A brand new investigation into an obscure class of galaxies generally known as Compact Symmetric Objects, or CSOs, has revealed that these objects are usually not solely what they appear. CSOs are lively galaxies that host supermassive black holes at their cores. Out of those monstrous black holes spring two jets touring in reverse instructions at practically the velocity of sunshine. However compared to different galaxies that boast fierce jets, these jets don’t lengthen out to nice distances—they’re much extra compact.
For a lot of many years, astronomers suspected that CSOs had been merely younger and that their jets would finally journey out to higher distances. Now, reporting in three totally different papers in The Astrophysical Journal, a Caltech-led crew of researchers has concluded that CSOs are usually not younger however reasonably lead comparatively brief lives.
“These CSOs are usually not younger,” explains Anthony (Tony) Readhead, the Robinson Professor of Astronomy, Emeritus, who led the investigation. “You would not name a 12-year-old canine younger though it has lived a shorter life than an grownup human. These objects are a distinct species all of their very own that reside and die out in 1000’s of years reasonably than the hundreds of thousands of years which can be widespread in galaxies with larger jets.”
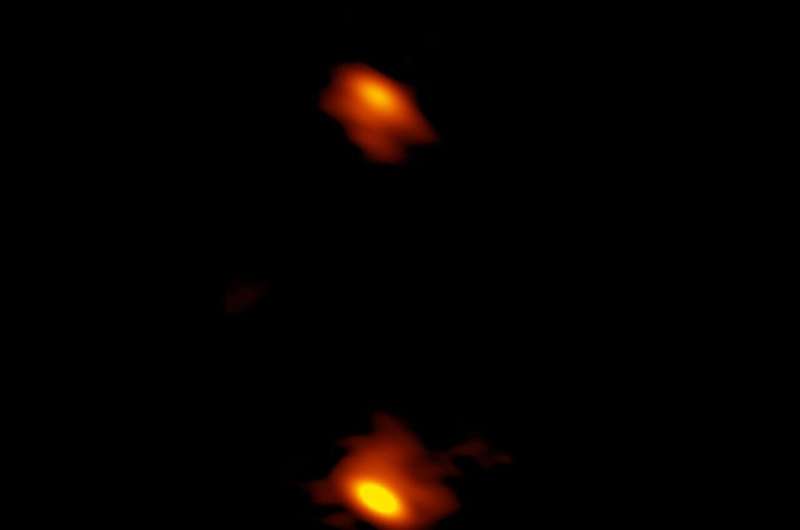
Within the new research, the crew reviewed literature and previous observations of greater than 3,000 CSO candidates, verifying 64 as actual and figuring out a further 15 CSOs. All these objects had been beforehand noticed by the Nationwide Radio Astronomy Observatory’s Very Lengthy Baseline Array (VLBA), and a few had been noticed by different high-resolution radio telescopes.
“The VLBA observations are probably the most detailed in astronomy, offering photographs with particulars equal to measuring the width of a human hair at a distance of 100 miles,” Readhead says.
The crew’s evaluation concludes that CSOs expel jets for five,000 years or much less after which die out.
“The CSO jets are very energetic jets however they appear to close off,” says Vikram Ravi, assistant professor of astronomy at Caltech and a co-author of one of many research. “The jets cease flowing from the supply.”
As for what’s fueling the short-lived jets, the scientists consider the trigger is a tidal disruption occasion (TDE), which happens when a single star wanders too near a supermassive black hole and is devoured.
“We predict {that a} single star will get ripped aside, after which all that vitality is channeled into jets alongside the axis the black hole is spinning round,” Readhead says. “The large black hole begins out invisible to us, after which when it consumes a star, increase—the black hole has gas, and we are able to see it.”
