NASA’s beloved Mars rover Opportunity – nicknamed Oppy – launched on July 7, 2003, and ended up surpassing all expectations. It was designed to final 90 Martian days and journey 1,000 meters. Nevertheless it lasted 15 years and traveled greater than 28 miles (45 km) earlier than lastly succumbing to a dust storm.
July 7, 2003: Alternative heads to Mars
Alternative blasted off on its journey to Mars on July 7, 2003. After touring for some seven months by way of space, Alternative landed in Mars’ Meridiani Planum on January 25, 2004. This was three weeks after its twin rover Spirit touched down on the opposite aspect of the planet. Spirit stopped shifting throughout Mars’ floor in 2009, and it stopped sending again indicators to Earth in 2010.
However Alternative – designed to final for 90 Martian days and journey 1,100 yards (1,000 meters) – vastly surpassed all expectations in its endurance, scientific worth and longevity. The rover’s mission successfully resulted in 2018 (formally in 2019) after some 15 years exploring the floor of Mars.
Extremely, along with exceeding its life expectancy by 60 instances, the rover traveled greater than 28 miles (45 km) by the point it reached its most acceptable closing resting spot in Mars’ Perseverance Valley. The Alternative rover stopped speaking with Earth when a extreme Mars-wide dust storm blanketed its location in June 2018. Presumably, the storm affected the rover’s solar panels. Alternative’s closing communication was, in the end, acquired on June 10, 2018.
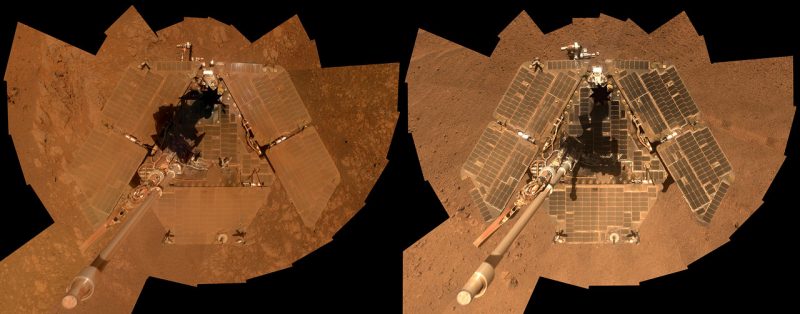
The lengthy goodbye
NASA, nevertheless, didn’t know that but. All through the late summer time and fall of 2018, engineers within the Area Flight Operations Facility at NASA’s Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) performed a multifaceted, eight-month restoration technique to attempt to get the rover to speak. They despatched greater than 1,000 instructions to the rover … however there was no response. In what turned a months-long outpouring of emotion, space followers on Twitter and different social media platforms started utilizing the hashtags #ThankYouOppy and #GoodnightOppy.
Area engineers made their final try to revive Alternative on February 12, 2019. They began with a “wake-up tune” performed within the management room at JPL. The mission’s principal investigator, Steve Squyres, had chosen I’ll Be Seeing You, as carried out by Billie Vacation. At 8:10 p.m., Vacation’s wistful voice floated up from the command ground:
I’ll be seeing you in all of the previous acquainted locations that this coronary heart of mine embraces.
As was anticipated by that point, these closing efforts at communication had been to no avail. Alternative remained silent on the floor of Mars. Undertaking supervisor John Callas advised the gang of NASA staff gathered for the farewell transmission:
This can be a onerous day. Regardless that it’s a machine and we’re saying goodbye, it’s nonetheless very onerous and really poignant, however we had to try this. We got here to that time.

Alternative, the little rover that might
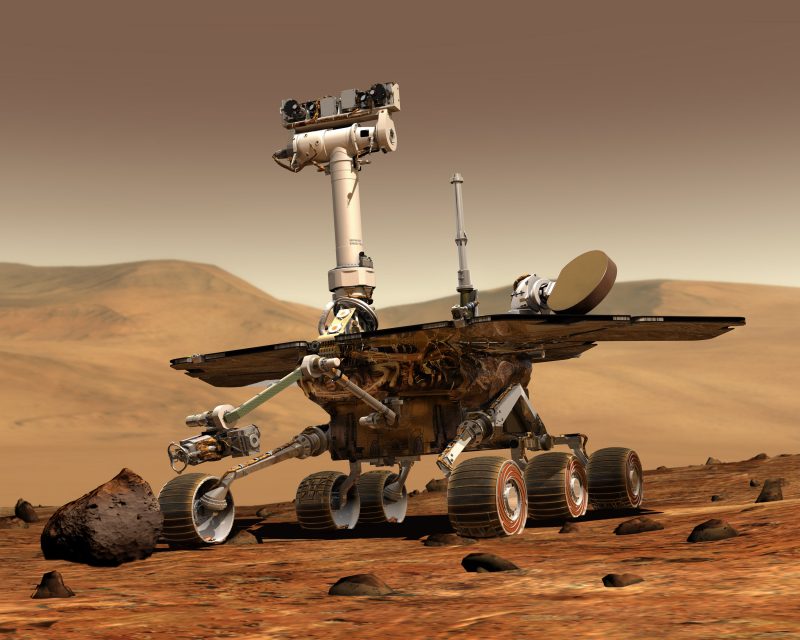
From the day Alternative landed, a crew of mission engineers, rover drivers and scientists on Earth collaborated to get the rover from one geologic website on Mars to the following. They plotted workable avenues over rugged terrain so the 384-pound (174-kilogram) Martian explorer might maneuver round and over rocks and boulders and climb gravel-strewn slopes as steep as 32 levels (an off-Earth document). It might additionally probe crater flooring, summit hills and traverse potential dry riverbeds. Its closing enterprise introduced it to the western limb of Perseverance Valley. General, Alternative’s achievements embody:
– Setting a one-day Mars driving document on March 20, 2005, when it traveled 721 ft (220 meters).
– Returning greater than 217,000 photographs, together with 15 360-degree colour panoramas.
– Exposing the surfaces of 52 rocks to disclose recent mineral surfaces for evaluation.
– Clearing 72 further targets with a brush to arrange them for inspection with spectrometers and a microscopic imager.
– Discovering hematite, a mineral that varieties in water, at its touchdown website.
– Discovering sturdy indications at Endeavour Crater of the motion of historical water much like the drinkable water of a pond or lake on Earth.
Within the video under, Steve Squyres speaks about Alternative’s mission and its significance.
Overcoming challenges
All these accomplishments weren’t with out the occasional extraterrestrial obstacle. In 2005 alone, Alternative misplaced steering to one in every of its entrance wheels and a caught heater threatened to severely restrict the rover’s accessible energy. A Martian sand ripple additionally nearly trapped it for good. Two years later, a two-month dust storm imperiled the rover. In 2015, Alternative misplaced use of its 256-megabyte flash reminiscence. In 2017, it misplaced steering to its different entrance wheel.
Every time the rover confronted an impediment, Alternative’s crew on Earth found out an answer that enabled the rover to bounce again. Nevertheless, the large dust storm that took form in the summertime of 2018 proved an excessive amount of for historical past’s most senior Mars explorer.

Farewell #Oppy and we thanks.#ThanksOppy https://t.co/ZhS2IOzWJH
— Stream Lightyear on Disney+ so we will get a sequel (@BrandonWNichols) February 14, 2019
Backside line: NASA’s Alternative rover launched to Mars on July 7, 2003. It formally ended its mission on February 13, 2019.
Read more: Media We Love: Good Night Oppy Review




