A lifeless zone within the ocean is as dangerous because it sounds, and having no details about lifeless zones’ scope and path is worse. Nevertheless, scientists at Michigan State College (MSU) have found a birds-eye technique to foretell the place, when, and the way lengthy lifeless zones may persist throughout giant coastal areas.
“Understanding the place these lifeless zones are and the way they might change over time is the primary essential step to mitigating these crucial issues. However it’s not simple through the use of conventional strategies, particularly for large-scale monitoring efforts,” stated Yingjie Li, who did the work as a Ph.D. pupil at MSU’s Heart for System Integration and Sustainability (CSIS). He’s presently a postdoctoral researcher at Stanford College.
Useless zones—technically often called hypoxic—are water bodies degraded to the purpose the place aquatic life can’t survive due to low oxygen ranges. They’re an issue primarily in coastal areas the place fertilizer runoff feeds algae blooms, which then die, sink to the water’s backside and decay. That decay eats up oxygen dissolved within the water, suffocating residing life akin to fish and different organisms that make up vibrant residing waters.
Useless zones might be onerous to establish and monitor, and often have been noticed by water samples. However as reported in Distant Sensing of the Surroundings, scientists have found out a novel manner to make use of satellite views to grasp what’s taking place deep under the ocean’s floor. They used the Gulf of Mexico on the mouth of the Mississippi River as an illustration website.
The group supplemented information from water sampling with other ways to make use of satellite views over time. Along with predicting the dimensions of hypoxic zones, the examine gives further data on the place, when, and the way lengthy hypoxic zones stick with better element, and allows modeling hypoxic zones at near-real-time.
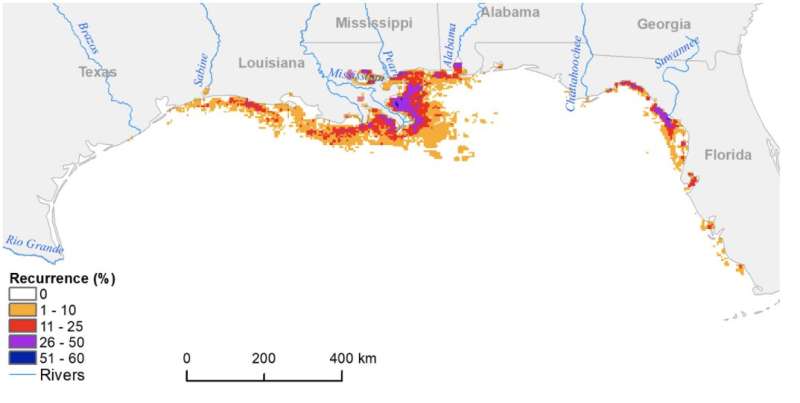
Since 1995, at the very least 500 coastal lifeless zones have been reported close to coasts masking a mixed space bigger than the UK, endangering fisheries, recreation and the general well being of the seas. Local weather change is prone to exacerbate hypoxia.
The analysis group notes the necessity to provoke a world coast observatory community to synthesize and share information for higher understanding, predicting and speaking the altering coasts. At the moment, such information is issue to come back by. And the stakes are larger, as fertilizer utilized in a area can change into runoff in a single a part of a physique of water miles away. The group factors out that the telecoupling framework, which allows understanding of human and pure interactions close to and much, can be helpful to see the large image of an issue.
“Damages to our coastal waters are a telecoupling drawback that spans far past the dead zones—distant locations that apply extreme fertilizers for meals manufacturing and much more distant locations that demand meals. Thus, it’s important we take a holistic view whereas using new strategies to achieve a real understanding,” stated Jianguo “Jack” Liu, MSU Rachel Carson Chair in Sustainability and CSIS director.
Apart from, Li and Liu, “Satellite tv for pc prediction of coastal hypoxia within the northern Gulf of Mexico” was written by Drs. Samuel Robinson and Lan Nguyen from the College of Calgary.
Extra data:
Yingjie Li et al, Satellite tv for pc prediction of coastal hypoxia within the northern Gulf of Mexico, Distant Sensing of Surroundings (2022). DOI: 10.1016/j.rse.2022.113346
Supplied by
Michigan State University
Quotation:
Satellites solid crucial eye on coastal lifeless zones (2022, November 21)
retrieved 21 November 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-11-satellites-critical-eye-coastal-dead.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




