Astronomers have discovered an ever-growing variety of rocky exoplanets, together with some about the identical dimension and mass as Earth, orbiting distant stars. Scientists have thought that these worlds kind in comparatively benign areas round their stars, that’s, in locations the place ultraviolet radiation from their stars is comparatively delicate. Such radiation from stars can destroy the molecules which can be the constructing blocks for rocky planets. However on November 30, 2023, a world workforce of researchers presented an alternate view. Utilizing the James Webb Space Telescope, they discovered, for the primary time, that rocky planets can kind even in excessive radiation environments.
Webb detected all kinds of planet-building molecules in a radiation-soaked area of a planet-forming disk, or protoplanetary disk, within the Lobster nebula (NGC 6537). It is only one of many disks within the nebula, 5,500 light-years away. These disks of dust and gasoline round younger stars are the place new planets are born.
The researchers published their peer-reviewed leads to The Astrophysical Journal Letters on November 30, 2023.
The 2024 lunar calendars are here! Best Christmas gifts in the universe! Check ’em out here.
Constructing blocks of rocky exoplanets
Identical to residing organisms, planets are comprised of molecular constructing blocks. This may embody water, carbon and plenty of others. Loads of components play in to what a planet will probably be like, together with the atmosphere it kinds in round its star. Whether it is too near the star, ultraviolet gentle can break aside lots of these molecules.
Therefore, scientists have thought that one of the best place for rocky planets to kind is the place there may be much less radiation. As in, a extra benign area a bit farther out from their stars.
Webb makes stunning discovery
However now, Webb has made an surprising discovery. It has discovered constructing blocks of rocky planets in an excessive and hostile atmosphere in a protoplanetary disk about 5,500 light-years away within the Lobster nebula. Protoplanetary disks are huge flattened rotating disks of dust and gasoline round younger stars. It’s in these disks that planets – of all types – can kind. The younger stars within the Lobster nebula are huge, emitting way more ultraviolet radiation than smaller stars.
The Lobster nebula is a large star-forming complicated, and likewise one of many closest to us. Webb is the one telescope that presently can examine planet-forming disks in such complexes. Lead creator María Claudia Ramírez-Tannus, on the Max Planck Institute for Astronomy in Germany, stated:
Webb is the one telescope with the spatial decision and sensitivity to review planet-forming disks in huge star-forming areas.
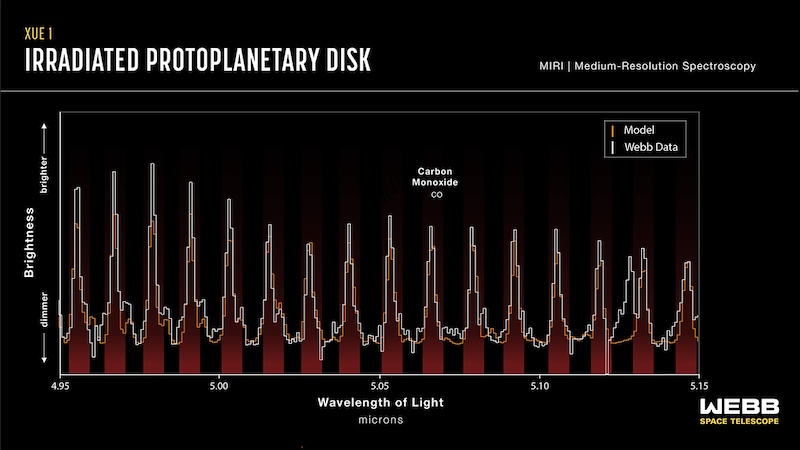
Webb focused 15 protoplanetary disks within the Lobster nebula. In considered one of them, referred to as XUE 1, Webb detected water, carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide, acetylene and partially crystalline silicate dust. All of these are constructing blocks for rocky planets.
