The 5-hundred-meter Aperture Spherical Telescope (FAST), situated in China, is presently the world’s largest and most refined radio observatory. Whereas its major goal is to conduct large-scale impartial hydrogen surveys (the most typical aspect within the universe), research pulsars, and detect Quick Radio Bursts (FRBs), scientists have deliberate to make use of the array within the Seek for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI). Integral to this area of research is the seek for technosignatures, indicators of technological exercise that point out the presence of a sophisticated civilization.
Whereas many potential technosignatures have been proposed for the reason that first surveys started within the Sixties, radio transmissions are nonetheless thought of the most definitely and stay probably the most studied. In a latest survey, a global group of SETI researchers performed a focused search of 33 exoplanet methods utilizing a brand new methodology they name the “MBCM blind search mode.” Whereas the group detected two “particular alerts” utilizing this mode, they dismissed the concept they had been transmissions from a sophisticated species. However, their survey demonstrated the effectiveness of this new blind mode and will result in believable candidate alerts sooner or later.
The survey was performed by researchers representing the FAST collaboration, Breakthrough Pay attention, and a number of universities and institutes. This included the Institute for Frontiers in Astronomy and Astrophysics at Beijing Regular College, the Beijing Academy of Science and Know-how, the House Sciences Laboratory (SSL) at UC Berkeley, the Institute for Astronomical Science at Dezhou College, the School of Physics and Digital Engineering at Qilu Regular College, and the College of Glasgow. The paper that describes their work has been accepted for publication by the Astrophysical Journal.
The primary SETI experiment (Venture Ozma) happened in 1960 below the course of Professor Frank Drake, for whom the Drake Equation is known as. Since then, most SETI experiments have looked for radio communications as technosignatures attributable to their effectiveness at propagating via interstellar space. The earliest experiments searched at particular frequencies, just like the absorption line of impartial hydrogen (21 cm) and hydroxyl (18 cm), which correspond to radio frequencies of 1.4 and 1.6 gigahertz (GHz).
However with the development of know-how, the accessible bandwidth of SETI methods has expanded into the tens of GHz vary. As well as, SETI surveys have come to depend on a technique often called Multibeam Coincidence Matching (MBCM) to handle RFI and filter it out of their sign noise. Dr. Vishal Gajjar—a researcher on the SETI Institute, UC Berkeley, and a co-author on the research—defined to Universe Immediately through e-mail:
“Single-dish radio telescopes observe a small portion of the sky, often called a beam, which is in regards to the measurement of the tip of a pencil held at arm’s size. Regardless of their accuracy, these telescopes usually choose up interference from close by terrestrial sources. To beat this subject, some telescopes are outfitted with a number of beams, permitting them to watch a number of small areas of the sky on the similar time. By looking for alerts of curiosity in all beams concurrently, we are able to decide if a sign is actually from a supply within the sky or if it’s a results of interference. When a sign is detected in a number of beams, it’s prone to be terrestrial interference.”
In line with Gajjar, MCBM is taken into account higher than typical strategies for 3 most important causes. These embody:
- Elevated accuracy and robustness: MBCM can remove false constructive detections attributable to terrestrial interference, leading to extra correct outcomes. MBCM is much less vulnerable to interference from terrestrial sources, making it extra strong and dependable than typical strategies.
- Sooner processing: MBCM will be carried out in real-time, making it sooner than conventional strategies that require post-processing.
- Elevated protection: MBCM permits for a wider area of view by utilizing a number of beams, offering extra protection than a single beam.
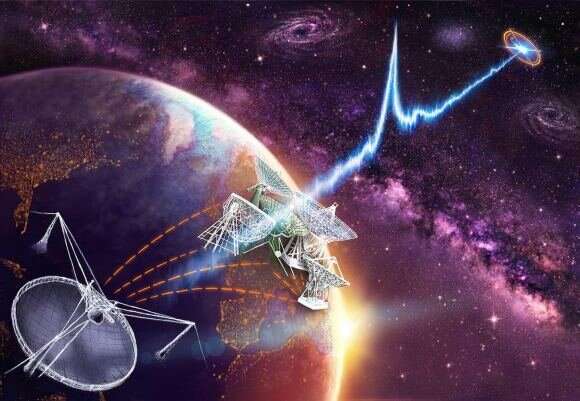
This third benefit was integral to the work of Dr. Gajjar and the worldwide group. The FAST telescope is the world’s largest radio array and is provided with a 19-beam receiver, permitting astronomers to concurrently observe 19 completely different positions within the sky. When paired with FAST’s devices, the MCMB approach successfully eliminates sources of interference and ensures correct observations. For his or her research, the group noticed 33 close by exoplanets utilizing the standard MBCM technique and a brand new search methodology they name the “MBCM blind search mode.”
