About 4.5 billion years in the past, a small planet smashed into the younger Earth, flinging molten rock into space. Slowly, the particles coalesced, cooled and solidified, forming our moon. This situation of how the Earth’s moon got here to be is the one largely agreed upon by most scientists. However the particulars of how precisely that occurred are “extra of a choose-your-own-adventure novel,” based on researchers within the College of Arizona Lunar and Planetary Laboratory who revealed a paper in Nature Geoscience.
The findings provide necessary insights into the evolution of the lunar inside, and doubtlessly for planets such because the Earth or Mars.
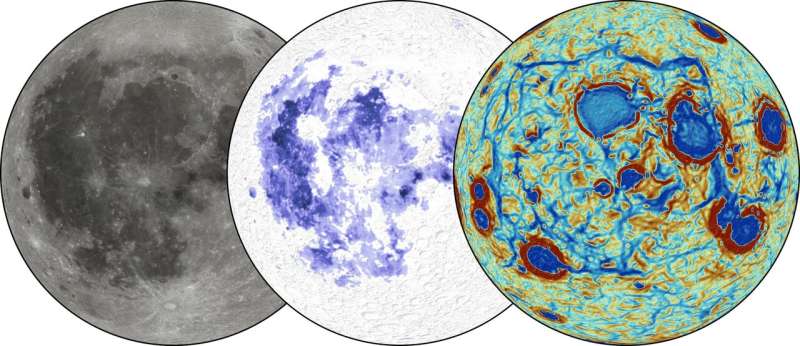
Most of what’s recognized concerning the origin of the moon comes from analyses of rock samples, collected by Apollo astronauts greater than 50 years in the past, mixed with theoretical models. The samples of basaltic lava rocks introduced again from the moon confirmed surprisingly excessive concentrations of titanium. Later satellite observations discovered that these titanium-rich volcanic rocks are primarily positioned on the moon’s nearside, however how and why they bought there has remained a thriller—till now.
As a result of the moon shaped quick and sizzling, it was possible coated by a worldwide magma ocean. Because the molten rock progressively cooled and solidified, it shaped the moon’s mantle and the brilliant crust we see once we lookup at a full moon at night time. However deeper beneath the floor, the younger moon was wildly out of equilibrium. Fashions recommend that the final dregs of the magma ocean crystallized into dense minerals together with ilmenite, a mineral containing titanium and iron.
“As a result of these heavy minerals are denser than the mantle beneath, it creates a gravitational instability, and you’d anticipate this layer to sink deeper into the moon’s inside,” stated Weigang Liang, who led the analysis as a part of his doctoral work at LPL.
Someway, within the millennia that adopted, that dense materials did sink into the inside, blended with the mantle, melted and returned to the floor as titanium-rich lava flows that we see on the floor as we speak.
“Our moon actually turned itself inside out,” stated co-author and LPL affiliate professor Jeff Andrews-Hanna. “However there was little bodily proof to make clear the precise sequence of occasions throughout this crucial phase of lunar historical past, and there’s a lot of disagreement within the particulars of what went down—actually.”
Did this materials sink because it shaped somewhat at a time, or abruptly after the moon had totally solidified? Did it sink into the inside globally after which stand up on the close to facet, or did it migrate to the close to facet after which sink? Did it sink in a single massive blob, or a number of smaller blobs?
“With out proof, you possibly can decide your favourite mannequin. Every mannequin holds profound implications for the geologic evolution of our moon,” stated co-lead creator Adrien Broquet of the German Aerospace Middle in Berlin, who did the work throughout his time as a postdoctoral analysis affiliate at LPL.
In a earlier study, led by Nan Zhang at Peking College in Beijing, who can be a co-author on the newest paper, fashions predicted that the dense layer of titanium-rich materials beneath the crust first migrated to the close to facet of the moon, presumably triggered by an enormous impression on the far facet, after which sunk into the inside in a community of sheetlike slabs, cascading into the lunar inside nearly like waterfalls. However when that materials sank, it left behind a small remnant in a geometrical sample of intersecting linear our bodies of dense titanium-rich materials beneath the crust.
