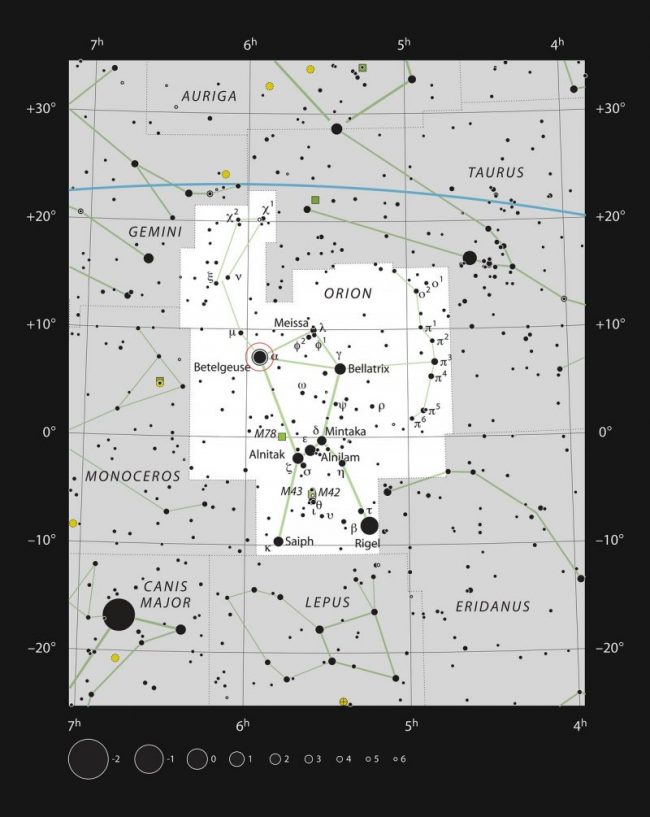
Search for Mintaka in Orion’s Belt
See the three stars at Orion the Hunter’s midsection? These stars are Alnitak, Alnilam and Mintaka. In truth, they’re very noticeable and well-known in lots of cultures as Orion’s Belt. To the Aymara people of Bolivia, Peru and Chile, they signify a celestial bridge. And there’s good cause for that. These stars hyperlink the sky’s northern and southern hemispheres.
Think about Mintaka, which is the Belt’s westernmost star. It sits nearly instantly astride the celestial equator: the projection of Earth’s equator onto the stellar sphere.
So the place can you discover Mintaka and the constellation Orion? In late November, from world wide, Orion rises in your jap sky round 9 p.m. and climbs highest for the night time round 1 to 2 a.m. native time.
When daybreak is breaking, or about to interrupt, say round 5 to six a.m., the Hunter sits low in your western sky.
The 2024 lunar calendars are here! Best Christmas gifts in the universe! Check ’em out here.
Mintaka shines on the celestial equator
Mintaka’s location on the celestial equator makes it a superb guidepost for locating instructions right here on Earth. That’s, Mintaka and the opposite stars of the Celestial Bridge are seen worldwide. From everywhere in the world, Mintaka rises due east, units due west, and stays within the sky for 12 hours. It climbs to its highest level within the sky halfway between rising and setting.
When it’s highest within the sky, if this star shines at your zenith (your straight-overhead level), you then should be at the equator.
If this star shines within the southern half of your sky, you then should be north of the equator.
If this star shines within the northern half of your sky, you then should be south of the equator.
The story of the Celestial Bridge is one in all many in regards to the constellation Orion. That’s as a result of it’s so noticeable on our sky’s dome. So look ahead to it while you’re exterior one night quickly!
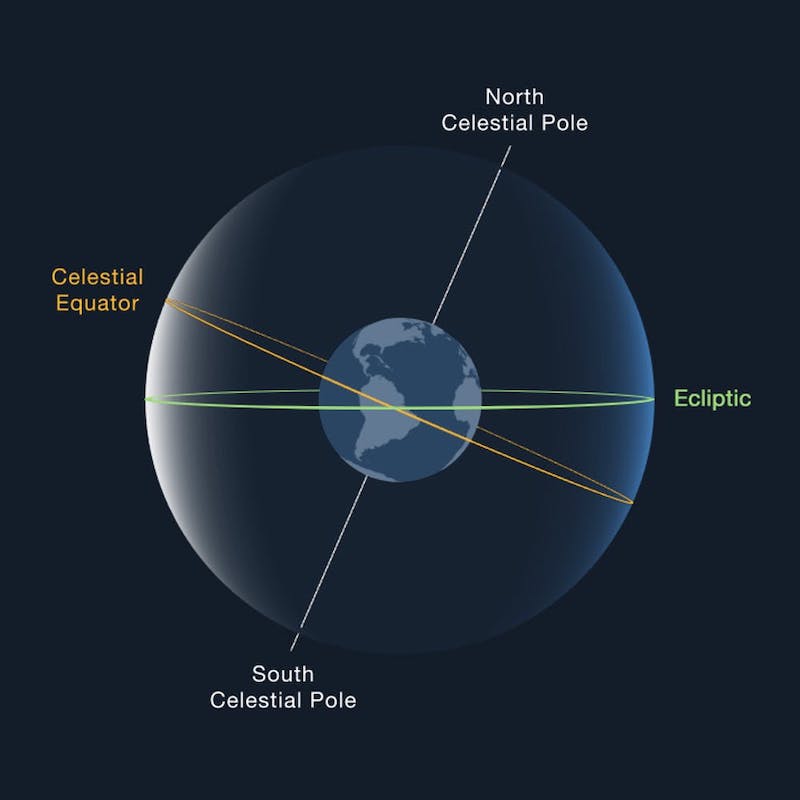
Backside line: The indigenous Aymara folks of the Andes and Altiplano areas of South America see the well-known sky function we all know as Orion’s Belt as a celestial bridge between the sky’s Northern and Southern Hemispheres. In truth, its westernmost star, Mintaka, lies instantly on the celestial equator.