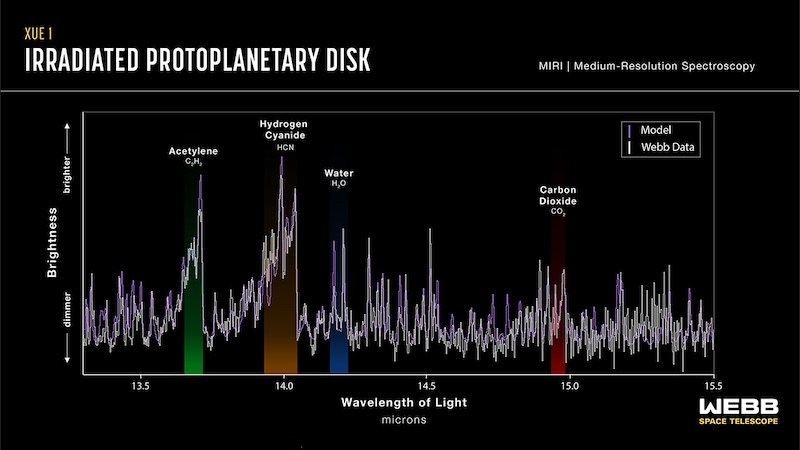
One of the crucial excessive environments in our galaxy
What’s thrilling is the molecules are within the inside area of the disk, which is very irradiated by its star. These areas are a number of the most excessive identified in our galaxy. The truth that Webb has confirmed the existence of the molecules reveals that rocky planets can, certainly, kind in such hostile environments.
The researchers say that XUE 1 has probably been uncovered to intense radiation ever because it first fashioned. And but the rocky planet-forming molecules are nonetheless there. Co-author Rens Waters at Radboud College within the Netherlands said:
We discover that the inside disk round XUE 1 is remarkably just like these in close by star-forming areas. We’ve detected water and different molecules like carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, hydrogen cyanide and acetylene. Nonetheless, the emission discovered was weaker than some fashions predicted. This may indicate a small outer disk radius.
Co-author Lars Cuijpers, additionally at Radboud College, added:
We had been shocked and excited as a result of that is the primary time that these molecules have been detected below these excessive circumstances.
Excellent news for rocky exoplanets
So, why is that this vital? Surprisingly, the outcomes present that the circumstances within the inside disk of XUE 1 are just like these in protoplanetary disks round lower-mass stars. Which means that the vary of environments the place rocky planets can kind is way bigger than beforehand thought. If rocky planets can kind round each low-mass and high-mass stars, in each benign and excessive environments, then there are most likely many extra on the market than astronomers had beforehand calculated.
The paper stated:
Our findings indicate that the inside areas of extremely irradiated disks can retain related bodily and chemical circumstances to disks in low-mass star-forming areas, thus broadening the vary of environments with related circumstances for inside disk rocky planet formation to essentially the most excessive star-forming areas in our galaxy.
And if such worlds are considerable, then probably extra of them might be liveable.
How widespread are rocky exoplanets?
However simply how widespread are rocky planets, total? As Ramírez-Tannus noted:
XUE 1 reveals us that the circumstances to kind rocky planets are there, so the following step is to test how widespread that’s. We’ll observe different disks in the identical area to find out the frequency with which these circumstances might be noticed.
Researchers might want to conduct further observations, nevertheless, to find out the speed of rocky planet formation in excessive environments. Because the paper said:
XUE 1 reveals that the circumstances for terrestrial planet formation can even occur in excessive environments. Nonetheless, the remaining observations from the XUE program are essential to determine the frequency with which this happens.
Additionally on the finish of November, researchers from the U.Okay., Germany and the U.S. said they found the primary identified protoplanetary disk in one other galaxy! This one is within the Large Magellanic Cloud, 160,000 light-years away.
Backside line: NASA’s James Webb Area Telescope has discovered molecular constructing blocks of rocky exoplanets in a area beforehand considered too excessive and hostile.
Source: XUE: Molecular Inventory in the Inner Region of an Extremely Irradiated Protoplanetary Disk
Read more: Weird rocky exoplanets unlike any seen before
Read more: 1st planet-forming disk found in another galaxy




