Mathew Barlow, a professor of local weather science at UMass Lowell, wrote this text.
Final week, extraordinarily chilly Arctic air and extreme winter climate swept southward into a lot of the U.S., breaking each day low temperature records from Montana to Texas. Tens of thousands and thousands of individuals have been affected by dangerously cold temperatures. And heavy lake-effect snow and snow squalls have had extreme results throughout the Nice Lakes and Northeast areas.
These extreme chilly occasions happen when the polar jet stream – the acquainted jet stream of winter that runs alongside the boundary between Arctic and extra temperate air – dips deeply southward, bringing the chilly Arctic air to areas that don’t usually expertise it.
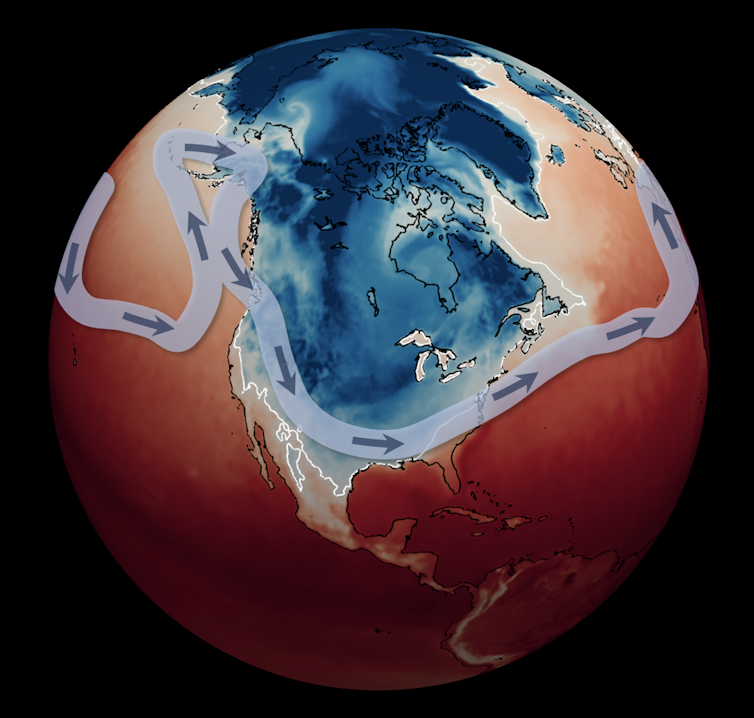
The stratospheric polar vortex
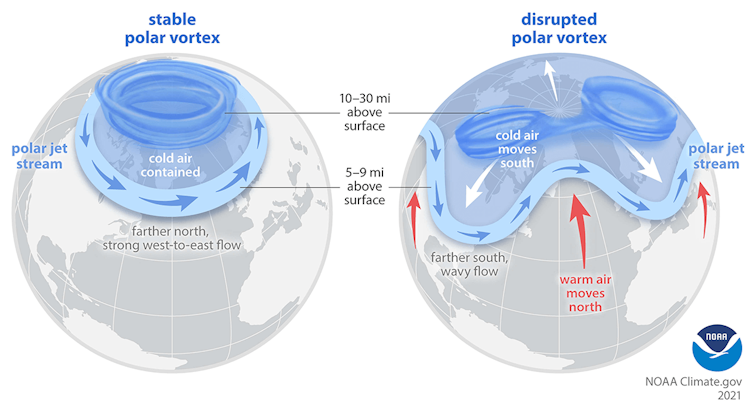
An fascinating facet of those occasions is that they usually happen in affiliation with modifications to a different river of air even larger above the jet stream: the stratospheric polar vortex, an excellent stream of air shifting across the North Pole in the course of the stratosphere.
When this stratospheric vortex turns into disrupted or stretched, it will probably distort the jet stream as properly, pushing it southward in some areas and inflicting chilly air outbreaks.
