There are 8 billion of us now. The UN says when the inhabitants peaks across the yr 2100, there will be 11 billion human souls. Our inhabitants progress is colliding with the pure world on a larger scale than ever, and we’re dropping between 200 and a pair of,000 species annually, in keeping with the World Wildlife Federation.
An Engineer from the UK says that one method to mitigate the injury from the conflict between humanity and nature is to create extra habitat. We might do this by constructing Terran ecosystem preserves on Mars.
Paul L. Smith is a Civil Engineer within the School of Engineering on the College of Bristol, UK. In an article within the Worldwide Journal of Astrobiology, he explains how we might construct a nature protect on Mars that might act as an extraterrestrial nature reserve (ETNR.) The ETNR would act as each a “psychological refuge and botanical backyard,” in keeping with Smith.
On the face of it, the concept might sound absurd or preposterous. However Smith is an engineer and has thought this out. He is not saying that an ETNR on Mars is imminent. He takes the lengthy view: that people will proceed to place stress on Earth and that we’ll colonize Mars. He says that ETNRs ought to be a part of any colonization effort. Smith is not the primary to consider this concept. He leans on a number of earlier analysis by others.
Earlier than you’ll be able to consider how clever this may be, you need to consider how attainable it may be. Who higher than an engineer to dig into that query?
Martian day size is just like Earth’s, in order that foundational piece is sufficient to get began. Mars is way colder, however programs to maintain an enclosed spherical protect exist already, so the temperature may be managed with out an excessive amount of complexity. The Martian floor is dry, however ample frozen water exists underground, so the issue of a water provide is not insurmountable.
Mars’ and Earth’s atmospheric makeups are wildly completely different, however that is one of many simpler issues to deal with. An enclosed atmosphere may be engineered to have no matter ambiance is fascinating. Vegetation itself can regulate the atmosphere to a point. The temperature and stress are two of the better components to manage.
These are the fundamentals, however far more confounding points come up when a extra detailed evaluation is completed. And Smith’s evaluation is detailed.
The Martian radiation atmosphere is the place issues can start to get difficult. With out an ozone layer like Earth’s, the Martian floor is uncovered to harmful ranges of ionizing UV radiation. “Mars’ harsh floor UV flux is sterilizing because of skinny ambiance and lack of great ozone,” Smith writes. Some UV radiation is fascinating and is a part of some creatures’ metabolisms. People want some UV to stimulate the manufacturing of vitamin D. However Earth life varieties should not tailored to elevated UV and would want sufficient safety.
“Fortuitously, glass/plastic combos can exclude dangerous wavelengths while transmitting helpful UV and visual gentle,” Smith explains, “so flux in CTTEs (Containted Terran-Kind Ecosystem) may be managed.”
Magnetic fields are a extra open query. We all know that the magnetic discipline protects Earth from cosmic rays and that it prevents the solar wind from stripping the ozone layer away. However we do not have a full understanding of the ways in which Earth’s magnetic fields play a task in life. Some creatures use magnetoreception emigrate and transfer round. Some name magnetoreception the “biggest thriller in animal biology,” and that puzzle must be understood higher. Might we engineer a man-made magnetic field in a CTTE?
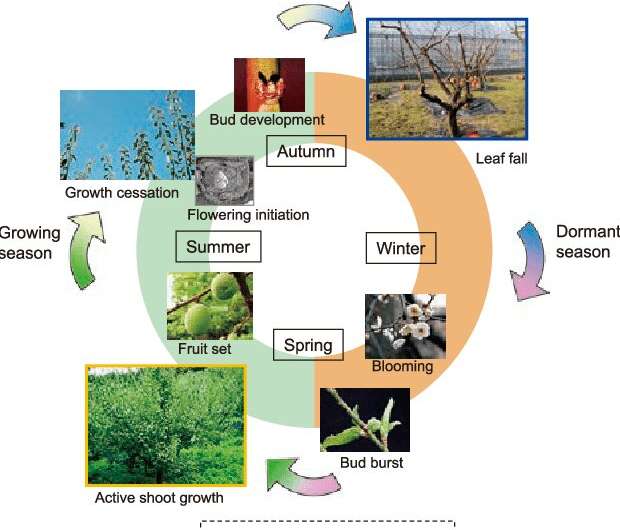
Earth life modifications because the seasons change, too. The make-up of the biome modifications, and that must be managed. Mars’ seasonal variability is way completely different than Earth’s, so seasons must be engineered. “Temporality determines important developmental levels, particular person physiologies and interspecific relationships, whereas timing of abiotic occasions influences world nutrient fluxes,” Smith explains.