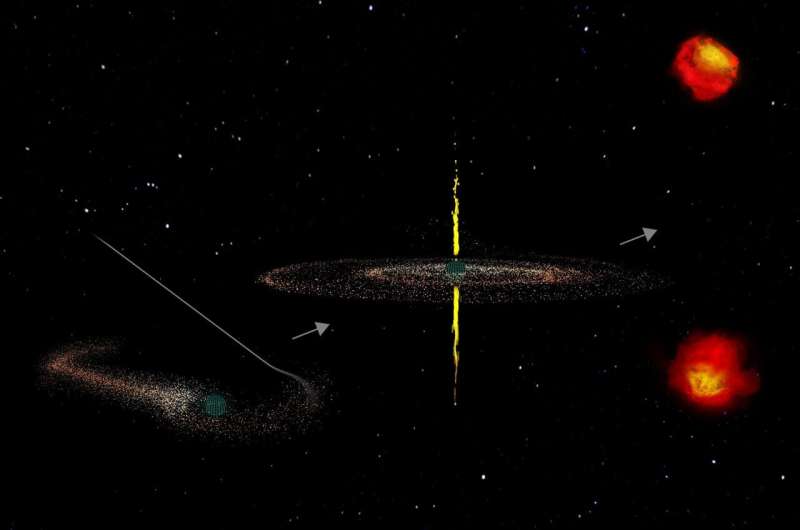
Readhead first suspected that CSOs could be fueled by TDEs again within the Nineteen Nineties, however he says the concept went largely unnoticed by the scientific neighborhood. “The speculation was all however forgotten as a result of years glided by earlier than observational proof started to mount for TDEs,” he says. On the time of his unique speculation, solely three CSOs had been discovered.
Quick ahead to 2020. Readhead, who had paused his research of CSOs to delve into totally different issues in radio astronomy, determined it was time to revisit the subject. He gathered a few of his colleagues collectively on Zoom, and so they determined to comb by literature and weed out objects that had been misclassified as CSOs. Over the following two years, the crew investigated greater than 3,000 CSO candidates, narrowing the group right down to solely dozens that had the factors to be actual CSOs.
Finally, an image started to emerge of CSOs as a wholly distinct household with jets that die out a lot prior to their gigantic brethren, reminiscent of these of the extraordinarily highly effective Cygnus A, a galaxy that shoots out extraordinarily highly effective jets that glow brightly at radio wavelengths. These jets stretch to distances of about 230,000 light-years in every course and final tens of hundreds of thousands of years. In distinction, the CSO jets lengthen to about 1,500 light-years at most and die out by about 5,000 years.
Based on the astronomers, the CSO jets probably type when a supermassive black hole snacks on not simply any star, however a considerable one.

“The TDEs we have beforehand seen solely lasted for a number of years,” Ravi says. “We predict that the exceptional TDEs powering CSOs final far longer as a result of the disrupted stars are very giant in dimension, very huge, or each.”
By analyzing the various assortment of CSO radio photographs, the researchers say they’ll hint how the objects age over time, nearly like a photograph album of a CSO’s life to watch how its jets evolve. The youthful CSOs have shorter jets which can be nearer to the black holes, whereas the older objects have jets that stretch additional out from their black hole.
Although a lot of the jets die out, the scientists estimate that one in 100 will go onto to grow to be long-lived like these of Cygnus A. In these uncommon instances, the galaxies are probably merging with different galaxies, a turbulent course of that gives a big amount of gas.
If the discoveries of Readhead and his crew are confirmed with further observations, the CSOs will present a complete new avenue for learning how huge stars on the facilities of galaxies work together with supermassive black holes.
“These objects are certainly a definite inhabitants with their very own distinct origin, and it’s as much as us now to study extra about them and the way they got here to be,” Readhead says. “With the ability to research these objects on timescales of years to many years reasonably than hundreds of thousands of years has opened the door to a complete new laboratory for learning supermassive black holes and the numerous sudden and unpredictable surprises they maintain.”
Extra info:
S. Kiehlmann et al, Compact Symmetric Objects. I. Towards a Complete Bona Fide Catalog, The Astrophysical Journal (2024). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad0c56
S. Kiehlmann et al, Compact Symmetric Objects. II. Affirmation of a Distinct Inhabitants of Excessive-luminosity Jetted Energetic Galaxies, The Astrophysical Journal (2024). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad0cc2
A. C. S Readhead et al, Compact Symmetric Objects. III. Evolution of the Excessive-luminosity Department and a Attainable Reference to Tidal Disruption Occasions, The Astrophysical Journal (2024). DOI: 10.3847/1538-4357/ad0c55
Supplied by
California Institute of Technology
Quotation:
Sleeping supermassive black holes woke up briefly by shredded stars (2024, March 26)
retrieved 26 March 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-03-supermassive-black-holes-awakened-briefly.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