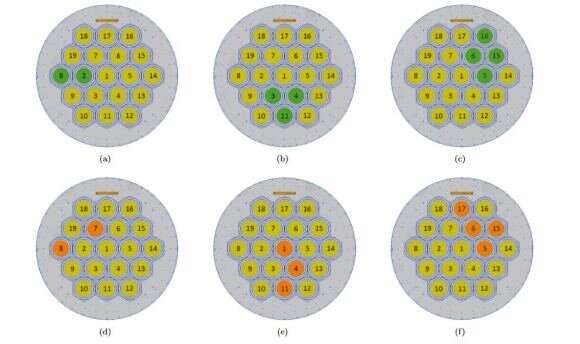
As they point out of their paper, the blind search mode was impressed by the multibeam blind search mode that was lately developed to review FRBs. The essential thought is to make use of all 19 of FAST’s beams to seek for ETI alerts, the place the central beam (Beam 1) tracks a goal whereas the others function reference beams. If a sign covers non-adjacent beams, greater than 4 adjoining beams, or three or extra beams in a line, the group categorized the sign as RFI. In addition they determine 4 beam protection preparations that would point out radio alerts which can be ETI in origin.
As illustrated within the diagram beneath, these included any one among FAST’s 19 beams, two of the adjoining beams (Determine 1a), three adjoining beams forming an equilateral triangle (Determine 1b), and 4 adjoining beams forming a compact rhombus (Determine 1c). Any beam protection preparations that didn’t match into these 4 classes (just like the three examples within the second line of the diagram) had been thought of false positives and rejected. As Gajjar indicated, this paper builds on earlier work the place they performed focused observations with FAST of the identical 33 exoplanetary methods:
“Throughout these observations, we aimed the central beam of our 19-beam receiver at every particular person goal and solely analyzed knowledge from the central beam the place the goal was located. If a sign of curiosity was detected, we cross-checked the identical frequency throughout different beams to remove terrestrial interference. Within the current paper, we carry out a extra complete search by blindly looking for alerts throughout all 19 beams, whatever the presence of any exoplanetary system within the area of view. This strategy permits us to conduct an agnostic search with out prior data of any potential targets of curiosity current in our beams.”
After scanning these 33 exoplanets, the group discerned two quite uncommon and intriguing alerts. As Gajjar associated, whereas it was difficult to guage these alerts (as they solely appeared in a single beam), after a radical examination, they decided that they had been simply RFI interference:
“One of many alerts was solely current in one of many two polarizations of the telescope. Usually, sky-based sources would present comparable depth in each polarizations over an extended interval of statement, however this wasn’t the case for the primary sign, making it straightforward to dismiss. The second sign was extra intriguing because it confirmed the identical depth in each polarizations. Upon nearer inspection, we found that the frequency of the second sign was very near recognized sources of interference.”
In one other case, additional examination of the info revealed a sign in a single beam with a really low signal-to-noise (STN) ratio. The group additionally rejected this sign as a result of its conduct was much like different cases of RFI that they had recognized. Whereas no clear technosignatures had been detected, the survey was invaluable due to the way in which it examined the group’s silent mode approach. What’s extra, the 2 alerts recognized are becoming targets for follow-up observations, which could possibly be performed by Breakthrough Pay attention (the biggest SETI effort ever mounted) within the coming years.
“It is a groundbreaking stride within the area of SETI,” mentioned Gajjar. “In SETI, this system has been deployed for the primary time. This distinctive approach will be helpful as a result of it reduces the quantity of false positives, permitting for a extra environment friendly seek for alerts from extraterrestrial civilizations. By decreasing the quantity of interference, multibeam coincidence rejection will increase the sensitivity of the search and makes it simpler to detect weak alerts which may in any other case be neglected.”
Extra data:
Xiao-Grasp Luan et al, Multibeam Blind Search of Focused SETI Observations towards 33 Exoplanet Techniques with FAST, arXiv (2023). DOI: 10.48550/arxiv.2301.10890
Supplied by
Universe Today
Quotation:
The world’s largest radio telescope simply scanned 33 exoplanets for a sign from aliens (2023, February 8)
retrieved 8 February 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-02-world-largest-radio-telescope-scanned.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Other than any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