“Photoperiod and winter chilling are concerned in temperate vegetation’ phenology.” Phenology contains issues like bud set, bud break, and flowering in vegetation. It additionally contains extra complicated animal conduct like migration, breeding, and egg laying. These behaviors are intimately synchronized in nature, amongst people and amongst completely different species. Replicating that will probably be an enormous problem.
People clearly do not breed seasonally, however we’re not remoted from the seasons, particularly in temperate areas. “Seasons additionally imbue traits important to psychological restoration, e.g., autumn shade, winter silence, spring flowers and summer season leafiness,” Smith writes, and he isn’t flawed.
One other distinction between Mars and Earth that may be missed are lunar cycles. Earth’s moon is very large and has a strong affect. Tiny Phobos and Deimos, Mars’s pair of potato-shaped moons, have virtually no impact on Mars. Even when Mars had been vigorous and had oceans, these two small rocks could not generate tides. In actual fact, there could also be areas on Mars’ floor the place the moons are by no means even seen.
Smith describes Earth’s moon as a zeitgeber, “a rhythmically occurring pure phenomenon which acts as a cue within the regulation of the physique’s circadian rhythms,” in keeping with the dictionary definition. Martian day size is just like Earth’s, so diurnal rhythms is probably not a difficult difficulty.
Mars receives solely 43% of the daylight that Earth does. Analysis exhibits that it is sufficient for photosynthesis, however plant progress charges on Mars will not match Earth’s with out synthetic augmentation. That is one other impediment that may be overcome by engineering and know-how, but it surely makes an ETNR extra complicated.
Smith talks about inserting nature preserves in subterranean lava tubes, which would offer UV safety and different advantages. In these cases, synthetic gentle augmentation could be required.
An ETNR would want soil. Mars has a basaltic crust that incorporates many vitamins obligatory for Terran vegetation. “Basalt-derived soils with volcanic ash are good agricultural soils,” Smith writes whereas referencing different analysis. “Crushed basalt can enhance soil pH, whereas its dissolution releases helpful vitamins, together with phosphorus.” Phosphorus is likely one of the three major vitamins vegetation must develop: nitrogen, phosphorus, and potassium.
There’s most likely ample nitrogen in Martian soil for vegetation to develop, however vegetation additionally want 16 different micronutrients. “These are all reported from Mars or Mars meteorites,” Smith writes. However different chemical substances are concerned in soil fertility that are not instantly consumed by vegetation. It is a difficult puzzle.
Earth soil not solely incorporates all of the vitamins vegetation want. It is also filled with microbes and creatures like Earthworms. These creatures are a part of the dwelling system in Earth’s soil. Will the whole system should be recreated? In that case, that is a rare stage of sophistication. Analysis exhibits that a few of this may be replicated within the Martian regolith, however that analysis was performed on replicated Martian grime. How assured can we be that we will construct a whole soil system on Mars?
Martian regolith additionally incorporates larger ranges of poisons than Earth soil. There are greater ranges of perchlorates on Mars, making the regolith poisonous to life varieties. There are additionally much more iron oxides in Martian regolith, and when mixed with elevated ranges of perchlorates and hydrogen peroxide, it is a extremely poisonous combine. Can remediation take care of that? Presumably. In actual fact, constructing soil from scratch is a important constructing block for an ETNR and could be one of the vital complicated duties.
Then there are Martian dust storms. A few of Mars’ regolith is so positive it is despatched aloft in storms which might be typically bigger than the continental US. It collects on surfaces and is an issue for solar panels on Martian landers. It additionally lowers the quantity of solar power reaching the floor, placing additional pressure on photosynthesis.
Mars’ decrease gravity needs to be accounted for, too. Martian gravity is barely 38% of Earth’s, and gravity is likely one of the components that modulate plant progress. Might a towering evergreen tree develop in Mars’ decreased gravity?
