The science of learning gravitational waves simply acquired an enormous enhance due to the European House Company. Its science program committee simply accepted the Laser Interferometer House Antenna—affectionately often known as LISA—for official planning and constructing. Meaning gravitational wave astronomers will take their subsequent steps to seize details about gravity waves from space.
LISA—or one thing prefer it—has been on the drawing boards because the Eighties. The present LISA observatory was proposed a couple of decade later and scientists flew a “pathfinder mission” to check out its principal design. Now, it should be a full-fledged set of three spacecraft set to launch in 2035 and will revolutionize gravitational wave research.
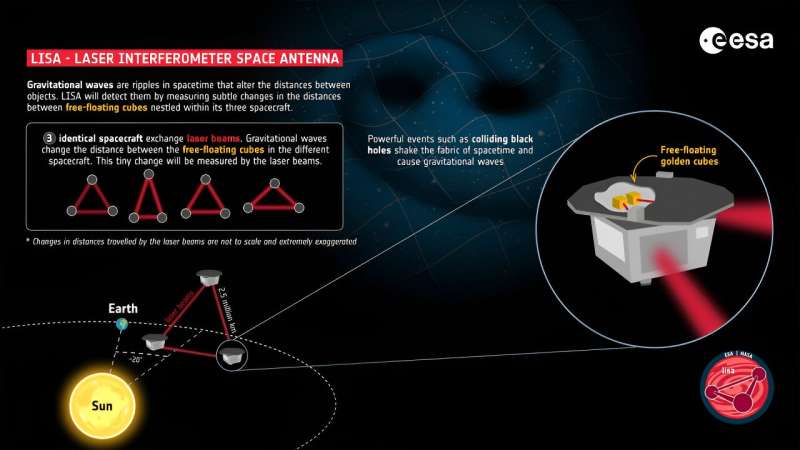
The spacecraft constellation will maneuver into three separate positions in an Earth-like heliocentric orbit. Primarily, they will kind a triangle, joined collectively by laser beams that can every shoot throughout 2.5 million kilometers of space. These beams would be the prime gravitational wave detectors. When a wave passes by, it is going to change the size of every laser “arm.”
Subtle devices onboard will file the adjustments and ship that information again to Earth for evaluation. The differential adjustments within the size of every arm will inform scientists essential details about the objects that collided to create the waves. If all goes properly, LISA will grow to be the primary space-based observatory devoted solely to those ripples within the material of spacetime.
The subsequent steps
The choice to forge forward with LISA is a proper step known as “adoption.” It principally says that the know-how for the mission and the idea and timeline are good to go. That permits the company to go forward with constructing the spacecraft and its instrumentation. From this level, the company is now free to solicit and choose contractors for fabrication. The design and meeting course of may start as early as January 2025.
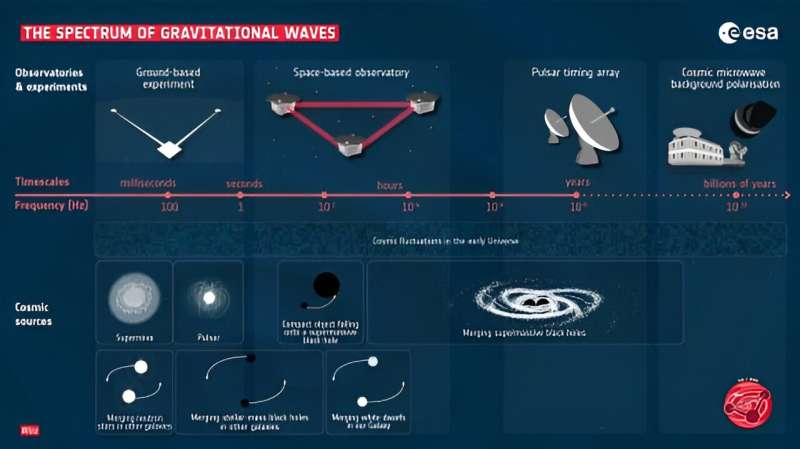
LISA’s growth will not be straightforward, in accordance with lead challenge scientist Nora Lützgendorf. “LISA is an endeavor that has by no means been tried earlier than,” she mentioned. “Utilizing laser beams over distances of a number of kilometers, ground-based instrumentation can detect gravitational waves coming from occasions involving star-sized objects—akin to supernova explosions or merging of hyper-dense stars and stellar-mass black holes. To increase the frontier of gravitational research we should go to space. Due to the large distance traveled by the laser alerts on LISA, and the very good stability of its instrumentation, we are going to probe gravitational waves of decrease frequencies than is feasible on Earth, uncovering occasions of a special scale, all the way in which again to the daybreak of time.”
Defending LISA from exterior influences in space
In fact, space presents distinctive challenges to the spacecraft’s mission. In that regard, LISA faces some related kinds of points that LIGO and others meet on the bottom. For instance, the bottom rumbles from heavy vans driving by disturb the LIGO devices. Meaning its scientists need to filter out any non-gravitational-wave disturbances.
There aren’t vans in space, fortunately, however LISA will face some non-gravitational-wave forces akin to mild strain and the solar wind. Scientists will get round these with some very intelligent spacecraft designs. Every of the three craft can be geared up with telescopes, lasers, and check plenty product of gold-coated gold and platinum.
To guard the check plenty from exterior influences (which may “push round” the plenty), they are going to float freely contained in the spacecraft. The outer hulls of the craft will take up the surface influences. Thrusters will regulate the spacecraft in place and hold the plenty from experiencing something besides the goal gravitational waves. The consequence must be a really “clear” seize of gravitational wave information from distant objects and occasions within the universe.
LISA’s gravitational wave targets
This intricate mission ought to be capable of seize the ripples in spacetime produced when large objects collide. That features the mergers of supermassive black holes on the hearts of galaxies. In our personal galaxy, LISA ought to be capable of detect the mergers of white dwarfs or neutron stars. Its information ought to give astronomers exact details about the distances to those occasions and even their areas.
“For hundreds of years now we have been learning our cosmos via capturing mild. Coupling this with the detection of gravitational waves is bringing a very new dimension to our notion of the universe,” mentioned LISA challenge scientist Oliver Jennrich. “If we think about that, to this point, with our astrophysics missions, now we have been watching the cosmos like a silent film, capturing the ripples of spacetime with LISA can be an actual game-changer, like when sound was added to movement photos.”
One very thrilling chance that LISA may allow is the detection of the very first seconds after the Huge Bang occurred. That is as a result of gravitational waves from that seminal occasion will carry distance and depth info. Not solely that, however LISA information will even assist astronomers measure the enlargement charge of the universe all through time. If all this involves go, it is going to show the usefulness of gravitational waves as a novel means of measuring issues within the cosmos.
Offered by
Universe Today
Quotation:
The space-based gravitational wave observatory LISA will get the inexperienced mild (2024, January 30)
retrieved 30 January 2024
from https://phys.org/information/2024-01-space-based-gravitational-observatory-lisa.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal examine or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




