Northwestern College and the College of California San Diego (UC San Diego) astrophysicists have found the tightest ultracool dwarf binary system ever noticed.
The 2 stars are so shut that it takes them lower than one Earth day to revolve round one another. In different phrases, every star’s “12 months” lasts simply 20.5 hours.
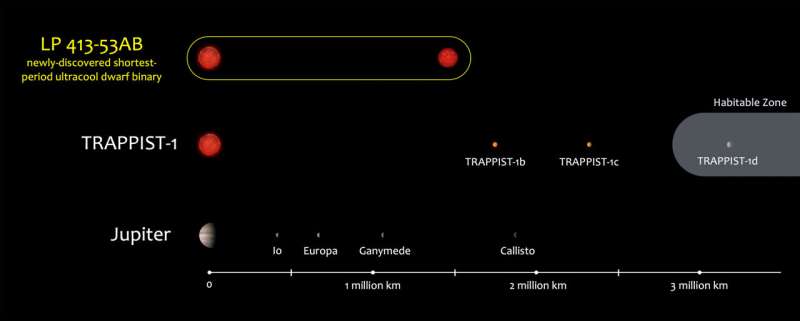
The newly found system, named LP 413-53AB, consists of a pair of ultracool dwarfs, a category of very low-mass stars which might be so cool that they emit their mild primarily within the infrared, making them fully invisible to the human eye. They’re nonetheless one of the vital widespread forms of stars within the universe.
Beforehand, astronomers had solely detected three short-period ultracool dwarf binary methods, all of that are comparatively younger—as much as 40 million years previous. LP 413-53AB is estimated to be billions of years previous—comparable age to our sun—however has an orbital period that’s not less than 3 times shorter than the all ultracool dwarf binaries found to date.
“It is thrilling to find such an excessive system,” stated Chih-Chun “Dino” Hsu, a Northwestern astrophysicist who led the research. “In precept, we knew these methods ought to exist, however no such methods had been recognized but.”
Hsu will current this analysis throughout a press briefing on the 241st Meeting of the American Astronomical Society in Seattle. “Discovery of the shortest-period ultracool dwarf binary” will happen on Tuesday, Jan. 10, as a part of a session on “Stars and Their Exercise.”
Hsu is a postdoctoral researcher in physics and astronomy at Northwestern’s Weinberg School of Arts and Sciences and a member of Northwestern’s Middle for Interdisciplinary Exploration and Analysis in Astrophysics (CIERA). He started this research whereas a Ph.D. scholar at UC San Diego, the place he was suggested by Professor Adam Burgasser.
The group first found the unusual binary system whereas exploring archival knowledge. Hsu developed an algorithm that may mannequin a star primarily based on its spectral knowledge. By analyzing the spectrum of sunshine emitted from a star, astrophysicists can decide the star’s chemical composition, temperature, gravity and rotation. This evaluation additionally reveals the star’s movement because it strikes towards and away from the observer, generally known as radial velocity.
When inspecting the spectral knowledge of LP 413-53AB, Hsu seen one thing unusual. Early observations caught the system when the celebrities had been roughly aligned and their spectral lines overlapped, main Hsu to imagine it was only one star. However as the celebrities moved of their orbit, the spectral traces shifted in reverse instructions, splitting into pairs in later spectral data. Hsu realized there have been truly two stars locked into an extremely tight binary.
Utilizing highly effective telescopes on the W.M. Keck Observatory, Hsu determined to look at the phenomenon for himself. On March 13, 2022, the group turned the telescopes towards the constellation Taurus, the place the binary system is situated, and noticed it for 2 hours. Then, they adopted up with extra observations in July, October and December.
“After we had been making this measurement, we might see issues altering over a few minutes of remark,” Burgasser stated. “Most binaries we observe have orbit durations of years. So, you get a measurement each few months. Then, after some time, you’ll be able to piece collectively the puzzle. With this technique, we might see the spectral traces shifting aside in actual time. It is superb to see one thing occur within the universe on a human time scale.”
The observations confirmed what Hsu’s mannequin predicted. The gap between the 2 stars is about 1% of the space between the Earth and the sun. “That is exceptional, as a result of after they had been younger, one thing like 1 million years previous, these stars would have been on high of one another,” stated Burgasser.
The group speculates that the celebrities both migrated towards one another as they advanced, or they may have come collectively after the ejection of a 3rd—now misplaced—stellar member. Extra observations are wanted to check these concepts.
Hsu additionally stated that by finding out comparable star methods researchers can be taught extra about doubtlessly liveable planets past Earth. Ultracool dwarfs are a lot fainter and dimmer than the sun, so any worlds with liquid water on their surfaces—an important ingredient to kind and maintain life—would should be a lot nearer to the star. Nonetheless, for LP 413-53AB, the liveable zone distance occurs to be the identical because the stellar orbit, making it inconceivable to kind liveable planets on this system.
“These ultracool dwarfs are neighbors of our sun,” Hsu stated. “To establish doubtlessly liveable hosts, it is useful to begin with our close by neighbors. But when shut binaries are widespread amongst ultracool dwarfs, there could also be few liveable worlds to be discovered.”
To completely discover these situations, Hsu, Burgasser and their collaborators hope to pinpoint extra ultracool dwarf binary methods to create a full knowledge pattern. New observational knowledge might assist strengthen theoretical fashions for binary-star formation and evolution. Till now, nevertheless, discovering ultracool binary stars has remained a uncommon feat.
“These methods are uncommon,” stated Chris Theissen, research co-author and a Chancellor’s Postdoctoral Fellow at UC San Diego. “However we do not know whether or not they’re uncommon as a result of they not often exist or as a result of we simply do not discover them. That is an open-ended query. Now we have now one knowledge level that we will begin constructing on. This knowledge had been sitting within the archive for a very long time. Dino’s instrument will allow us to search for extra binaries like this.”
Offered by
Northwestern University
Quotation:
Ultracool dwarf binary stars break information (2023, January 10)
retrieved 10 January 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-01-ultracool-dwarf-binary-stars.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any truthful dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is supplied for info functions solely.