“Experiments point out 0.3 g (
“From such proof, it’s conceivable that some vegetation will tolerate Mars’ gravity,” Smith writes. “Nevertheless, forest perform can also be influenced.”
Gravity impacts extra than simply plant progress. It governs a mess of different issues that must be accounted for. “Leaf and propagule fall, leaping, flight, deadwood collapse, raindrop affect and drainage of water contribute dynamism,” Smith explains. However decrease gravity might present some advantages, too. Mars’ decrease gentle might contribute to “leggy” progress in vegetation, weaker stems, and fewer vigorous progress general. Decrease gravity may steadiness a few of these damaging results.
Smith factors out that attempting to recreate a particular Earth forest biome is counterproductive. They’re far too complicated to duplicate. “Earth’s forests owe their assemblages to environmental and evolutionary pressures that may differ from these in Martian CTTEs. No single forest meals internet has been absolutely mapped, canopies themselves probably comprise over 100 000 trophic hyperlinks, difficult duplication.” As an alternative, a terrestrial ecosystem could be a brand new internet of life that might take time to determine itself in Mars’ atmosphere. The purpose could be to introduce species and see which of them tailored, permitting time for a brand new hybrid ecosystem to develop.
“ETNR designers ought to take into account species as ecological cogs that may be assembled into practical ecosystems. Replication of Earth forests is at present unfeasible, however improvement of latest ecosystems, functioning in sudden methods, is conceivable. Mars’ forests wouldn’t resemble or perform precisely like Earth’s forests however might nonetheless ship marvel; autumn at 0.38 g providing dreamlike leaf fall,” he writes.
There’s much more element in Smith’s article. This can be a large subject, and we’re solely starting to grapple with all the problems. For instance, if ETNRs are supposed to present respite for people on Mars, we want a few of the proper species. “Woodland with out birdsong or butterflies is a poor TTE. Such lack could exacerbate homesickness,” he explains. What a haunting feeling to wander by way of a silent forest. Alternatively, we might all do with out mosquitoes.
What about moral constraints? Not all of our efforts will probably be profitable. Do we’ve got the appropriate to move different lifeforms to an ETNR, solely to look at them endure and die if they cannot stand up to situations? Or would the whole effort be a part of sustaining all Earth life within the occasion of a calamity, so their struggling could be alongside ours?
These are complicated questions with out easy solutions.
Our understanding of how life all works collectively is much from full. We’re nonetheless mystified when teams of whales seashore themselves or when there is a huge fowl die-off. We won’t anticipate to “freeze” situations in an ETNR in order that there are by no means die-offs. These can result in new niches exploitable by different lifeforms. That is nature, and if we will attempt to recreate it, we’ve got to simply accept it.
Smith emphasizes one other level that typically will get misplaced in these kinds of discussions. Homo sapiens clearly did not evolve in a vacuum. We advanced alongside different lifeforms, and we will not survive with out them. At a really primary stage, our guts are colonized by micro organism—an vital a part of the human microbiome—and with out them, we’re screwed. On this primary organic stage, we want different lifeforms to outlive, and so they, in flip, depend on different lifeforms. The net of life is awfully complicated.
It is an awesome query: Do we’ve got the information to rebuild a contained Earthly ecosystem on Mars? However asking that query results in one other foreboding query:
Are we forcing ourselves right into a place the place we’ve got to reply the primary one earlier than we’re prepared?
Even when we by no means get to Mars or construct an ETNR, the thought train drives residence this level: Nature is the overarching construction that governs our lives, and we want it greater than it wants us. And we’ve got a duty to maintain nature alive.
“From a biocentric perspective, world leaders ought to be involved about the way forward for life within the Universe and humanity’s position in its safety and promulgation,” Smith writes. “On a planet of restricted habitability, this can be a important obligation. The survival of life, in any type, is the final word biocentric precedence.”
Extra info:
Paul L. Smith, Extraterrestrial nature reserves (ETNRs), Worldwide Journal of Astrobiology (2022). DOI: 10.1017/S1473550422000398
Supplied by
Universe Today
Quotation:
Ought to we construct a nature reserve on Mars? (2022, December 1)
retrieved 1 December 2022
from https://phys.org/information/2022-12-nature-reserve-mars.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




