by Kavli Institute for the Physics and Arithmetic of the Universe, The College of Tokyo
A group of researchers has analyzed greater than 1 million galaxies to discover the origin of the present-day cosmic constructions, as reported in a latest research published in Bodily Assessment D as an Editors’ Suggestion.
Till as we speak, exact observations and analyses of the cosmic microwave background (CMB) and large-scale construction (LSS) have led to the institution of the usual framework of the universe, the so-called ΛCDM mannequin, the place chilly dark matter (CDM) and darkish power (the cosmological constant, Λ) are important traits.
This mannequin means that primordial fluctuations have been generated on the beginning of the universe, or within the early universe, which acted as triggers, resulting in the creation of all issues within the universe together with stars, galaxies, galaxy clusters, and their spatial distribution all through space. Though they’re very small when generated, fluctuations develop with time because of the gravitational pulling drive, ultimately forming a dense area of dark matter, or a halo. Then, completely different halos repeatedly collided and merged with each other, resulting in the formation of celestial objects corresponding to galaxies.
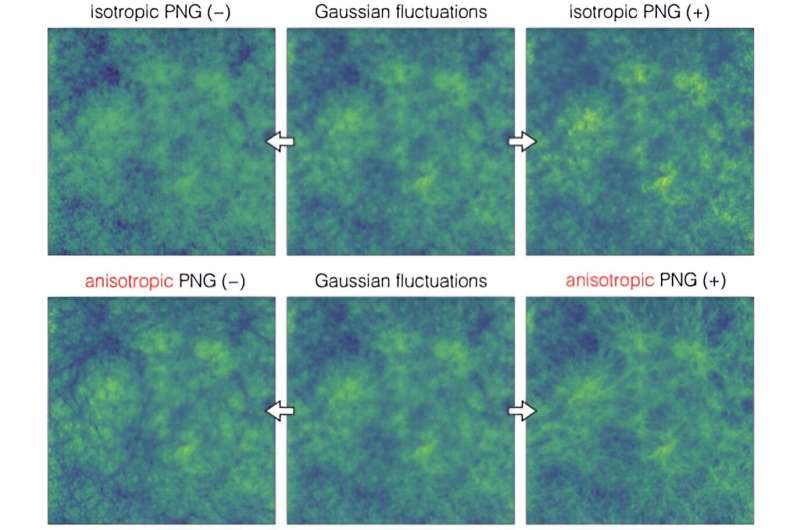
For the reason that nature of the spatial distribution of galaxies is strongly influenced by the character of the primordial fluctuations that created them to start with, statistical analyses of galaxy distributions have been actively performed to observationally discover the character of primordial fluctuations. Along with this, the spatial sample of galaxy shapes distributed over a large space of the universe additionally displays the character of the underlying primordial fluctuations (Determine 1).
Nevertheless, standard evaluation of large-scale construction has centered solely on the spatial distribution of galaxies as factors. Extra not too long ago, researchers have began finding out galaxy shapes, as a result of it not solely gives further info, however it additionally gives a unique perspective into the character of the primordial fluctuations (Determine 2).
A group of researchers, led by at-the-time Kavli Institute for the Physics and Arithmetic of the Universe (Kavli IPMU) graduate scholar Toshiki Kurita (presently a postdoctoral researcher on the Max Planck Institute for Astrophysics), and Kavli IPMU Professor Masahiro Takada developed a technique to measure the facility spectrum of galaxy shapes, which extracts key statistical info from galaxy form patterns by combining the spectroscopic information of spatial distribution of galaxies and imaging information of particular person galaxy shapes.
The researchers concurrently analyzed the spatial distribution and form sample of roughly 1 million galaxies from the Sloan Digital Sky Survey (SDSS), the world’s largest survey of galaxies as we speak.
Consequently, they efficiently constrained statistical properties of the primordial fluctuations that seeded the formation of the construction of the complete universe.
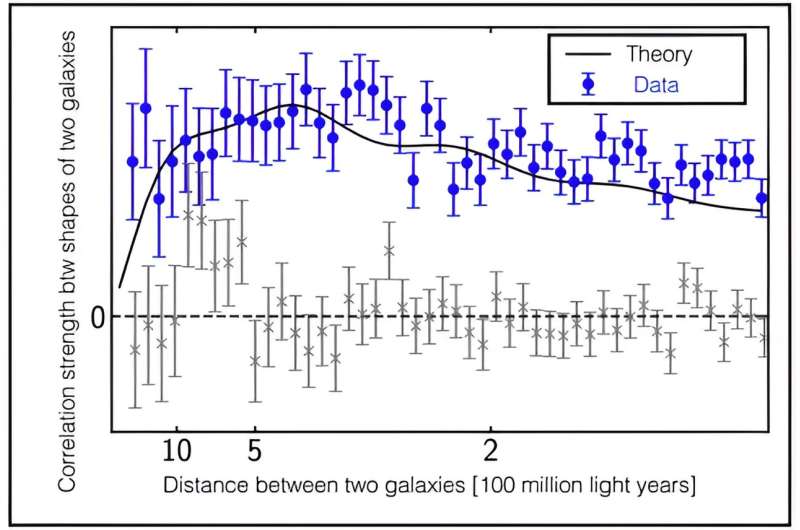
They discovered a statistically important alignment of the orientations of two galaxies’ shapes greater than 100 million mild years aside (Determine 3). Their outcome confirmed correlations exist between distant galaxies whose formation processes are apparently impartial and causally unrelated.
“On this analysis, we have been in a position to impose constraints on the properties of the primordial fluctuations via statistical evaluation of the ‘shapes’ of quite a few galaxies obtained from the large-scale construction information. There are few precedents for analysis that makes use of galaxy shapes to discover the physics of the early universe, and the analysis course of, from the development of the concept and improvement of study strategies to the precise information evaluation, was a sequence of trial and error.
“Due to that, I confronted many challenges. However I’m glad that I used to be in a position to accomplish them throughout my doctoral program. I consider that this achievement would be the first step to open up a brand new analysis area of cosmology utilizing galaxy shapes,” mentioned Kurita.
Moreover, an in depth investigation of those correlations confirmed they’re according to the correlations predicted by inflation, and don’t exhibit a non-Gaussian function of the primordial fluctuation.
“This analysis is the results of Toshiki’s doctoral dissertation. It is a great analysis achievement wherein we developed a technique to validate a cosmological mannequin utilizing galaxy shapes and galaxy distributions, utilized it to information, after which examined the physics of inflation. It was a analysis matter that nobody had ever accomplished earlier than, however he did all three steps: idea, measurement, and software. Congratulations! I’m very happy with the truth that we have been in a position to do all three steps. Sadly, I didn’t make the good discovery of detecting a brand new physics of inflation, however we’ve got set a path for future analysis. We are able to anticipate to open up additional areas of analysis utilizing the Subaru Prime Focus Spectrograph,” mentioned Takada.
The strategies and outcomes of this research will enable researchers sooner or later to additional take a look at inflation idea.
Extra info:
Toshiki Kurita et al, Constraints on anisotropic primordial non-Gaussianity from intrinsic alignments of SDSS-III BOSS galaxies, Bodily Assessment D (2023). DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevD.108.083533. On arXiv: DOI: 10.48550/arXiv.2302.02925
Offered by
Kavli Institute for the Physics and Arithmetic of the Universe, The College of Tokyo
Quotation:
Researchers research 1,000,000 galaxies to learn the way the universe started (2023, December 22)
retrieved 22 December 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-12-million-galaxies-universe-began.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for info functions solely.




