Astronomers have recognized for many years that the universe is increasing. After they use telescopes to look at faraway galaxies, they see that these galaxies are transferring away from Earth.
To astronomers, the wavelength of light a galaxy emits is longer the sooner the galaxy is transferring away from us. The farther away the galaxy is, the extra its mild has shifted towards the longer wavelengths on the crimson aspect of the spectrum—so the upper the “redshift.”
As a result of the pace of sunshine is finite, quick, however not infinitely quick, seeing one thing far-off means we’re trying on the factor the way it regarded previously. With distant, high-redshift galaxies, we’re seeing the galaxy when the universe was in a youthful state. So “excessive redshift” corresponds to the early occasions within the universe, and “low redshift” corresponds to the late occasions within the universe.
However as astronomers have studied these distances, they’ve realized that the universe is not only increasing—its fee of growth is accelerating. And that growth fee is even sooner than the main concept predicts it ought to be, leaving cosmologists like me puzzled and in search of new explanations.
Darkish power and a cosmological fixed
Scientists name the supply of this acceleration darkish power. We’re not fairly positive what drives darkish power or the way it works, however we predict its conduct might be defined by a cosmological constant, which is a property of spacetime that contributes to the growth of the universe.
Albert Einstein initially got here up with this fixed—he marked it with a lambda in his concept of basic relativity. With a cosmological constant, because the universe expands, the power density of the cosmological fixed stays the identical.
Think about a field filled with particles. If the amount of the field will increase, the density of particles would lower as they unfold out to take up all of the space within the field. Now think about the identical field, however as the amount will increase, the density of the particles stays the identical.
It does not appear intuitive, proper? That the power density of the cosmological fixed doesn’t lower because the universe expands is, after all, very bizarre, however this property helps clarify the accelerating universe.
A typical mannequin of cosmology
Proper now, the main concept, or standard model, of cosmology is called “Lambda CDM.” Lambda denotes the cosmological fixed describing darkish power, and CDM stands for chilly dark matter. This mannequin describes each the acceleration of the universe in its late levels in addition to the growth fee in its early days.
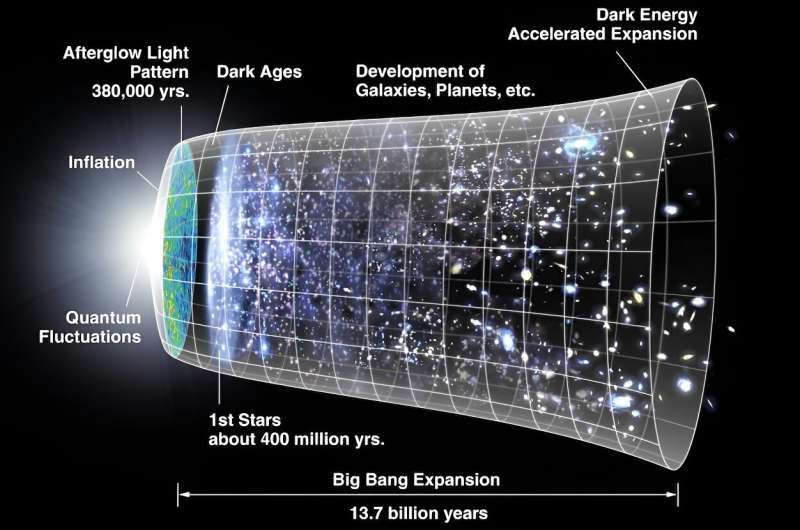
Particularly, the Lambda CDM explains observations of the cosmic microwave background, which is the afterglow of microwave radiation from when the universe was in a “hot, dense state” about 300,000 years after the Large Bang. Observations utilizing the Planck satellite, which measures the cosmic microwave background, led scientists to create the Lambda CDM mannequin.
Becoming the Lambda CDM mannequin to the cosmic microwave background permits physicists to foretell the worth of the Hubble constant, which is not truly a relentless however a measurement describing the universe’s present growth fee.
However the Lambda CDM mannequin is not good. The growth fee scientists have calculated by measuring distances to galaxies, and the growth fee as described in Lambda CDM utilizing observations of the cosmic microwave background, do not line up. Astrophysicists name that disagreement the Hubble pressure.
The Hubble pressure
Over the previous few years, I have been researching ways to elucidate this Hubble pressure. The strain could also be indicating that the Lambda CDM mannequin is incomplete and physicists ought to modify their mannequin, or it might point out that it is time for researchers to provide you with new concepts about how the universe works. And new concepts are all the time essentially the most thrilling issues for a physicist.
One method to clarify the Hubble pressure is to change the Lambda CDM mannequin by altering the growth fee at low redshift, at late occasions within the universe. Modifying the mannequin like this may help physicists predict what kind of bodily phenomena is likely to be inflicting the Hubble pressure.
As an example, possibly darkish power just isn’t a cosmological constant however as a substitute the results of gravity working in new methods. If that is so, darkish power would evolve because the universe expands—and the cosmic microwave background, which exhibits what the universe regarded like only some years after its creation, would have a distinct prediction for the Hubble fixed.
However, my team’s latest research has discovered that physicists cannot clarify the Hubble pressure simply by altering the growth fee within the late universe—this entire class of options falls quick.
Creating new fashions
To check what varieties of options might clarify the Hubble pressure, we developed statistical tools that enabled us to check the viability of the complete class of fashions that change the growth fee within the late universe. These statistical tools are very versatile, and we used them to match or mimic totally different fashions that might probably match observations of the universe’s expansion rate and may provide an answer to the Hubble pressure.
The fashions we examined embrace evolving darkish power fashions, the place darkish power acts otherwise at totally different occasions within the universe. We additionally examined interacting darkish energy-dark matter fashions, the place dark energy interacts with dark matter, and modified gravity fashions, the place gravity acts otherwise at totally different occasions within the universe.
However none of those might totally clarify the Hubble pressure. These outcomes counsel that physicists ought to research the early universe to grasp the supply of the stress.
Supplied by
The Conversation
This text is republished from The Conversation below a Inventive Commons license. Learn the original article.![]()
Quotation:
The universe is increasing sooner than concept predicts—physicists are attempting to elucidate the mismatch (2023, November 15)
retrieved 15 November 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-11-universe-faster-theory-predictsphysicists-mismatch.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




