A pancake stack of radioactivity-sensitive movies carried by means of the sky by a balloon was capable of take the world’s most correct image of a neutron star’s gamma ray beam. To realize this, Kobe College researchers mixed the oldest methodology of capturing radioactive radiation with the latest knowledge capturing methods and a intelligent time-recording system.
The celebrities shine their gentle on us within the full vary of the spectrum of sunshine, from infra-red to gamma rays. For every of those bands, totally different sensing gear is required. Essentially the most difficult one is gamma rays, well-known for being a high-energy product of nuclear fission, as a result of their very quick wavelength implies that they do not work together with matter in the identical approach as different types of gentle and thus cannot be deflected with lenses or detected by customary sensors. Thus, there’s a hole in our skill to detect the sunshine coming from fascinating stellar objects comparable to supernovae and their remnants.
To resolve this situation, Kobe College astrophysicist Aoki Shigeki and his workforce turned to the very first materials that was used to detect radioactivity, photographic movies.
“Our group has been specializing in the wonderful functionality of emulsion movie to hint gamma rays with excessive precision and proposed that it may turn into a wonderful gamma-ray telescope by introducing a number of fashionable knowledge seize and evaluation options,” explains Aoki.
Primarily based on the excessive sensitivity of those movies and a novel, automated, high-speed means of extracting knowledge from them, the physicists’ thought was to stack up a couple of of them to precisely seize the trajectory of the particles that the gamma ray produces on affect, similar to a single pancake might seize the place you poke a straw into it, however it takes a complete stack to file the straw’s route.
-

A single pancake might seize the place you poke a straw into it, however it takes a complete stack to file the straw’s route. Equally, Kobe College researchers may precisely picture a gamma-ray-emitting pulsar (the sky’s lighthouses) with a stack of radioactivity-sensitive movies on a balloon. To have the ability to inform the orientation of the dangling gondola relative to the celebrities, they added a star digital camera and a tool to timestamp the gamma-rays’ impacts. Credit score: Kobe College
-
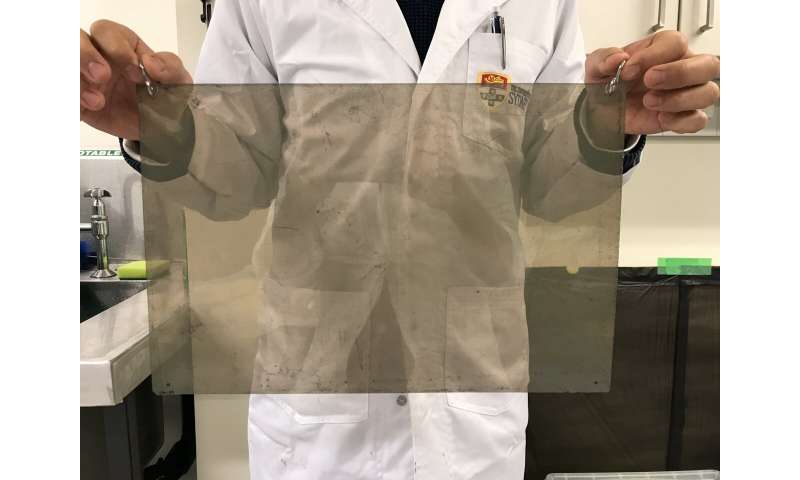

A bit of the emulsion movie after improvement. The traces of the particles produced by gamma ray impacts might be seen as tiny greyish dots all through the aircraft. Credit score: GRAINE collaboration
To cut back atmospheric interference, they then mounted the stack of movies onto a scientific statement balloon to raise it to a peak between 35 and 40 kilometers. Nevertheless, since a balloon is swaying and twisting within the wind, the route of the “telescope” shouldn’t be secure, in order that they added a set of cameras to file the gondola’s orientation relative to the celebrities at any time. However this created one other situation, as a result of as anyone who has ever taken {a photograph} with lengthy publicity is aware of, photographic film doesn’t file the passage of time and so it’s not straight doable to know at what time any given gamma ray affect occurred.
To beat this drawback, they made the underside three layers of movie transfer backwards and forwards at common however totally different speeds, similar to the palms of a clock. From the relative dislocation of the traces in these decrease plates they might then calculate the exact time of the affect and thus correlate it with the cameras’ footage.
They’ve now printed the primary picture ensuing from this setup within the journal The Astrophysical Journal. It’s the most correct picture ever produced of the Vela pulsar, a fast-spinning neutron star that tasks a beam of gamma rays into the sky like a lighthouse at evening.
“We captured a total of a number of trillion tracks with an accuracy of 1/10,000 millimeters. By including time info and mixing it with perspective monitoring info, we have been capable of decide ‘when’ and ‘the place’ the occasions originated with such precision that the ensuing decision was greater than 40 occasions increased than that of typical gamma-ray telescopes,” Aoki summarizes his group’s achievements.
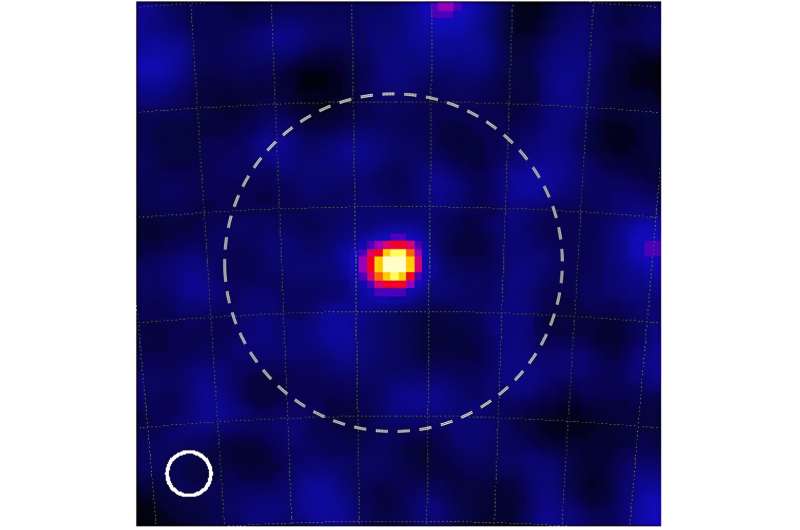
Whereas these outcomes are spectacular already, the brand new method opens the opportunity of capturing extra particulars on this frequency band of sunshine than ever earlier than.
The Kobe College researcher explains, “By the use of scientific balloon-borne experiments, we will try to contribute to many areas of astrophysics, and specifically to open up gamma-ray telescopy to ‘multi-messenger astronomy’ the place simultaneous measurements of the identical occasion captured by means of totally different methods are required. Primarily based on the success of the 2018 balloon experiment these knowledge have been generated with, we are going to broaden the statement space and time in upcoming balloon flights and are wanting ahead to scientific breakthroughs within the subject of gamma-ray astronomy.”
Extra info:
First emulsion γ-ray telescope imaging of the Vela pulsar by the GRAINE 2018 balloon-borne experiment, The Astrophysical Journal (2023). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad0973
Supplied by
Kobe University
Quotation:
Pancake stack of radioactivity-sensitive movies captures most correct image of star’s gamma ray beam (2023, December 21)
retrieved 21 December 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-12-pancake-stack-radioactivity-sensitive-captures-accurate.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




