out out whether or not life ever has existed on Enceladus, or nonetheless does.
Backside line: NASA’s Webb Area Telescope has noticed the most important water plume on Enceladus ever seen. Particulars concerning the evaluation outcomes will likely be printed in a brand new paper.




