Japan’s Aerospace Exploration Company despatched the Hayabusa2 spacecraft to 162173 Ryugu in 2019, an asteroid in orbit close to Earth that’s comprised of rocky fragments originating from a bigger mum or dad physique. A number of rovers introduced samples from the asteroid’s floor again all the way down to Earth for scientists to review.
The samples are indicative of chemically primitive meteorites, much like Ivuna-type chondrites, and include specific chemical compounds that counsel the presence of water. Particularly, alterations of the asteroid’s floor by water on the mum or dad physique, at estimated temperatures as much as 150°C, produced secondary minerals (together with phyllosilicates, carbonates, sulfides and oxides) and the researchers aimed to know the timescale and situations over which these adjustments occurred.
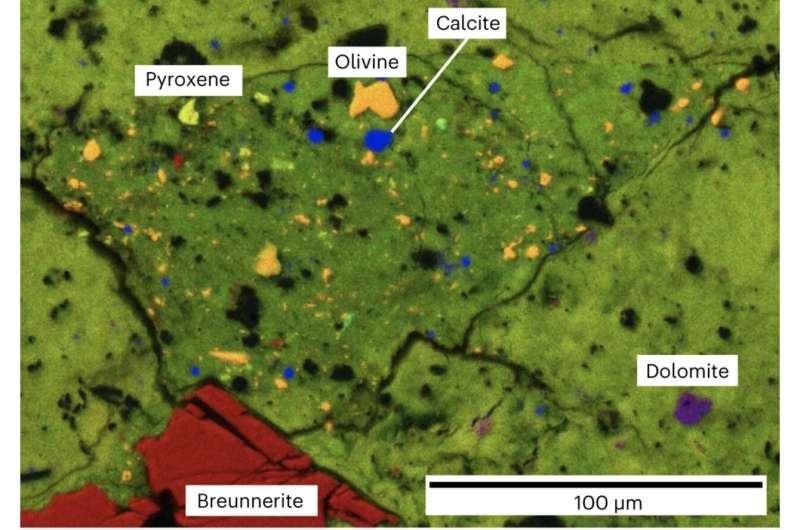
Charting the asteroid’s formation, collaborative research by 89 scientists from world universities and analysis institutes, printed in Nature Geoscience, focuses on two specific compounds: calcium carbonate (calcite) and calcium–magnesium carbonate (dolomite). The carbon source for these carbonates is postulated to be carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide, methane and/or organic matter that will have shaped within the solar nebula, the gaseous cloud from which the solar system is claimed to have originated.
The samples had been inspected utilizing specialist microscopes for petrology (the examine of rocks), whereby crystals of each calcite (<10 micrometres in dimension) and dolomite (10s of micrometres) had been recognized, with the latter dominating by comparability.
Measurements of carbon and oxygen isotopes (two or extra types of the identical ingredient with totally different atomic lots) assist to disclose the temperature and oxygen situations of the setting when the mineral was deposited. These values had been variable and far larger than these for calcite on Earth, with 18O/16O ratios being 24-46‰ (elements per thousand) larger and 13C/12C 65-108‰ larger.
Conversely, dolomite measurements had been way more restricted being 31-36‰ for 18O/16O and 67-75‰ for 13C/12C. Consequently, the analysis staff conclude that calcite shaped on the asteroid first over a variety of temperatures and oxygen situations, earlier than dolomite crystallized in a way more restricted setting, with secure excessive carbon dioxide ranges and temperature estimates of 37 ± 10°C. These findings are distinctive to the Ryugu and Ivunu asteroids, not being recognized in different hydrous meteorites so far.
The bigger variation in oxygen isotope ratios in calcite crystals is recommended to partially end result from formation temperatures ranging broadly from 0-150°C, however not solely this as in any other case the carbon isotopes could be anticipated to point out a optimistic correlation, which they don’t. As an alternative, the researchers point out that the 18O/16O of water and 13C/12C of carbonate ions diverse by time and space.
Because of this, they hypothesize that 18O/16O ratios had been larger throughout early solar system formation, previous to aqueous alteration of the asteroid, and this has subsequently decreased by time as extra of the crystals had been shaped by way of water-rock interactions. The isotopic distinction between calcite and dolomite crystals is subsequently resolved by the previous crystallizing from much less ‘developed’ fluids previous to the latter, the place calcium was additionally extra simply leached from the rock than magnesium.
4 eventualities are thought of to clarify the variability in 13C/12C: 1) Rayleigh-type isotopic fractionation whereby 12C-rich compounds are preferentially launched (corresponding to methane), 2) fractional crystallization the place the formation of early carbonates adjustments the composition of the remaining reservoir from which subsequent carbonates can crystallize, 3) mixing of a number of carbon reservoirs with totally different 13C/12C ratios, and 4) various oxygen and hydrogen brought about adjustments within the isotopes forming carbon monoxide, carbon dioxide and methane, from which carbon is obtained for the crystals.
Of those eventualities, Rayleigh-type isotopic fractionation is discounted as it will trigger larger 13C/12C ratios in dolomite forming from ‘extra developed’ fluids, when the alternative is noticed within the samples. Equally, fractional crystallization is dominated out, as is mixing of carbon reservoirs, as the blending instances for the Ryugu asteroid could be too quick.
Due to this fact, it’s the latter situation of various oxygen that’s prompt as the principle driver of adjustments in 13C/12C ratios. This resulted from the oxidation of iron within the rock by water and is measured primarily based upon the manufacturing of hydrogen launched from the water. The speculation matches observations of accelerating iron within the meteorite with progressive alteration.
Total, the 13C-rich setting is famous to be uncommon within the solar system past carbonates in meteorites and the analysis staff counsel the mum or dad physique of the Ryugu meteorite shaped inside a chilly fringe of the solar nebula.
Extra data:
Wataru Fujiya et al, Carbonate file of temporal change in oxygen fugacity and gaseous species in asteroid Ryugu, Nature Geoscience (2023). DOI: 10.1038/s41561-023-01226-y
© 2023 Science X Community
Quotation:
Ryugu asteroid origins within the solar nebula decoded by carbonates (2023, August 15)
retrieved 15 August 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-08-ryugu-asteroid-solar-nebula-decoded.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