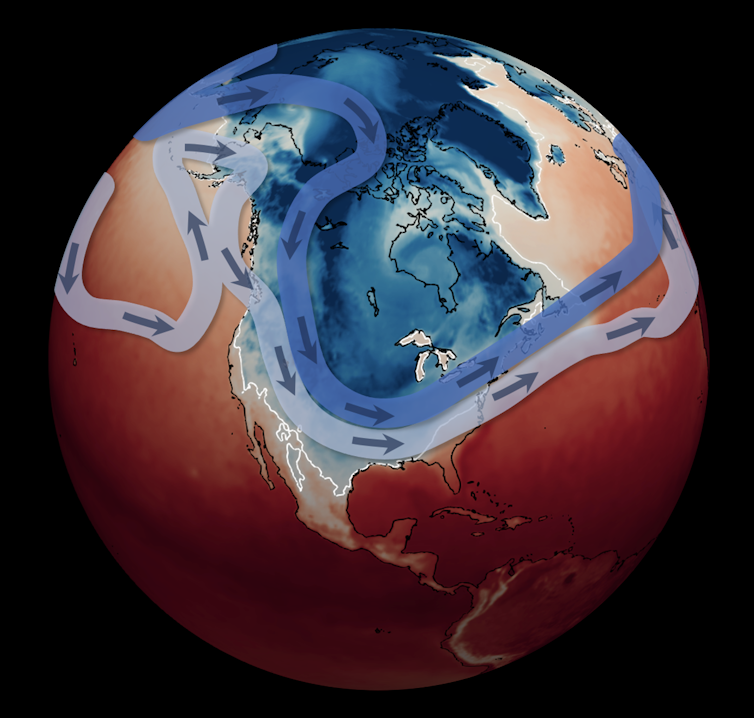
The January 2024 chilly snap
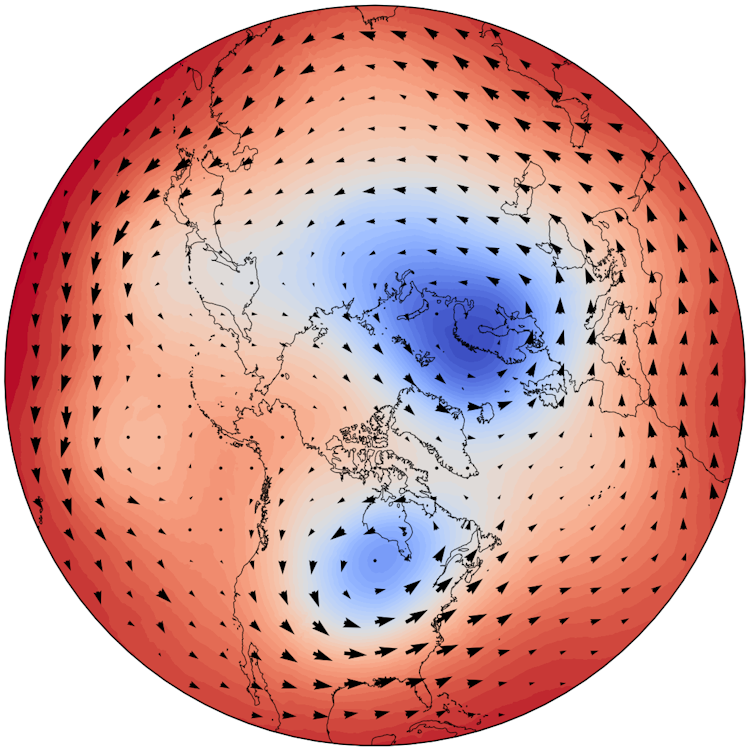
The present Arctic chilly blast suits into this sample, with the polar vortex stretched to this point over the U.S. within the decrease stratosphere that it has almost cut up in two. There are a number of causes that will have led to this stretching, however it’s possible associated to high-latitude weather within the prior two weeks.
No, chilly doesn’t contradict international warming
After Earth simply skilled its hottest year on record, it might appear shocking to set so many chilly data. However does this chilly snap contradict human-caused international warming? As an atmospheric and climate scientist, I can let you know, completely and unequivocally, it doesn’t.
No single climate occasion can show or disprove international warming. Many research have proven that the variety of excessive chilly occasions is clearly decreasing with international warming, as predicted and understood from bodily reasoning.
Whether or not international warming might, opposite to expectations, be enjoying some supporting function within the depth of those occasions is an open query. Some analysis suggests it does.
The function of the polar vortex in chilly waves
The February 2021 chilly wave that severely disrupted the Texas electric grid was additionally related to a stretched stratospheric polar vortex. My colleagues and I’ve supplied evidence suggesting that Arctic modifications related to international warming have elevated the probability of such vortex disruptions. The results of the improved excessive latitude warming referred to as Arctic amplification on regional snow cowl and sea ice might improve the climate patterns that, in flip, end in a stretched polar vortex.
Extra not too long ago, we’ve proven that for big areas of the U.S., Europe and Northeast Asia, whereas the variety of these extreme chilly occasions is clearly reducing – as anticipated with international warming – it does not appear that their depth is correspondingly reducing, regardless of the fast warming of their Arctic supply areas.
So, whereas the world can anticipate fewer of those extreme chilly occasions sooner or later, many areas want to stay ready for distinctive chilly when it does happen. A greater understanding of the pathways of affect between Arctic floor circumstances, the stratospheric polar vortex and mid-latitude winter climate would enhance our potential to anticipate these occasions and their severity.![]()
Mathew Barlow, Professor of Local weather Science, UMass Lowell
This text is republished from The Conversation beneath a Inventive Commons license. Learn the original article.
Backside line: Arctic modifications related to international warming have elevated the probability of disruptions within the polar vortex, which might trigger chilly snaps in southerly areas.




