The European Area Company’s Gaia Observatory has been working steadily on the Earth-sun L2 Lagrange Level for nearly a decade. As an astrometry mission, Gaia goals to assemble information on the positions, correct movement, and velocity of stars, exoplanets, and objects within the Milky Way and tens of 1000’s of neighboring galaxies. By the top of its major mission (scheduled to finish in 2025), Gaia may have noticed an estimated 1 billion astronomical objects, resulting in the creation of essentially the most exact 3D space catalog ever made.
Up to now, the ESA has performed three information releases from the Gaia mission, the newest (DR3) launched in June 2022. Along with the breakthroughs these releases have allowed, scientists are discovering further purposes for this astrometric information. In a latest research, a group of astronomers prompt that the variable star catalog from the Gaia Knowledge Launch 3 might be used to help within the Seek for Extraterrestrial Intelligence (SETI). By synchronizing the seek for transmissions with conspicuous occasions (like a supernova!), scientists might slim the seek for extraterrestrial transmissions.
The research was led by Andy Nilipour, an undergraduate student on the Yale College Division of Astronomy. He was joined by James R.A. Davenport, a Analysis Scientist on the College of Washington, Seattle; Adjunct Senior Astronomer Steve Croft from the Radio Astronomy Lab and the SETI Institute at UC Berkeley; and Andrew Siemion, the Bernard M. Oliver Chair for SETI Qualification at UC Berkeley, the Jodrell Financial institution Heart for Astrophysics (JBCA) on the College of Manchester, and the Institute of Area Sciences and Astronomy on the College of Malta.
This research, which was not too long ago printed in The Astronomical Journal (“Sign Synchronization Methods and Time Area SETI with Gaia DR3”), was Nilipour’s first tutorial research. As he defined in an interview with Yale Information, “My two mentors, Steve Croft, and James Davenport, selected this for me, the thought of growing a geometrical method for constraining [technosignature] searches. It is in all probability the most important problem in SETI proper now as a result of there are such a lot of potentialities for the placement of a transmission and the character of the sign.”
Put merely, technosignatures are proof of exercise that unambiguously demonstrates the presence of a complicated technological civilization. Up to now, the overwhelming majority of SETI experiments have looked for radio signals because the expertise is thought to be viable and radiowaves propagate properly by way of space—essentially the most superior and complete being Breakthrough Hear. These experiments additionally consisted of listening to numerous stars for a set interval within the hopes of discerning radio indicators coming from orbiting planets. However in recent times, scientists have expanded the vary of potential technosignatures and ]thought-about different strategies as properly.
Mentioned Nilipour, “There are many ideas about what technosignatures may seem like. The most typical type that we search for is narrowband radio emission, as a result of, based mostly on our pattern measurement of human expertise, this appears to be one thing {that a} technological civilization ought to be producing. Different types could be laser emission, shut encounters of stars at excessive velocities, and emission from a star abruptly and dramatically lowering.”
For his or her research, Nilipour and his group theorized that an clever civilization would perceive how troublesome it’s to observe all of the space surrounding their planet in each doable mode—radio, optical, infrared, ultraviolet, X-ray, gamma-ray, and so on. As such, they may decide to time their indicators of greeting (fingers crossed!) with a conspicuous astrophysical occasion that will draw the eye of observers—i.e., supernovae. Nilipour started engaged on this concept as a part of a summer season undergraduate program supplied by the Nationwide Science Basis (NSF) and the Breakthrough Hear Initiative on the Berkeley SETI Analysis Heart.