“Once we noticed these mannequin predictions, it was like a lightbulb went on,” stated Andrews-Hanna, “as a result of we see the very same sample once we have a look at refined variations within the moon’s gravity field, revealing a community of dense materials lurking beneath the crust.”
Within the new examine, the authors in contrast simulations of a sinking ilmenite-rich layer to a set of linear gravity anomalies detected by NASA’s GRAIL mission, whose two spacecraft orbited the moon between 2011 and 2012, measuring tiny variations in its gravitational pull. These linear anomalies encompass an enormous darkish area of the lunar close to facet coated by volcanic flows often called mare (Latin for “sea”).
The authors discovered that the gravity signatures measured by the GRAIL mission are according to ilmenite layer simulations, and that the gravity subject can be utilized to map out the distribution of the ilmenite remnants left after the sinking of nearly all of the dense layer.
“Our analyses present that the fashions and knowledge are telling one remarkably constant story,” Liang stated. “Ilmenite supplies migrated to the close to facet and sunk into the inside in sheetlike cascades, abandoning a vestige that causes anomalies within the moon’s gravity subject, as seen by GRAIL.”
The staff’s observations additionally constrain the timing of this occasion: The linear gravity anomalies are interrupted by the most important and oldest impression basins on the close to facet and due to this fact should have shaped earlier. Primarily based on these cross-cutting relationships, the authors recommend that the ilmenite-rich layer sank previous to 4.22 billion years in the past, which is according to it contributing to later volcanism seen on the lunar floor.
“Analyzing these variations within the moon’s gravity subject allowed us to peek beneath the moon’s floor and see what lies beneath,” stated Broquet, who labored with Liang to point out that the anomalies within the moon’s gravitational subject match what can be anticipated for the zones of dense titanium-rich materials predicted by laptop simulation fashions of lunar overturn.

Lopsided moon
Whereas the detection of lunar gravity anomalies offers proof for the sinking of a dense layer within the moon’s inside and permits for a extra exact estimate of how and when this occasion occurred, what we see on the floor of the moon provides much more intrigue to the story, based on the analysis staff.
“The moon is essentially lopsided in each respect,” Andrews-Hanna stated, explaining that the close to facet dealing with the Earth, and significantly the darkish area often called Oceanus Procellarum area, is decrease in elevation, has a thinner crust, is essentially coated in lava flows, and has excessive concentrations of sometimes uncommon components like titanium and thorium.
The far facet differs in every of those respects. Someway, the overturn of the lunar mantle is considered associated to the distinctive construction and historical past of the close to facet Procellarum area. However the particulars of that overturn have been a matter of appreciable debate amongst scientists.
“Our work connects the dots between the geophysical proof for the inside construction of the moon and laptop fashions of its evolution,” Liang added.
“For the primary time now we have bodily proof exhibiting us what was taking place within the moon’s inside throughout this crucial stage in its evolution, and that is actually thrilling,” Andrews-Hanna stated. “It seems that the moon’s earliest historical past is written beneath the floor, and it simply took the best mixture of fashions and knowledge to unveil that story.”
“The vestiges of early lunar evolution are current beneath the crust as we speak, which is mesmerizing,” Broquet stated. “Future missions, comparable to with a seismic community, would permit a greater investigation of the geometry of those buildings.”
Liang added, “When the Artemis astronauts finally land on the moon to start a brand new period of human exploration, we may have a really totally different understanding of our neighbor than we did when the Apollo astronauts first set foot on it.”
Extra data:
Adrien Broquet, Vestiges of a lunar ilmenite layer following mantle overturn revealed by gravity knowledge, Nature Geoscience (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41561-024-01408-2. www.nature.com/articles/s41561-024-01408-2
Supplied by
University of Arizona
Quotation:
Scientists clear up a long-standing thriller surrounding the moon’s ‘lopsided’ geology (2024, April 8)
retrieved 8 April 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-04-scientists-mystery-moon-lopsided-geology.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for data functions solely.




