A global analysis crew led by a researcher from the College of Vienna has for the primary time straight detected stellar winds from three sun-like stars by recording the X-ray emission from their astrospheres, and positioned constraints on the mass loss charge of the celebs by way of their stellar winds.
Astrospheres, stellar analogs of the heliosphere that surrounds our solar system, are extremely popular plasma bubbles blown by stellar winds into the interstellar medium, a space full of gasoline and dust. The examine of the stellar winds of low-mass stars just like the sun permits us to grasp stellar and planetary evolution, and in the end the historical past and way forward for our personal star and solar system. Stellar winds drive many processes that evaporate planetary atmospheres into space and due to this fact result in atmospheric mass loss.
Though escape charges of planets over an hour or perhaps a yr are tiny, they function over lengthy geological intervals. The losses accumulate and is usually a decisive issue for a planet evolving right into a liveable world or an airless rock.
Regardless of their significance for the evolution of each stars and planets, winds of sun-like stars are notoriously troublesome to constrain. Primarily composed of protons and electrons, additionally they include a small amount of heavier extremely charged ions (e.g. oxygen, carbon). It’s these ions that, by capturing electrons from the neutrals of the interstellar medium across the star, emit X-rays.
X-ray emission from astrospheres detected
A global analysis crew led by Kristina Kislyakova, Senior Scientist on the Division of Astrophysics of the College of Vienna, has detected for the primary time the X-ray emission from the astrospheres round three sun-like stars, so-called fundamental sequence stars that are stars within the prime of their life, and has thus recorded such winds for the primary time straight, permitting them to put constraints on the mass loss charge of the celebs by way of their stellar winds.
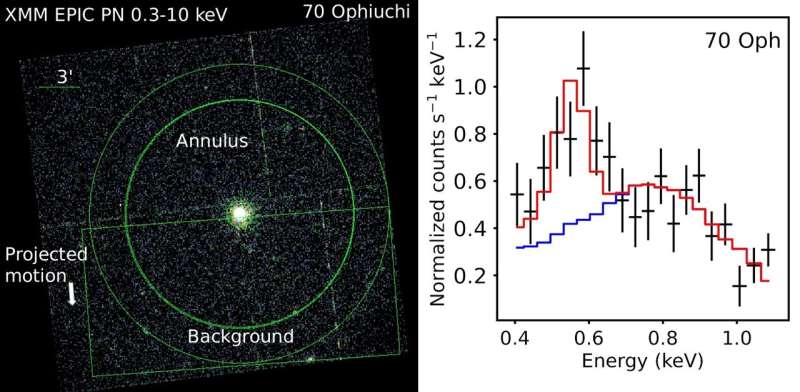
These outcomes, primarily based on observations with the XMM-Newton space telescope, are at present printed in Nature Astronomy. The researchers noticed the spectral fingerprints (so-called spectral strains) of the oxygen ions with XMM-Newton and have been in a position to decide the amount of oxygen and in the end the total mass of stellar wind emitted by the celebs.
For the three stars with detected astrospheres, named 70 Ophiuchi, epsilon Eridani, and 61 Cygni, the researchers estimated their mass loss charges to be 66.5±11.1, 15.6±4.4, and 9.6±4.1 instances the solar mass loss charge, respectively. Because of this the winds from these stars are a lot stronger than the solar wind, which could be defined by stronger magnetic exercise of those stars.
“Within the solar system, solar wind cost alternate emission has been noticed from planets, comets, and the heliosphere and offers a pure laboratory to review the solar wind’s composition,” explains the lead writer of the examine, Kislyakova.
“Observing this emission from distant stars is far more tough because of the faintness of the sign. Along with that, the space to the celebs makes it very troublesome to disentangle the sign emitted by the astrosphere from the precise X-ray emission of the star itself, a part of which is ‘unfold’ over the field-of-view of the telescope resulting from instrumental results.
“We’ve got developed a brand new algorithm to disentangle the stellar and the astrospheric contributions to the emission and detected cost alternate alerts originating from stellar wind oxygen ions and the encompassing impartial interstellar medium of three main-sequence stars.
“This has been the primary time X-ray cost alternate emission from astrospheres of such stars has been detected. Our estimated mass loss charges can be utilized as a benchmark for stellar wind fashions and increase our restricted observational proof for the winds of sun-like stars.”
Co-author Manuel Güdel, additionally of the College of Vienna, provides, “There have been worldwide efforts over three a long time to substantiate the presence of winds round sun-like stars and measure their strengths, however to date solely oblique proof primarily based on their secondary results on the star or its surroundings alluded to the existence of such winds; our group beforehand tried to detect radio emission from the winds however might solely place higher limits to the wind strengths whereas not detecting the winds themselves.
“Our new X-ray primarily based outcomes pave the way in which to discovering and even imaging these winds straight and finding out their interactions with surrounding planets.”
“Sooner or later, this methodology of direct detection of stellar winds in X-rays can be facilitated because of future excessive decision devices, just like the X-IFU spectrometer of the European Athena mission,” explains CNRS researcher Dimitra Koutroumpa, a co-author of the examine.
“The excessive spectral decision of X-IFU will resolve the finer construction and emission ratio of the oxygen strains (in addition to different fainter strains), which are exhausting to differentiate with XMM’s CCD decision, and supply further constraints on the emission mechanism; thermal emission from the celebs, or non-thermal cost alternate from the astrospheres.”
Extra data:
X-ray detection of astrospheres round three main-sequence stars and their mass-loss charges., Nature Astronomy (2024). DOI: 10.1038/s41550-024-02222-x
Supplied by
University of Vienna
Quotation:
Stellar winds of three sun-like stars detected for the primary time (2024, April 12)
retrieved 12 April 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-04-stellar-sun-stars.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