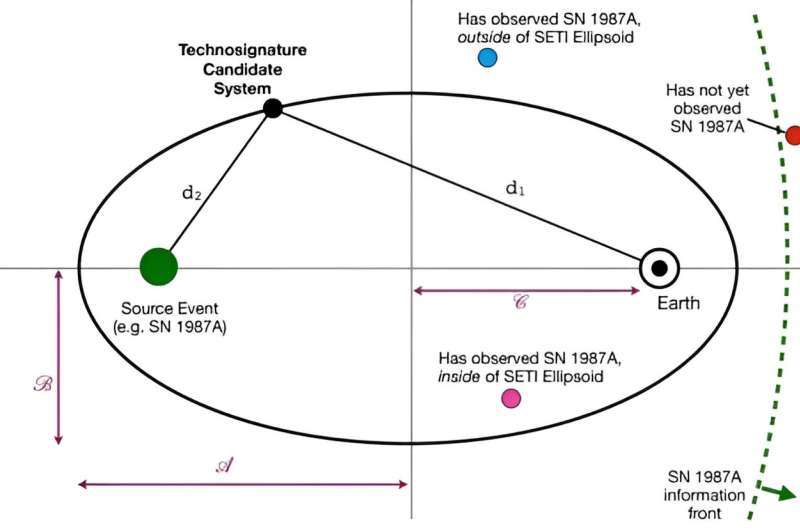
As a primary step, Nilipour and his colleagues selected 4 historic supernovae from the previous 1,000 years and examined how lengthy it took gentle from their explosions to succeed in Earth. As Nilipour defined, “We merged two looking out frameworks—the ellipsoid technique, which synchronizes indicators to a conspicuous astronomical occasion, and the Seto technique, which is tied to geometric angles and never distance—and utilized them to 4 occasions.
“We selected 4 traditionally documented supernovae from the years 1054, 1572, 1604, and 1987, respectively. On this case, a supernova would act like a lighthouse, a standard focus for the sender of the sign and the receiver of the sign—us.”
They decided that the sunshine attributable to these 4 occasions took 6,300 years, 8,970 years, 16,600 years, and 168,000 years to succeed in Earth (respectively). They then in contrast these outcomes to gentle indicators from over 10 million stars recorded by the Gaia observatory that have been included within the DR3 catalog. This revealed 465 stars whose gentle took the identical period of time to succeed in Earth and 403 stars whose gentle indicators traveled to Earth from an advantageous angle in relation to those supernovae. Whereas not one of the 868 methods yielded proof of technosignatures, their outcomes have offered vital constraints for future searches.

As Nilipour indicated, their technique can be used to look by way of different archival information to tease out doable indicators of technosignatures.
“Discovering a technosignature would have been unimaginable, however this actually was extra about exhibiting a technique that we are able to use sooner or later. What we have completed right here will be utilized to further Gaia information, to information from TESS [the Transiting Exoplanet Survey Satellite], and to different information because it turns into accessible. We’re presently working the identical sort of study utilizing a brand new supernova within the galaxy M101 that turned seen in Could of this 12 months, which is the closest supernova in over a decade.”
Given the variety of stars in our galaxy alone, the quantity of background noise, the time-sensitive nature of transmissions, and (as if that wasn’t sufficient) the probability of acquiring false positives, trying to find potential technosignatures is a particularly daunting activity. Had been it doable to observe each sector of the sky—indefinitely and in a number of wavelengths concurrently—it could simply be a matter of time earlier than transmissions might be heard (assuming anybody on the market was transmitting). Sadly, we do not have the time or the assets for such thorough all-sky protection.
Herein lies the worth of analysis like this, which successfully narrows the search by exploring several types of technosignatures, frequency ranges, and places within the night time sky. Little by little, SETI researchers are bettering the chances of an unambiguous detection that may be confirmed by follow-up research. If there’s a needle to be discovered within the cosmic haystack, we’ll discover it in the end. Regardless of the boundaries imposed on us by such a big universe and so many potentialities, it’s nonetheless only a matter of time.
Extra data:
Andy Nilipour et al, Sign Synchronization Methods and Time Area SETI with Gaia DR3, The Astronomical Journal (2023). DOI: 10.3847/1538-3881/acde79
Supplied by
Universe Today
Quotation:
Variable stars can inform us the place and when to seek for extraterrestrials (2023, August 3)
retrieved 3 August 2023
from https://phys.org/information/2023-08-variable-stars-extraterrestrials.html
This doc is topic to copyright. Aside from any honest dealing for the aim of personal research or analysis, no
half could also be reproduced with out the written permission. The content material is offered for data functions solely.




